Urine Protein/Creatinine Ratios during Labor: A Prospective Observational Study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Urine Protein/Creatinine Ratios during Labor: A Prospective Observational Study
Vaya W Tanamai et al. PLoS One. 2016.
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the utility of urine protein/creatinine ratio (uPCR) measurements among healthy parturients at term we performed a prospective cohort study at a community teaching hospital.
Methods: Serial urine samples were collected. Ninety-three women contributed 284 urine samples. uPCRs were determined. Multiple imputation and paired sampled analysis was performed when appropriate.
Results: Two-thirds (63/93) of women had at least one measured uPCR ≥ 0.3. One-third (31/93) had a uPCR ≥ 0.3 at admission, including 39.1% (9/23) of women not in labor. Median (IQR) uPCRs increased during labor and after delivery: latent phase/no labor, 0.15 (0.06-0.32); active phase, 0.29 (0.10-0.58); early postpartum, 0.45 (0.18-1.36) (all p < 0.04). Median uPCRs were significantly < 0.3 in the latent phase and significantly > 0.3 in the immediate postpartum period (p < 0.01). Women who labored before cesarean delivery had the highest early postpartum uPCRs: median (IQR) 1.16 (0.39-1.80). A negative urine dipstick protein result did not exclude uPCR ≥ 0.3. uPCRs were similar when compared by method of urine collection.
Conclusion: uPCR ≥ 0.3 is common among healthy women with uncomplicated pregnancies at term. uPCR increases during labor and is not a reliable measure of pathologic proteinuria at term or during the peripartum period.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declated that no competing interests exist.
Figures
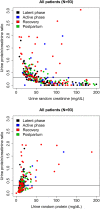
Fig 1. Urine protein/creatinine ratio (uPCR) by urine creatinine and protein concentrations.
uPCR measurements plotted by urine random creatinine (top) and protein (bottom) concentrations and colored by phase of labor and delivery admission. Horizontal line on each graph represents uPCR = 0.3.
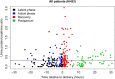
Fig 2. Urine protein/creatinine ratio (uPCR) measurements in all 284 urine samples from 93 women plotted against the timing of the sample collection relative to delivery time.
The phase of labor at the time of sample collection is shown for each individual sample by one of four different colors. The horizontal line represents the threshold uPCR value of 0.3.
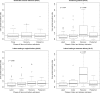
Fig 3. Box plots of urine protein/creatinine ratio (uPCR) measurements by phase of labor at the time of collection and subsequent delivery outcome.
uPCR measurements from samples collected before and after delivery among women who had a scheduled cesarean delivery without labor (top left), all laboring women (top right), laboring women who delivered vaginally (bottom left), and laboring women who subsequently delivered by cesarean (bottom right) are shown. The horizontal line on each graph represents the threshold uPCR value of 0.3. When the distribution of observed uPCR values is significantly different than the threshold value of 0.3, the p-value (Mann-Whitney u test) is shown.
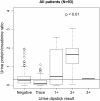
Fig 4. Box plots of urine protein/creatinine ratio (uPCR) measurements by urine protein dipstick result.
The horizontal line on each graph represents the threshold uPCR value of 0.3. When the distribution of observed uPCR values is significantly different than the threshold value of 0.3, the p-value (Mann-Whitney u test) is shown. Three uPCR outlier values (4.9, 6.1, and 8.9 in the Negative, 1+, and 2+ groups, respectively) are not shown.
Similar articles
- Comparisons of urine protein-to-creatinine ratios and their dynamic change patterns during labor at term between normal pregnant women and women with pregnancy induced hypertension.
Yang PY, Tsai YL, Chang YJ, Wang PH. Yang PY, et al. Int J Med Sci. 2022 Aug 15;19(9):1473-1481. doi: 10.7150/ijms.72926. eCollection 2022. Int J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36035364 Free PMC article. - Physiologic proteinuria in labor and postpartum: The results of the postpartum proteinuria trial (PoPPy).
Aziz MM, Kulkarni A, Shah L, Lashley S, Oyelese Y. Aziz MM, et al. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2018 Jul;13:22-24. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2018.04.019. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2018. PMID: 30177056 - Diagnostic accuracy of random urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio for proteinuria in patients with suspected pre-eclampsia.
Pasternak Y, Lifshitz D, Shulman Y, Hiersch L, Rimon E, Kuperminc M, Yogev Y, Ashwal E. Pasternak Y, et al. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2021 Jul;304(1):109-115. doi: 10.1007/s00404-020-05937-0. Epub 2021 Jan 1. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2021. PMID: 33386413 - Empiricism or rationalism: how should we measure proteinuria?
Methven S, MacGregor MS. Methven S, et al. Ann Clin Biochem. 2013 Jul;50(Pt 4):296-300. doi: 10.1177/0004563212473283. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Ann Clin Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23787260 Review.
Cited by
- Twenty-four-hour proteinuria levels are associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes among women with CKD.
Li Z, Chen S, Tan Y, Lv J, Zhao M, Chen Q, He Y. Li Z, et al. Clin Kidney J. 2023 Mar 10;16(10):1634-1643. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad044. eCollection 2023 Oct. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 37779840 Free PMC article. - Comparisons of urine protein-to-creatinine ratios and their dynamic change patterns during labor at term between normal pregnant women and women with pregnancy induced hypertension.
Yang PY, Tsai YL, Chang YJ, Wang PH. Yang PY, et al. Int J Med Sci. 2022 Aug 15;19(9):1473-1481. doi: 10.7150/ijms.72926. eCollection 2022. Int J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36035364 Free PMC article.
References
- Davey DA, MacGillivray I. The classification and definition of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988;158: 892–898. - PubMed
- Higby K, Suiter CR, Phelps JY, Siler-Khodr T, Langer O. Normal values of urinary albumin and total protein excretion during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994;171: 984–989. - PubMed
- Evans W, Lensmeyer JP, Kirby RS, Malnory ME, Broekhuizen FF. Two-hour urine collection for evaluating renal function correlates with 24-hour urine collection in pregnant patients. J Matern-Fetal Med. 2000;9: 233–237. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
Funded by the Danbury Hospital Development Fund. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical