Nutritional and therapeutic perspectives of Chia (Salvia hispanica L.): a review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Nutritional and therapeutic perspectives of Chia (Salvia hispanica L.): a review
Rahman Ullah et al. J Food Sci Technol. 2016 Apr.
Abstract
The ancient grain is becoming enormously popular in modern food regimen in many countries; the higher proportion of α-linolenic acid makes chia the superb source of omega-3 fatty (about 65 % of the oil content). Omega-3 fatty acid has been associated with a large number of physiological functions in human body. Chia seed is a potential source of antioxidants with the presence of chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, myricetin, quercetin, and kaempferol which are believed to have cardiac, hepatic protective effects, anti-ageing and anti-carcinogenic characteristics. It is also a great source of dietary fibre which is beneficial for the digestive system and controlling diabetes mellitus with higher concentration of beneficial unsaturated fatty acids, gluten free protein, vitamin, minerals and phenolic compounds. Therapeutic effects of chia in the control of diabetes, dyslipidaemia, hypertension, as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-blood clotting, laxative, antidepressant, antianxiety, analgesic, vision and immune improver is scientifically established.
Keywords: Chia; Fibre; Nutritional and therapeutic properties; Omega-3 fatty acids; Protein.
Figures
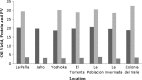
Fig. 1
Chemical characteristics of chia from various sources. Reference: Ayerza and Coates (2004). PV: Peroxide Value (meqO2/kg)
Similar articles
- Omega-3 fatty acids, phenolic compounds and antioxidant characteristics of chia oil supplemented margarine.
Nadeem M, Imran M, Taj I, Ajmal M, Junaid M. Nadeem M, et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2017 May 31;16(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0490-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28569164 Free PMC article. - Chia seeds: an ancient grain trending in modern human diets.
Melo D , Machado TB , Oliveira MBPP . Melo D , et al. Food Funct. 2019 Jun 19;10(6):3068-3089. doi: 10.1039/c9fo00239a. Food Funct. 2019. PMID: 31086922 Review. - Omega-3 fatty acids and oxidative stability of ice cream supplemented with olein fraction of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) oil.
Ullah R, Nadeem M, Imran M. Ullah R, et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Feb 7;16(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0420-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28173808 Free PMC article. - Ethnopharmacology, Nutritional Value, Therapeutic Effects, Phytochemistry, and Toxicology of Salvia hispanica L.: A Review.
Amtaghri S, Eddouks M. Amtaghri S, et al. Curr Top Med Chem. 2023;23(28):2621-2639. doi: 10.2174/0115680266248117230922095003. Curr Top Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37855294 Review. - Chia Seeds (Salvia hispanica L.): An Overview-Phytochemical Profile, Isolation Methods, and Application.
Knez Hrnčič M, Ivanovski M, Cör D, Knez Ž. Knez Hrnčič M, et al. Molecules. 2019 Dec 18;25(1):11. doi: 10.3390/molecules25010011. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31861466 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Physicochemical, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Rapeseed Lecithin Liposomes Loading a Chia (Salvia hispanica L.) Seed Extract.
Alemán A, Pérez-García S, Fernández de Palencia P, Montero MP, Gómez-Guillén MDC. Alemán A, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Apr 28;10(5):693. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050693. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33924836 Free PMC article. - Fatty Acid Composition of Pseudocereals and Seeds Used as Functional Food Ingredients.
Czerwonka M, Białek A. Czerwonka M, et al. Life (Basel). 2023 Jan 12;13(1):217. doi: 10.3390/life13010217. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36676166 Free PMC article. - The Nutritional and Functional Properties of Protein Isolates from Defatted Chia Flour Using Different Extraction pH.
Khushairay ESI, Ghani MA, Babji AS, Yusop SM. Khushairay ESI, et al. Foods. 2023 Aug 14;12(16):3046. doi: 10.3390/foods12163046. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37628045 Free PMC article. - Effect of Prunus dulcis and Salvia hispenica in the management of polycystic ovary syndrome in Wistar rats.
Ramachandran S, Nikitha J, Gopi C, Amala M, Dhanaraju MD. Ramachandran S, et al. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2020 Mar 19;15(2):122-128. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2020.02.002. eCollection 2020 Apr. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32368208 Free PMC article. - Mediterranean Gluten-Free Diet: Is It a Fair Bet for the Treatment of Gluten-Related Disorders?
Bascuñán KA, Elli L, Vecchi M, Scricciolo A, Mascaretti F, Parisi M, Doneda L, Lombardo V, Araya M, Roncoroni L. Bascuñán KA, et al. Front Nutr. 2020 Dec 2;7:583981. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2020.583981. eCollection 2020. Front Nutr. 2020. PMID: 33344491 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Ahmed M, Hamed R, Ali M, Hassan A, Babiker E. Proximate composition, antinutritional factors and protein fractions of guar gum seeds as influenced by processing treatments. Pak J Nutr. 2006;5(5):340–345.
- Alonso-Calderon A, Chávez-Bravo E, Rivera A, Montalvo-Paquini C, Arroyo-Tapia L (2013) ABCDLKF’K;GL’;LKG
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources