Description of a new tick species, Ixodes collaris n. sp. (Acari: Ixodidae), from bats (Chiroptera: Hipposideridae, Rhinolophidae) in Vietnam - PubMed (original) (raw)
Description of a new tick species, Ixodes collaris n. sp. (Acari: Ixodidae), from bats (Chiroptera: Hipposideridae, Rhinolophidae) in Vietnam
Sándor Hornok et al. Parasit Vectors. 2016.
Abstract
Background: In a recent study on ixodid bat ticks from Eurasia, a high genetic difference was found between Ixodes vespertilionis from Europe and Vietnam. Accordingly, it was proposed that I. vespertilionis is a species complex, with at least one additional, hitherto undescribed species. The aim of the present study was to investigate the morphology of bat ticks from Vietnam and to assess their taxonomic status in comparison with those collected in Europe.
Findings: Ixodid bat ticks (two females and two nymphs) collected from the pomona leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideros pomona) (Hipposideridae) and intermediate horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus affinis) (Rhinolophidae) in Vietnam showed major morphological differences from European isolates of I. vespertilionis, including the shape of the scutum, the enclosure and shape of porose areas, the presence of a caudo-lateral collar-like ridge ventrally on the basis capituli, polytrich coxae with short setae, and grouped (non-linear) arrangement of anterior pit sensillae in Haller's organ.
Conclusions: In this study the female and the nymph of an ixodid bat tick species from Vietnam are described for the first time. The genetic and morphological differences between I. vespertilionis Koch, 1844 and these bat ticks from Vietnam justify the status of the latter as a distinct species, Ixodes collaris Hornok n. sp.
Keywords: Bat tick; Ixodes collaris Hornok n. sp; Ixodes vespertilionis; New species; Rhinolophus affinis; Vietnam.
Figures
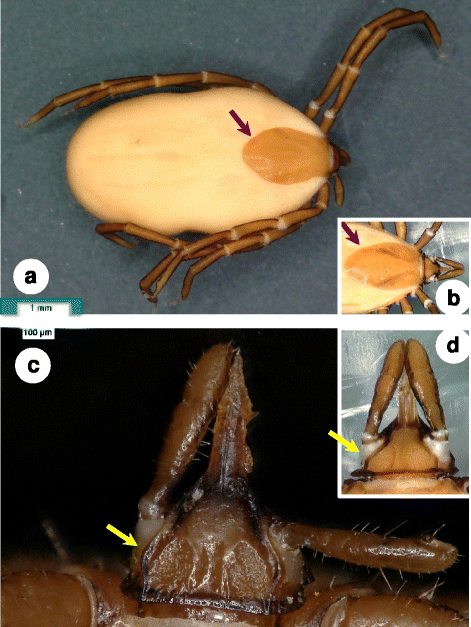
Fig. 1
Dorsal view of female of Ixodes collaris n. sp. a Holotype: posteriorly broad scutum (arrow), as contrasted to that of Ixodes vespertilionis female (b); c Basis capituli and palps of paratype No. 1. showing convex longitudinal flanks (arrow) enclosing the porose areas, which are longer than broad, as contrasted to those of I. vespertilionis female (d)
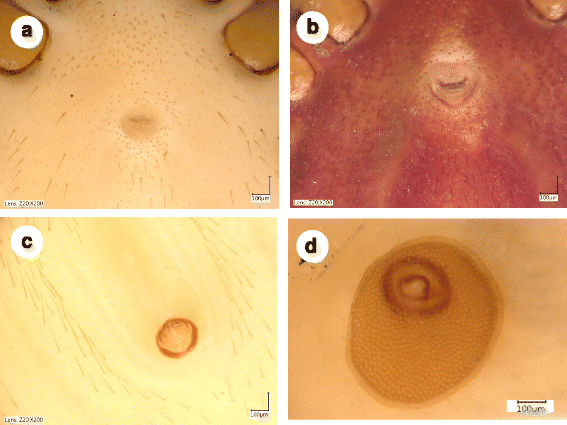
Fig. 2
Ventral idiosomal setae of a Ixodes collaris n. sp. (holotype) and b Ixodes vespertilionis in a similar state of engorgement. Note that I. collaris n. sp. has shorter setae anteriorly to the genital aperture than posteriorly, whereas setae of I. vespertilionis are similar in length both anteriorly and posteriorly to the genital aperture. I. collaris n. sp.: c perianal setae; d spiracular plate
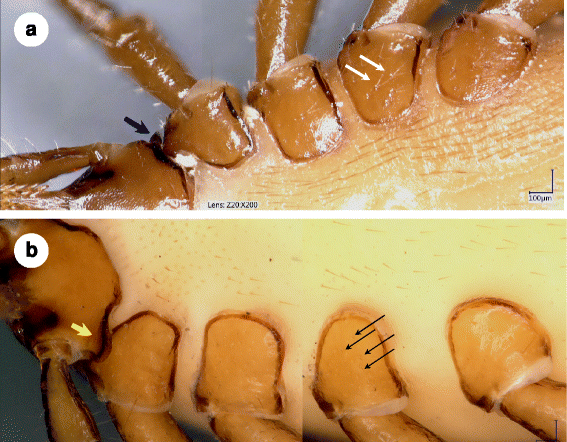
Fig. 3
Ventral view of female a Ixodes vespertilionis and b Ixodes collaris n. sp. (holotype). a I. vespertilionis shows lateral flange on basis capituli (blue arrow) and a few, long coxal setae (especially on coxa III: white arrows). Note: V-shaped arrangement of some of these setae is due to reflection. b I. collaris n. sp. with ventral collar on basis capituli (yellow arrow) and multiple, short coxal setae (black arrows)
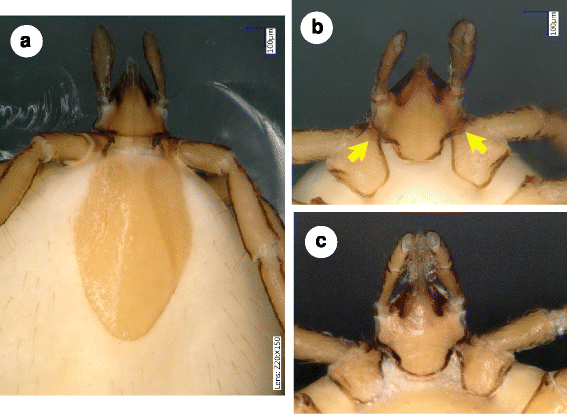
Fig. 4
Nymphs of Ixodes collaris n. sp. (paratype No. 2) (a, b) and I. vespertilionis (c). a I. collaris n. sp., dorsal view. b I. collaris n. sp., gnathosoma, ventral view. Note semitransparent collars extending above the first coxae (arrows). c Gnathosoma of I. vespertilionis, ventral view
Fig. 5
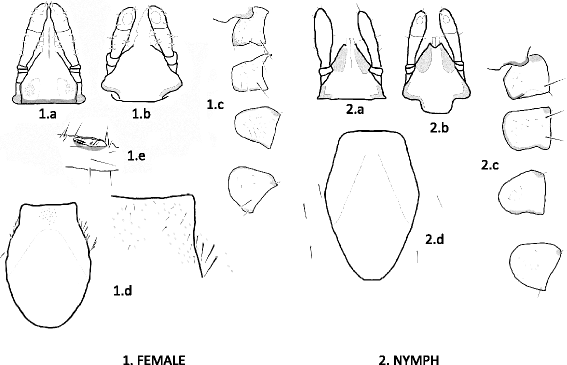
Drawings of structures with diagnostic importance in the female (1) and nymph (2) of Ixodes collaris n. sp. Labels: 1.a and 2.a, capitulum dorsal view; 1.b and 2b, capitulum ventral view; 1.c and 2.c, coxae (downward: I-IV) with the collar overlaying coxa I; 1.d and 2.d, scutum; 1.e, Haller’s organ
Similar articles
- Description of the male and the larva of Ixodes collaris Hornok, 2016 with drawings of all stages.
Hornok S, Murányi D, Kontschán J, Tu VT. Hornok S, et al. Parasit Vectors. 2019 Mar 26;12(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3365-3. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 30914054 Free PMC article. - The patterns of seasonal activity of Ixodes vespertilionis (Acari: Ixodidae) on Rhinolophus hipposideros in nursery colonies.
Piksa K, Górz A, Nowak-Chmura M, Siuda K. Piksa K, et al. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014 Feb;5(1):69-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.08.006. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014. PMID: 24252260 - New Locality Records of Ixodes granulatus and Ixodes vespertilionis (Acari: Ixodidae) From Tree-Shrews (Scandentia: Tupaiidae) and Bats (Chiroptera: Hipposideridae) in Laos.
Vongphayloth K, Douangboubpha B, Sanamxay D, Xayaphet V, Robbins RG, Apanaskevich DA, Sutherland IW, Brey PT. Vongphayloth K, et al. J Med Entomol. 2018 Jun 28;55(4):1035-1039. doi: 10.1093/jme/tjy019. J Med Entomol. 2018. PMID: 29897563 - First record of Ixodes simplex found on a human host, with a review of cases of human infestation by bat tick species occurring in Europe.
Péter Á, Barti L, Corduneanu A, Hornok S, Mihalca AD, Sándor AD. Péter Á, et al. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021 Jul;12(4):101722. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2021.101722. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021. PMID: 33865178 Review. - Review of the Ixodid tick fauna (Acari: Ixodidae) of Vietnam.
Kolonin GV. Kolonin GV. J Med Entomol. 1995 May;32(3):276-82. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/32.3.276. J Med Entomol. 1995. PMID: 7616517 Review.
Cited by
- A checklist of the ticks (Acari: Argasidae, Ixodidae) of Japan.
Kwak ML. Kwak ML. Exp Appl Acarol. 2018 Jun;75(2):263-267. doi: 10.1007/s10493-018-0259-6. Epub 2018 May 2. Exp Appl Acarol. 2018. PMID: 29721758 - Viral Hyperparasitism in Bat Ectoparasites: Implications for Pathogen Maintenance and Transmission.
Tendu A, Hughes AC, Berthet N, Wong G. Tendu A, et al. Microorganisms. 2022 Jun 16;10(6):1230. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10061230. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35744747 Free PMC article. Review. - Description of the male and the larva of Ixodes collaris Hornok, 2016 with drawings of all stages.
Hornok S, Murányi D, Kontschán J, Tu VT. Hornok S, et al. Parasit Vectors. 2019 Mar 26;12(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3365-3. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 30914054 Free PMC article. - Description of Ixodeslanigeri sp. nov., a new hard tick species (Acari, Ixodidae) collected from mouse-eared bats (Vespertilionidae, Myotis) in Vietnam.
Hornok S, Kontschán J, Takano A, Gotoh Y, Hassanin A, Tu VT. Hornok S, et al. Zookeys. 2024 Oct 14;1215:107-125. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.1215.123624. eCollection 2024. Zookeys. 2024. PMID: 39440030 Free PMC article. - Ixodes chilensis Kohls, 1956 (Acari: Ixodida: Ixodidae): re-description of the female, description of the nymph, and phylogenetic position inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences of the 16S rRNA gene.
González-Acuña D, Saracho-Bottero MN, Ossa G, Guglielmone AA, Nava S. González-Acuña D, et al. Syst Parasitol. 2018 Nov;95(8-9):959-967. doi: 10.1007/s11230-018-9818-9. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Syst Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 30155597
References
- Feider Z. Fauna of the Popular Republic of Romania. Bucharest: Academiei Republicii Populare Romane (In Romanian); 1965. Ixodoidea.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources