Angiostrongylus cantonensis Infection on Mayotte Island, Indian Ocean, 2007-2012 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Angiostrongylus cantonensis Infection on Mayotte Island, Indian Ocean, 2007-2012
Loïc Epelboin et al. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016.
Abstract
Introduction: Human angiostrongyliasis (HA) is a neurological helminthic disease caused by the lung worm Angiostrongylus cantonensis. It is suspected in the combination of travel or a residence in an endemic area and eosinophilic meningitis. In Mayotte, an island in the Indian Ocean, cases are rare but regular. The main objective of our study was to describe the epidemiological and diagnosis clues of HA in Mayotte. The secondary objectives were to evaluate the contribution of Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT- PCR) for the diagnosis of HA, delineate the characteristics of the local transmission and ascertain the presence of A. cantonensis in Achatina fulica, the potential vector of the disease.
Materials and methods: Between 2007 and 2012, all cases of eosinophilic meningitis were retrospectively included and investigated by RT- PCR in the CSF. Descriptive analysis was conducted for clinical, biological and radiological features, and were analyzed for all patients together with the search for prognostic factors for mortality. Concurrently, geolocalization and temporal parameters were studied to correlate the occurrence of the cases with rainfall seasons and snails were collected to enhance a parasitic carriage with real time PCR.
Results: During the 6-year period of the study, 14 cases were identified (2.3 cases/year) and 9 among 10 remaining CSF were positive in PCR. Among 14 cases of EM, 13 were less than 2 year-old children. The 1 year mortality rate was 5/14 (35.7%). Among survivors, 3/7 (42.8%) presented neurological sequelae. Factors associated with mortality were dysfunction of cranial nerves, abnormal brain imaging, and CSF glucose level inferior to 2 mmol/l. Occurrence of cases was temporarily and spatially correlated to the rainy season. Among the 64 collected giant snails, 6 (9.4%) were positive with A. cantonensis PCR. The likely main route of transmission was the children licking snails, carriers of the parasite.
Conclusion: In Mayotte, HA was mainly found in paediatric cases under 2 years old, and evidenced a life-threatening disease. PCR seems to be a promising tool in the definitive diagnosis of HA. Population should be aware of the role of A. fulica, and not let the children have direct contact with the snails.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
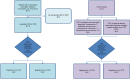
Fig 1. Flow chart of the study.
Ac: Angiostrongylus cantonensis; CSF: Cerebrospinal fluid; PCR: Polymerase Chain Reaction. * Eosinophilic meningitis: ≥ 10 eosinophils /mm3 in CSF or ≥10% WBC). ** Meningitis: ≥ 10 WBC in CSF.
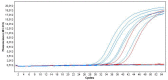
Fig 2. Amplification curves of six patients positive by Polymerase Chain Reaction and the positive control.
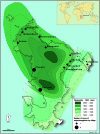
Fig 3. Map of the island of Mayotte representing the number and location of occurrence of the cases of angiostrongyliasis and the pluviometry curves.
Figure 3 was created using Illustrator CS5 (Adobe Systems, Inc.).
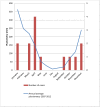
Fig 4. Monthly repartition of the cases and average pluviometry.
Similar articles
- First Evidence of Angiostrongyliasis Caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Guadeloupe, Lesser Antilles.
Dard C, Piloquet JE, Qvarnstrom Y, Fox LM, M'kada H, Hebert JC, Mattera D, Harrois D. Dard C, et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017 Mar;96(3):692-697. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.16-0792. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017. PMID: 28070007 Free PMC article. - Endemic angiostrongyliasis in the Brazilian Amazon: natural parasitism of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Rattus rattus and R. norvegicus, and sympatric giant African land snails, Achatina fulica.
Moreira VL, Giese EG, Melo FT, Simões RO, Thiengo SC, Maldonado A Jr, Santos JN. Moreira VL, et al. Acta Trop. 2013 Jan;125(1):90-7. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2012.10.001. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Acta Trop. 2013. PMID: 23072946 - Angiostrongylus cantonensis in the vector snails Pomacea canaliculata and Achatina fulica in China: a meta-analysis.
Song L, Wang X, Yang Z, Lv Z, Wu Z. Song L, et al. Parasitol Res. 2016 Mar;115(3):913-23. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4849-5. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Parasitol Res. 2016. PMID: 26621284 - Eosinophilic meningitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis: report of 17 cases.
Tsai HC, Liu YC, Kunin CM, Lee SS, Chen YS, Lin HH, Tsai TH, Lin WR, Huang CK, Yen MY, Yen CM. Tsai HC, et al. Am J Med. 2001 Aug;111(2):109-14. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(01)00766-5. Am J Med. 2001. PMID: 11498063 Review.
Cited by
- Alternative pathways in Angiostrongylus cantonensis (Metastrongyloidea: Angiostrongylidae) transmission.
Modrý D, Fecková B, Putnová B, Manalo SM, Otranto D. Modrý D, et al. Parasitology. 2021 Feb;148(2):167-173. doi: 10.1017/S0031182020001857. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Parasitology. 2021. PMID: 32981541 Free PMC article. - Angiostrongylus cantonensis induces energy imbalance and dyskinesia in mice by reducing the expression of melanin-concentrating hormone.
Huang H, Zhang Z, Xing M, Jin Z, Hu Y, Zhou M, Wei H, Liang Y, Lv Z. Huang H, et al. Parasit Vectors. 2024 Apr 23;17(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06267-9. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38654385 Free PMC article. - Tetraventricular Hydrocephalus Following Eosinophilic Meningitis due to Angiostrongylus cantonensis in a 14-Month-Old Boy From Mayotte: A Case Report.
Cattaneo C, Hoarau M, Valois S, Chamouine A, Dembele Y, Collet L, Sarton R. Cattaneo C, et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021 Jan 22;8(3):ofab031. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofab031. eCollection 2021 Mar. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33728356 Free PMC article. - Angiostrongylus cantonensis Meningo-Encephalitis in Children-Heightened Awareness Needed During Prolonged Wet Weather Conditions.
Hasan N, Nourse C, Heney C, Lee R, Kapoor V, Berkhout A. Hasan N, et al. J Paediatr Child Health. 2025 Mar;61(3):472-481. doi: 10.1111/jpc.16780. Epub 2025 Jan 17. J Paediatr Child Health. 2025. PMID: 39821425 Free PMC article. - The global risk of infectious disease emergence from giant land snail invasion and pet trade.
Gippet JMW, Bates OK, Moulin J, Bertelsmeier C. Gippet JMW, et al. Parasit Vectors. 2023 Oct 17;16(1):363. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-06000-y. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 37848903 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Chen HT. A new pulmonary nematode in Canton's rats, Pulmonem A. cantonensis n.g., n. sp. [in French]. Ann Parasitol. 1935;13:312–7.
- Rosen L, Laigret J, Bories S. Observations on an outbreak of eosinophilic meningitis on Tahiti, French Polynesia. American journal of hygiene. 1961;74:26–42. - PubMed
- Malvy D, Ezzedine K, Receveur MC, Pistone T, Crevon L, Lemardeley P, et al. Cluster of eosinophilic meningitis attributable to Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection in French policemen troop returning from the Pacific Islands. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2008;6(5):301–4. 10.1016/j.tmaid.2008.06.003 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources