The calpain system is associated with survival of breast cancer patients with large but operable inflammatory and non-inflammatory tumours treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
The calpain system is associated with survival of breast cancer patients with large but operable inflammatory and non-inflammatory tumours treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Sarah J Storr et al. Oncotarget. 2016.
Abstract
The calpains are a family of intracellular cysteine proteases that function in a variety of important cellular functions, including cell signalling, motility, apoptosis and survival. In early invasive breast cancer expression of calpain-1, calpain-2 and their inhibitor, calpastatin, have been associated with clinical outcome and clinicopathological factors.The expression of calpain-1, calpain-2 and calpastatin was determined using immunohistochemistry on core biopsy samples, in a cohort of large but operable inflammatory and non-inflammatory primary breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Information on treatment and prognostic variables together with long-term clinical follow-up was available for these patients. Diagnostic pre-chemotherapy core biopsy samples and surgically excised specimens were available for analysis.Expression of calpastatin, calpain-1 or calpain-2 in the core biopsies was not associated with breast cancer specific survival in the total patient cohort; however, in patients with non-inflammatory breast cancer, high calpastatin expression was significantly associated with adverse breast cancer-specific survival (P=0.035), as was low calpain-2 expression (P=0.031). Low calpastatin expression was significantly associated with adverse breast cancer-specific survival of the inflammatory breast cancer patients (P=0.020), as was low calpain-1 expression (P=0.003).In conclusion, high calpain-2 and low calpastatin expression is associated with improved breast cancer-specific survival in non-inflammatory large but operable primary breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. In inflammatory cases, high calpain-1 and high calpastatin expression is associated with improved breast cancer-specific survival. Determining the expression of these proteins may be of clinical relevance. Further validation, in multi-centre cohorts of breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, is warranted.
Keywords: breast cancer; calpain; calpastatin; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
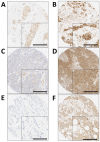
Figure 1. Representative photomicrographs following immunohistochemical staining of
A. low calpastatin, B. high calpastatin, C. low calpain-1, D. high calpain-1, E. low calpain-2 and F. high calpain-2 staining. Photomicrographs are shown at 100× magnification with 200× magnification inset box where scale bar shows 100μm.
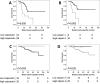
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier analysis of breast cancer specific survival showing the impact of high (black line) and low (grey line) calpastatin
A. and calpain-1 B. in patients with inflammatory breast cancer and calpastatin C. and calpain-2 D. expression in patients with non-inflammatory breast cancer in the core biopsy samples. Significance was determined using the log-rank test and the numbers shown below the Kaplan-Meier survival curves are the number of patients at risk at 0, 40, 80 and 120 months.
Similar articles
- Low calpain-9 is associated with adverse disease-specific survival following endocrine therapy in breast cancer.
Davis J, Martin SG, Patel PM, Green AR, Rakha EA, Ellis IO, Storr SJ. Davis J, et al. BMC Cancer. 2014 Dec 23;14:995. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-995. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25539577 Free PMC article. - Calpain-1 expression is associated with relapse-free survival in breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab following adjuvant chemotherapy.
Storr SJ, Woolston CM, Barros FF, Green AR, Shehata M, Chan SY, Ellis IO, Martin SG. Storr SJ, et al. Int J Cancer. 2011 Oct 1;129(7):1773-80. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25832. Epub 2011 Mar 8. Int J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21140455 - Calpain system protein expression and activity in ovarian cancer.
Zhang S, Deen S, Storr SJ, Chondrou PS, Nicholls H, Yao A, Rungsakaolert P, Martin SG. Zhang S, et al. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb;145(2):345-361. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2794-2. Epub 2018 Nov 17. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30448882 Free PMC article. - Calpain in Breast Cancer: Role in Disease Progression and Treatment Response.
Storr SJ, Thompson N, Pu X, Zhang Y, Martin SG. Storr SJ, et al. Pathobiology. 2015 Sep;82(3-4):133-41. doi: 10.1159/000430464. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Pathobiology. 2015. PMID: 26330354 Review. - [Calpain and calpastatin].
Murachi T. Murachi T. Rinsho Byori. 1990 Apr;38(4):337-46. Rinsho Byori. 1990. PMID: 2195187 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
- Dopamine and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein 32 kDa (DARPP-32) and survival in breast cancer: a retrospective analysis of protein and mRNA expression.
Kotecha S, Lebot MN, Sukkarn B, Ball G, Moseley PM, Chan SY, Green AR, Rakha E, Ellis IO, Martin SG, Storr SJ. Kotecha S, et al. Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 18;9(1):16987. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53529-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31740718 Free PMC article. - IL-6 and IL-10 are associated with good prognosis in early stage invasive breast cancer patients.
Ahmad N, Ammar A, Storr SJ, Green AR, Rakha E, Ellis IO, Martin SG. Ahmad N, et al. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2018 Apr;67(4):537-549. doi: 10.1007/s00262-017-2106-8. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2018. PMID: 29256156 Free PMC article. - Calpains, the proteases of two faces controlling the epithelial homeostasis in mammary gland.
García-Trevijano ER, Ortiz-Zapater E, Gimeno A, Viña JR, Zaragozá R. García-Trevijano ER, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Sep 19;11:1249317. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1249317. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37795261 Free PMC article. Review. - Calpain-2 inhibitor treatment preferentially reduces tumor progression for human colon cancer cells expressing highest levels of this enzyme.
Marciel MP, Rose AH, Martinez V, Horio DT, Hashimoto AS, Hoffmann FW, Bertino P, Hoffmann PR. Marciel MP, et al. Cancer Med. 2018 Jan;7(1):175-183. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1260. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 29210197 Free PMC article. - A framework for transcriptome-wide association studies in breast cancer in diverse study populations.
Bhattacharya A, García-Closas M, Olshan AF, Perou CM, Troester MA, Love MI. Bhattacharya A, et al. Genome Biol. 2020 Feb 20;21(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-1942-6. Genome Biol. 2020. PMID: 32079541 Free PMC article.
References
- Storr SJ, Carragher NO, Frame MC, Parr T, Martin SG. The calpain system and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:364–374. - PubMed
- Storr SJ, Pu X, Davis J, Lobo D, Reece-Smith AM, Parsons SL, Madhusudan S, Martin SG. Expression of the calpain system is associated with poor clinical outcome in gastro-oesophageal adenocarcinomas. J Gastroenterol. 2013;48:1213–1221. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical