BDNF-mediates Down-regulation of MicroRNA-195 Inhibits Ischemic Cardiac Apoptosis in Rats - PubMed (original) (raw)
BDNF-mediates Down-regulation of MicroRNA-195 Inhibits Ischemic Cardiac Apoptosis in Rats
Pengzhou Hang et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2016.
Abstract
Background: Our previous studies suggested that brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)/tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) axis inhibited cardiomyocyte apoptosis in myocardial infarction (MI). However, the relationship between BDNF and microRNA (miRNA) in cardiomyocytes are unclear. The present study was performed to investigate the role of miR-195 and the interplay between BDNF and miR-195 in ischemic cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
Methods: Male Wistar rats were subjected to coronary artery ligation, and primary neonatal rat ventricular myocytes were treated with hypoxia or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). BDNF level in rat ventricles was measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). miR-195 mimic, inhibitor or negative control was transfected into the cardiomyocytes. Cell viability and apoptosis were detected by MTT assay and TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining, respectively. Cardiac function and apoptosis were detected in MI rats intravenously injected with antagomiR-195. Luciferase assay, Western blot and Real-time RT-PCR were employed to clarify the interplay between miR-195 and BDNF.
Results: miR-195 level was dynamically regulated in response to MI and significantly increased in ischemic regions 24 h post-MI as well as in hypoxic or H2O2-treated cardiomyocytes. Meanwhile, BDNF protein level was rapidly increased in MI rats and H2O2-treated cardiomyocytes. Apoptosis in both hypoxic and H2O2-treated cardiomyocytes were markedly reduced and cell viability was increased by miR-195 inhibitor. Moreover, inhibition of miR-195 significantly improved cardiac function of MI rats. Bcl-2 but not BDNF was validated as the direct target of miR-195. Furthermore, BDNF abolished the pro-apoptotic role of miR-195, which was reversed by its scavenger TrkB-Fc.
Conclusion: Up-regulation of miR-195 in ischemic cardiomyocytes promotes ischemic apoptosis by targeting Bcl-2. BDNF mitigated the pro-apoptotic effect of miR-195 in rat cardiomyocytes. These findings may provide better understanding of the pro-apoptotic role of miR-195 in MI and suggest that BDNF/miR-195/Bcl-2 axis may be beneficial for limiting myocardial ischemic injury.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Bcl-2.; Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Myocardial ischemia; miR-195.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Figure 1
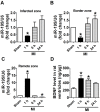
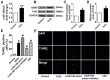
miR-195 and BDNF levels were dynamically regulated in different regions of rat myocardium in response to ischemic injury. (A, B) Real-time PCR analysis indicates that miR-195 is increased in the infarcted and border zones 24 h after myocardial infarction (MI). (C) miR-195 is decreased in remote zone in rat myocardium 24 h after MI. (D) BDNF level in ischemic zone of rat ventricles. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. sham, n = 3.
Figure 2
miR-195 mimic and inhibitor transfection validation. (A) Real-time PCR analysis indicated that miR-195 level was dramatically increased after transfecting with miR-195 mimic compared with control group. (B) miR-195 level was markedly decreased after transfecting with miR-195 inhibitor compared with control group. **p<0.01 vs. control, ***p<0.001 vs. control, n = 3.
Figure 3
miR-195 inhibitor attenuated hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. (A) Real-time PCR analysis indicates that miR-195 is increased in hypoxia-treated cardiomyocytes. (B) Statistical results of TUNEL-positive cells per field. (C) Representative images of TUNEL staining of cardiomyocyte showing the apoptotic cells (apoptotic cells stained in green and nucleus stained in blue with DAPI). *p<0.05 vs. control, #p<0.05 vs. hypoxia, n = 5, scale bar: 100 μm.
Figure 4
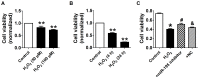
miR-195 inhibitor protected against cardiomyocyte injury induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). (A, B) Cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were exposed to different concentration of of H2O2 (50, 100 μM) for 4 h, or different timepoints (4 h, 24 h) at 100 μM. (C) MTT assay suggested that miR-195 inhibitor restored cell viability after H2O2 treatment. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs Control, #p<0.05 vs H2O2, &p<0.05 vs miR-195 inhibitor, n = 5.
Figure 5
miR-195 inhibitor attenuated H2O2-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. (A) Real-time PCR analysis indicates that miR-195 is increased in H2O2-treated cardiomyocytes. (B) Western blot bands of BDNF and TrkB in control and H2O2-treated cardiomyocytes. (C, D) Statistical results of protein level of BDNF and TrkB, *p<0.05, n = 5. (E) Statistical results of TUNEL-positive cells per field. (F) Representative images of TUNEL staining of cardiomyocyte showing the apoptotic cells (apoptotic cells stained in green and nucleus stained in blue with DAPI). *p<0.05 vs. control, #p<0.05 vs. H2O2, &p<0.05 vs. +miR-195 mimic, n = 5, scale bar: 100 μM.
Figure 6
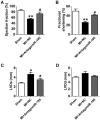
Improvement of cardiac function by antagomiR-195 in MI rats. (A) Ejection fractions. (B) Fractional shortening. (C) Left ventricular systolic diameter (LVDs). (D) Left ventricular diastolic diameter (LVDd). *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. sham, #p<0.05 vs. MI+NC, n = 5.
Figure 7
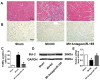
AntagomiR-195 inhibited cardiac injury and apoptosis by upregulating Bcl-2 in MI rats. (A) Representative HE staining pictures, scale bar: 50 μM. (B) Representative images of TUNEL staining in rat myocardium (apoptotic cells stained in brown), scale bar: 50 μM. (C) Statistical results of TUNEL-positive cells per field. (D) Western blot bands of Bcl-2 in sham, MI+NC and MI+antagomiR-195 rat hearts. (E) Statistical results of protein level of Bcl-2. *p<0.05 vs. sham, #p<0.05 vs. MI+NC, n = 5.
Figure 8
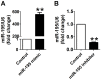
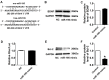
Target validation of miR-195. (A) Sequence alignment show between miR-195 and the binding sites in the 3'UTR of the Bdnf gene. (B) Representative western blot bands of BDNF. (C) Statistical results of protein level of BDNF in miR-195 mimic and NC group, n = 3. (D) The interaction between miR-195 and its binding sites in the 3'UTR of Bdnf was examined by luciferase assay in HEK293 cells, n = 3. (E) Representative western blot bands of Bcl-2. (F) Statistical results of protein level of Bcl-2 in miR-195 mimic and NC group, *p<0.05, vs. control, n = 3.
Figure 9
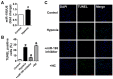
BDNF inhibited miR-195 expression and protected cardiomyocytes against H2O2-induced apoptosis. (A) Real-time PCR analysis indicates that miR-195 level is reduced by BDNF and restored by TrkB-Fc, *p<0.05, vs. control, #p<0.05 vs H2O2, &p<0.05 vs +BDNF, n = 5. (B) MTT assay showed that BDNF improved cell viability in H2O2-treated cardiomyocytes and was reversed by TrkB-Fc, *p<0.05, vs. control, #p<0.05 vs H2O2, &p<0.05 vs +BDNF, n = 5. (C) The quantitative presentation of apoptotic cells by Annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide (PI) staining, *p<0.05, vs. control, #p<0.05 vs H2O2, &p<0.05 vs +BDNF, n = 3. (D) Representative Annexin V-FITC/PI staining pictures.
Similar articles
- Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates TRPC3/6 channels and protects against myocardial infarction in rodents.
Hang P, Zhao J, Cai B, Tian S, Huang W, Guo J, Sun C, Li Y, Du Z. Hang P, et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2015 Mar 25;11(5):536-45. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.10754. eCollection 2015. Int J Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25892961 Free PMC article. - Inhibition of MicroRNA-124 Reduces Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis Following Myocardial Infarction via Targeting STAT3.
He F, Liu H, Guo J, Yang D, Yu Y, Yu J, Yan X, Hu J, Du Z. He F, et al. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(1):186-200. doi: 10.1159/000495173. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30439699 - MicroRNA-155 Promotes Myocardial Infarction-Induced Apoptosis by Targeting RNA-Binding Protein QKI.
Guo J, Liu HB, Sun C, Yan XQ, Hu J, Yu J, Yuan Y, Du ZM. Guo J, et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 May 5;2019:4579806. doi: 10.1155/2019/4579806. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31191799 Free PMC article. - Depletion of microRNA-92a Enhances the Role of Sevoflurane Treatment in Reducing Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Upregulating KLF4.
Wu Q, Wang H, He F, Zheng J, Zhang H, Cheng C, Hu P, Lu R, Yan G. Wu Q, et al. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2023 Dec;37(6):1053-1064. doi: 10.1007/s10557-021-07303-x. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2023. PMID: 35171385 Review. - BDNF and its signaling in cancer.
Malekan M, Nezamabadi SS, Samami E, Mohebalizadeh M, Saghazadeh A, Rezaei N. Malekan M, et al. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jun;149(6):2621-2636. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04365-8. Epub 2022 Sep 29. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36173463 Review.
Cited by
- Protective effects of melatonin in cisplatin-induced cardiac toxicity: possible role of BDNF-TNF-α signaling pathway.
Zhuo X, Jiang H. Zhuo X, et al. Acta Cir Bras. 2022 May 2;37(2):e370208. doi: 10.1590/acb370208. eCollection 2022. Acta Cir Bras. 2022. PMID: 35507972 Free PMC article. - Mitochondrial MiRNA in Cardiovascular Function and Disease.
Song R, Hu XQ, Zhang L. Song R, et al. Cells. 2019 Nov 21;8(12):1475. doi: 10.3390/cells8121475. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31766319 Free PMC article. Review. - H3K9me2 regulation of BDNF expression via G9a partakes in the progression of heart failure.
Yan F, Chen Z, Cui W. Yan F, et al. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Apr 19;22(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02621-w. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022. PMID: 35439934 Free PMC article. - MicroRNA-98 negatively regulates myocardial infarction-induced apoptosis by down-regulating Fas and caspase-3.
Sun C, Liu H, Guo J, Yu Y, Yang D, He F, Du Z. Sun C, et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 7;7(1):7460. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07578-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28784995 Free PMC article. - lncRNA FGD5 antisense RNA 1 upregulates RORA to suppress hypoxic injury of human cardiomyocyte cells by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis via miR‑195.
Cai X, Zhang P, Wang S, Hong L, Yu S, Li B, Zeng H, Yang X, Shao L. Cai X, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2020 Dec;22(6):4579-4588. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11558. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 33174051 Free PMC article.
References
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M. et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133:e38–e360. - PubMed
- Saraste A, Pulkki K, Kallajoki M, Henriksen K, Parvinen M, Voipio-Pulkki LM. Apoptosis in human acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1997;95:320–323. - PubMed
- Olivetti G, Quaini F, Sala R, Lagrasta C, Corradi D, Bonacina E, Gambert SR, Cigola E, Anversa P. Acute myocardial infarction in humans is associated with activation of programmed myocyte cell death in the surviving portion of the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1996;28:2005–2016. - PubMed
- Piro FR, di Gioia CR, Gallo P, Giordano C, d'Amati G. Is apoptosis a diagnostic marker of acute myocardial infarction? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2000;124:827–831. - PubMed
- Palojoki E, Saraste A, Eriksson A, Pulkki K, Kallajoki M, Voipio-Pulkki LM, Tikkanen I. Cardiomyocyte apoptosis and ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001;280:H2726–H2731. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources