DICERing macrophages for reprogramming TAMs - PubMed (original) (raw)
Editorial
DICERing macrophages for reprogramming TAMs
Mario Leonardo Squadrito et al. Cell Cycle. 2016 Dec.
No abstract available
Figures
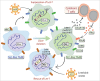
Figure 1.
Suppressing DICER activity reprograms TAMs. The genetic inactivation of Dicer induces M2-like TAMs (left, light blue cell) to acquire features of M1-like TAMs (right, light green cell). This is associated with the upregulation of genes denoting a pro-inflammatory signature, including the T cell chemoattractants Cxcl9 and Cxcl10. The production of CXCL9 and 10 by the reprogrammed TAMs enhances CTL infiltration in the tumors; in turn, CTL-derived IFNγ exacerbates M1 programming of the TAMs. Restoring the expression of Let-7 in the _Dicer_-deficient TAMs using DICER-independent lentiviral vectors and a haematopoietic -cell transplantation strategy (bottom, light blue cell) attenuates the pro-inflammatory gene signature and partly rescues M2-like activation of TAMs. Conversely, blocking Let-7 activity with a LIN28A-expressing lentiviral vector (top, light green cell) prompts cultured macrophages to acquire M1-like features, including immunostimulatory properties.
Comment on
- doi: 10.1038/ncb3371
Similar articles
- Taming TAMs in brain metastases.
Seton-Rogers S. Seton-Rogers S. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022 Jan;22(1):2-3. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00426-1. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34799680 No abstract available. - Comprehensive Proteomics Analysis Reveals Metabolic Reprogramming of Tumor-Associated Macrophages Stimulated by the Tumor Microenvironment.
Liu D, Chang C, Lu N, Wang X, Lu Q, Ren X, Ren P, Zhao D, Wang L, Zhu Y, He F, Tang L. Liu D, et al. J Proteome Res. 2017 Jan 6;16(1):288-297. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00604. Epub 2016 Nov 3. J Proteome Res. 2017. PMID: 27809537 - Tumor-Associated Macrophages as Target for Antitumor Therapy.
Sawa-Wejksza K, Kandefer-Szerszeń M. Sawa-Wejksza K, et al. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2018 Apr;66(2):97-111. doi: 10.1007/s00005-017-0480-8. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2018. PMID: 28660349 Free PMC article. Review. - Proton irradiation orchestrates macrophage reprogramming through NFκB signaling.
Genard G, Wera AC, Huart C, Le Calve B, Penninckx S, Fattaccioli A, Tabarrant T, Demazy C, Ninane N, Heuskin AC, Lucas S, Michiels C. Genard G, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jun 27;9(7):728. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0757-9. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29950610 Free PMC article. - Leukemoid reaction in pancreatic cancer: a case report and review of the literature.
Qureshi KM, Raman AK, Tan D, Fakih MG. Qureshi KM, et al. JOP. 2006 Nov 10;7(6):631-4. JOP. 2006. PMID: 17095843 Review.
Cited by
- Nanomedicines for dysfunctional macrophage-associated diseases.
He H, Ghosh S, Yang H. He H, et al. J Control Release. 2017 Feb 10;247:106-126. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.12.032. Epub 2017 Jan 3. J Control Release. 2017. PMID: 28057522 Free PMC article. Review. - Precision Targeting of Tumor Macrophages with a CD206 Binding Peptide.
Scodeller P, Simón-Gracia L, Kopanchuk S, Tobi A, Kilk K, Säälik P, Kurm K, Squadrito ML, Kotamraju VR, Rinken A, De Palma M, Ruoslahti E, Teesalu T. Scodeller P, et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 7;7(1):14655. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14709-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29116108 Free PMC article.
References
- Biswas SK, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: cancer as a paradigm. Nat Immunol 2010; 11:889-96; PMID:20856220; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ni.1937 - DOI - PubMed
- De Palma M, Lewis CE. Macrophage regulation of tumor responses to anticancer therapies. Cancer Cell 2013; 23:277-86; PMID:23518347; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2013.02.013 - DOI - PubMed
- Lewis CE, Harney AS, Pollard JW. The multifaceted role of perivascular macrophages in tumors. Cancer Cell 2016; 30:18-25; PMID:27411586; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.05.017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Squadrito ML, Pucci F, Magri L, Moi D, Gilfillan GD, Ranghetti A, Casazza A, Mazzone M, Lyle R, Naldini L, et al.. miR-511-3p modulates genetic programs of tumor-associated macrophages. Cell Rep 2012; 1:141-54; PMID:22832163; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2011.12.005 - DOI - PubMed
- Baer C, Squadrito ML, Laoui D, Thompson D, Hansen SK, Kiialainen A, Hoves S, Ries CH, Ooi CH, De Palma M. Suppression of microRNA activity amplifies IFN-gamma-induced macrophage activation and promotes anti-tumour immunity. Nat Cell Biol 2016; 18:790-802; PMID:27295554; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncb3371 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources