Lizard tail regeneration as an instructive model of enhanced healing capabilities in an adult amniote - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Lizard tail regeneration as an instructive model of enhanced healing capabilities in an adult amniote
Thomas P Lozito et al. Connect Tissue Res. 2017 Mar.
Abstract
The ability to regenerate damaged or lost tissues has remained the lofty goal of regenerative medicine. Unfortunately, humans, like most mammals, suffer from very minimal natural regenerative capabilities. Certain non-mammalian animal species, however, are not so limited in their healing capabilities, and several have attracted the attention of researchers hoping to recreate enhanced healing responses in humans. This review focuses on one such animal group with remarkable regenerative abilities, the lizards. As the closest relatives of mammals that exhibit enhanced regenerative abilities as adults, lizards potentially represent the most relevant model for direct comparison and subsequent improvement of mammalian healing. Lizards are able to regenerate amputated tails and exhibit adaptations that both limit tissue damage in response to injury and initiate coordinated regenerative responses. This review summarizes the salient aspects of lizard tail regeneration as they relate to the overall regenerative process and also presents the relevant information pertaining to regrowth of specific tissues, including skeletal, muscular, nervous, and vascular tissues. The goal of this review is to introduce the topic of lizard tail regeneration to new audiences with the hope of expanding the knowledge base of this underutilized but potentially powerful model organism.
Keywords: Cartilage; lizard; muscle; peripheral nerve; regeneration; salamander; spinal cord.
Figures
Fig. 1
Examples of limb and tail regeneration in amphibians and lizards. (A, B) Morphological comparison of (A) salamander (Ambystoma mexicanum) and (B) frog (Xenopus laevis) forelimbs before (left) and 8 weeks after (right) amputation. Salamanders regenerate new limbs, while frogs regenerate cartilage spikes. (C, D) Histological analysis (pentachrome) of regenerated (C) salamander and (D) frog limbs. Salamanders regenerate all the skeletal elements of the upper arm and hand, while frogs regenerate a single cartilage spike. (E, F) Histological (pentachrome) and (E, F Insets) morphological analysis of (E) salamander tail 5-weeks post amputation and (F) lizard (Anolis carolinensis) tail 2 weeks post-amputation. (G) Salamander (top) and lizard (bottom) tails 10 weeks after amputation analyzed by micro computed tomography. The regenerated salamander, but not lizard, skeleton segments. Pentachrome stains cartilage green, bone orange, muscle red, and spinal cord and epidermis purple. Dashed lines denote amputation planes. c, carpal; cr, cartilage rod; cs, cartilage spike; ct, cartilage tube; h, humerus; m, muscle; mc, metacarpal; nc, notochord; p, phalanges; r, radius; rm, regenerated muscle; rsc, regenerated spinal cord; ru, radio-ulna; sc, spinal cord; u, ulna; ve, vertebra. Bar = 1 mm.
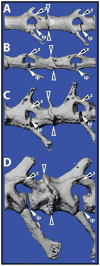
Fig. 2
Autotomous lizard tail vertebrae contain fracture planes. Original tails of (A) Anolis carolinensis, (B) Hemidactylus frenatus, (C) Heteronotia binoei, and (D) Hoplodactylus duvaucelii analyzed by micro computed tomography and highlighting the diversity of fracture plane position and structure. Open arrowheads denote intravertebral fracture plane. White-filled arrowheads mark intervertebral pads (ip). Black-filled arrowheads identify Z-joints (z). Bar = 100 μm.
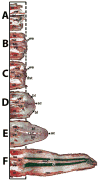
Fig. 3
Representative lizard tails (A) 0, (B) 3, (C) 6, (D) 9, (E) 12, (F) 15, (G) and 28 days following tail loss highlighting the important structures involved with tail regrowth. ac, apical cap; bl, blastema; ct, cartilage tube; dst, degenerated stump tissue; m, muscle; rm, regenerated muscle; rsc, regenerated spinal cord; sc, spinal cord; we, wound epithelium; ve, vertebra.
Fig. 4
Regenerated lizard tails are able to re-regenerate following amputation. (A,B) Mature lizard tail regenerates with CTs were amputated in (1) the original tail vertebra (Orig), (2) the proximal regenerated tail (Prox), or (3) the distal regenerated tail (Dist). (A) Morphological and (B) microCT analyses of an intact mature lizard regenerate showing relative position of amputation sites. (B) The skeletons of original, but not regenerated, tail regions. Fracture planes (fp) are present in (C–E) Following 4 weeks of regeneration, tails amputated in the (C) original tail, (D) proximal regenerate, or (E) distal regenerates were analyzed for overall regenerate elongation. fp, fracture plane. Bar = 0.5 cm.
Fig. 5
Micro computed tomography scans of original lizard tail terminal vertebrae 2, and 6, and 9 days post-autotomy (DPA) analyzed by micro computed tomography. The distal portions of terminal vertebrae are completely degraded by 9 DPA. Bar = 100 μm.
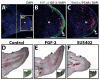
Fig. 6
(A–C) Analysis of signaling molecules and cell proliferation markers within the regenerating lizard tail. Lizard tail blastemas (9 days following tail loss) were immunostained for IGF-2, FGF-2, Wnt5a, and PCNA. Panels B and C depict higher magnification views of region identified in Panel A. Dashed lines denote amputation planes. (D–F) Effects of FGF-2 and the FGF inhibitor SU5402 on lizard tail regeneration. Beads soaked in (D) vehicle control, (E) 100 μg/ml FGF-2, (F) or 2 mg/ml SU5402 were implanted in lizard tail blastemas. Following 7 days of growth, the tails were collected and analyzed by collagen type II immunohistochemistry. Insets of each panel depict gross tail morphology. Stars denote bead implantation sites. (D) Control tails exhibit normal ependymal tube extension. (E) Tails treated with FGF-2-soaked beads exhibit ependymal tube branches that invade toward implantation sites. (F) Tails treated with SU5402-soaked beads exhibit stunted ependymal tube invasion. ac, apical cap; bl, blastema; et, ependymal tube; ct, cartilage tube. Bar = 2 mm.
Fig. 7
Close-up of extreme proximal cartilage tube highlighting its resemblance to a fracture callus. ct, cartilage tube; hc, hypertrophic chondrocytes; oc, ossification center; po, periosteum; ve, vertebra. Bar = 100 μm.
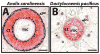
Fig. 8
Comparison of cartilage tube perichondrium calcification between two species of lizards. Cross-sections of mature regenerated tails of (A) _Anolis carolinensi_s and (B) the gecko Dactylocnemis pacificus analyzed by histology (von Kossa / Safranin O). Cartilage stains red, and calcified tissues stain black. The perichondrium of the Anolis cartilage tube calcifies, while the gecko cartilage tube resists calcification. ct, cartilage tube; pc, perichondrium; rsc, regenerated spinal cord. Bar = 50 μm.
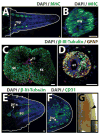
Fig. 9
Lizard tail muscle, spinal cord, peripheral nerve, and blood vessel regeneration. (A) Lizard tail 21 days post amputation (DPA) immunostained for muscle marker myosin heavy chain (MHC). Regenerated muscles begin as distinct myomeres. (B) Close-up of a regenerated muscle myomere. (C) Original and (D) regenerated tail spinal cords analyzed immunostained for neural marker β-III-tubulin and glial cell marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). (E, F) Lizard tail 9 DPA immunostained for (E) β-III-tubulin and (F) the blood vessel marker CD31. (E) Peripheral nerves regenerate from dorsal root ganglia in tail stumps into tail blastemas. (F) Blood vessels form at the distal lizard tail blastema tip (G) Blood vessels also form at the distal salamander tail blastema tip. Black arrowhead marks prominent vascular bed. Inset depicts gross morphology of entire salamander tail blastema. Dashed lines denote amputation planes, and solid lines trace tail outlines. bl, blastema; drg, dorsal root ganglion; pn, peripheral nerve; sc, spinal cord. Bar = 25 μm.
Fig. 10
The lizard spinal cord is necessary and sufficient for inducing regenerated tails in lizards. (A, B) Morphological comparison of lizard tails (A) with and (B) without intact spinal cords two weeks after tail loss. (A) Lizard tails with intact spinal cords regenerate new tails, but (B) tails with disrupted spinal cords fail to regenerate. Dashed line marks amputation plane. (C, D) Morphologies of lizard tails (C) with or (D) without spinal cord implants. After two weeks, (C) tails treated with exogenous spinal cord implants develop ectopic tails at implantation sites, while (D) control tails that did not receive exogenous spinal cord implants did not exhibit any growth. ect, ectopic tail. Bar = 1 mm.
Similar articles
- Histochemical, Biochemical and Cell Biological aspects of tail regeneration in lizard, an amniote model for studies on tissue regeneration.
Alibardi L. Alibardi L. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2014 Jan;48(4):143-244. doi: 10.1016/j.proghi.2013.12.001. Epub 2014 Jan 1. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2014. PMID: 24387878 Review. - Differences in neural stem cell identity and differentiation capacity drive divergent regenerative outcomes in lizards and salamanders.
Sun AX, Londono R, Hudnall ML, Tuan RS, Lozito TP. Sun AX, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Aug 28;115(35):E8256-E8265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1803780115. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30104374 Free PMC article. - Tail regeneration and other phenomena of wound healing and tissue restoration in lizards.
Jacyniak K, McDonald RP, Vickaryous MK. Jacyniak K, et al. J Exp Biol. 2017 Aug 15;220(Pt 16):2858-2869. doi: 10.1242/jeb.126862. J Exp Biol. 2017. PMID: 28814609 Review. - Developmental and adult-specific processes contribute to de novo neuromuscular regeneration in the lizard tail.
Tokuyama MA, Xu C, Fisher RE, Wilson-Rawls J, Kusumi K, Newbern JM. Tokuyama MA, et al. Dev Biol. 2018 Jan 15;433(2):287-296. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.10.003. Epub 2017 Dec 25. Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29291978 Free PMC article. - The anatomy and histology of caudal autotomy and regeneration in lizards.
Gilbert EA, Payne SL, Vickaryous MK. Gilbert EA, et al. Physiol Biochem Zool. 2013 Nov-Dec;86(6):631-44. doi: 10.1086/673889. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Physiol Biochem Zool. 2013. PMID: 24241061 Review.
Cited by
- Introducing dorsoventral patterning in adult regenerating lizard tails with gene-edited embryonic neural stem cells.
Lozito TP, Londono R, Sun AX, Hudnall ML. Lozito TP, et al. Nat Commun. 2021 Oct 14;12(1):6010. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26321-9. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34650077 Free PMC article. - Multi-species comparisons of snakes identify coordinated signalling networks underlying post-feeding intestinal regeneration.
Perry BW, Andrew AL, Mostafa Kamal AH, Card DC, Schield DR, Pasquesi GIM, Pellegrino MW, Mackessy SP, Chowdhury SM, Secor SM, Castoe TA. Perry BW, et al. Proc Biol Sci. 2019 Jul 10;286(1906):20190910. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2019.0910. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Proc Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31288694 Free PMC article. - De Novo Transcriptome Sequencing and Analysis of Differential Gene Expression among Various Stages of Tail Regeneration in Hemidactylus flaviviridis.
Patel S, Ranadive I, Buch P, Khaire K, Balakrishnan S. Patel S, et al. J Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 14;10(2):24. doi: 10.3390/jdb10020024. J Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35735915 Free PMC article. - Downregulation of lizard immuno-genes in the regenerating tail and myogenes in the scarring limb suggests that tail regeneration occurs in an immuno-privileged organ.
Vitulo N, Dalla Valle L, Skobo T, Valle G, Alibardi L. Vitulo N, et al. Protoplasma. 2017 Nov;254(6):2127-2141. doi: 10.1007/s00709-017-1107-y. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Protoplasma. 2017. PMID: 28357509 - Inducing Vertebrate Limb Regeneration: A Review of Past Advances and Future Outlook.
Davidian D, Levin M. Davidian D, et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2022 May 17;14(4):a040782. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a040782. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2022. PMID: 34400551 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Lozito TP, Tuan RS. Lizard tail regeneration: regulation of two distinct cartilage regions by Indian hedgehog. Developmental Biology. 2015;399(2):249–62. - PubMed
- Delorme SL, Lungu IM, Vickaryous MK. Scar-free wound healing and regeneration following tail loss in the leopard gecko, Eublepharis macularius. Anatomical record. 2012;295(10):1575–95. - PubMed
- Bellairs AD, Bryant SV. Autotomy and Regeneration in Reptiles. In: Billet CGaF., editor. The Biology Of The Reptilia. Vol. 15. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 1985. pp. 303–410.
- Alibardi L. In: Morphological and Cellular Aspects of Tail and Limb Regeneration in Lizards: A Model System With Implications for Tissue Regeneration in Mammals. Korf H-W, editor. Springer; 2010. - PubMed
- Chablais F, Jazwinska A. IGF signaling between blastema and wound epidermis is required for fin regeneration. Development. 2010;137(6):871–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials