Data for default network reduced functional connectivity in meditators, negatively correlated with meditation expertise - PubMed (original) (raw)
Data for default network reduced functional connectivity in meditators, negatively correlated with meditation expertise
Aviva Berkovich-Ohana et al. Data Brief. 2016.
Abstract
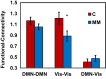
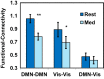
FMRI data described here was recorded during resting-state in Mindfulness Meditators (MM) and control participants (see "Task-induced activity and resting-state fluctuations undergo similar alterations in visual and DMN areas of long-term meditators" Berkovich-Ohana et al. (2016) [1] for details). MM participants were also scanned during meditation. Analyses focused on functional connectivity within and between the default mode network (DMN) and visual network (Vis). Here we show data demonstrating that: 1) Functional connectivity within the DMN and the Visual networks were higher in the control group than in the meditators; 2) Data show an increase for the functional connectivity between the DMN and the Visual networks in the meditators compared to controls; 3) Data demonstrate that functional connectivity both within and between networks reduces during meditation, compared to the resting-state; and 4) A significant negative correlation was found between DMN functional connectivity and meditation expertise. The reader is referred to Berkovich-Ohana et al. (2016) [1] for further interpretation and discussion.
Figures
Fig. 1
The significant Group×Network_FC interaction, showing reduced resting-state functional connectivity values for the mindfulness meditation (MM) group compared to the control (C) group. *p<.05.
Fig. 2
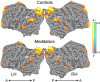
A qualitative demonstration of resting state functional connectivity (unfolded brain view), derived from bilateral Prc as a seed. Colour bar indicates positive correlations in yellow, and negative correlations in blue. LH, left hemisphere; RH, right hemisphere; Prc – precuneus; IPL – inferior parietal lobule; A, anterior; P, posterior.
Fig. 3
The significant Condition×Network_FC interaction, showing reduced functional connectivity values during meditation compared to resting-state for the MM group. *p<.05; **p<.001.
Similar articles
- Functional connectivity changes in meditators and novices during yoga nidra practice.
Fialoke S, Tripathi V, Thakral S, Dhawan A, Majahan V, Garg R. Fialoke S, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 5;14(1):12957. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63765-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38839877 Free PMC article. - From State-to-Trait Meditation: Reconfiguration of Central Executive and Default Mode Networks.
Bauer CCC, Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Díaz JL, Pasaye EH, Barrios FA. Bauer CCC, et al. eNeuro. 2019 Dec 4;6(6):ENEURO.0335-18.2019. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0335-18.2019. Print 2019 Nov/Dec. eNeuro. 2019. PMID: 31694816 Free PMC article. - Advanced Meditation Alters Resting-State Brain Network Connectivity Correlating With Improved Mindfulness.
Vishnubhotla RV, Radhakrishnan R, Kveraga K, Deardorff R, Ram C, Pawale D, Wu YC, Renschler J, Subramaniam B, Sadhasivam S. Vishnubhotla RV, et al. Front Psychol. 2021 Nov 18;12:745344. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.745344. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34867626 Free PMC article. - How Does Meditation Affect the Default Mode Network: A Systematic Review.
Zagkas D, Bacopoulou F, Vlachakis D, Chrousos GP, Darviri C. Zagkas D, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1425:229-245. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-31986-0_22. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37581797 - Functional Connectivity of Prefrontal Cortex in Various Meditation Techniques - A Mini-Review.
Rathore M, Verma M, Nirwan M, Trivedi S, Pai V. Rathore M, et al. Int J Yoga. 2022 Sep-Dec;15(3):187-194. doi: 10.4103/ijoy.ijoy_88_22. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Int J Yoga. 2022. PMID: 36949839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Mindfulness-Enhanced Computerized Cognitive Training for Depression: An Integrative Review and Proposed Model Targeting the Cognitive Control and Default-Mode Networks.
Bursky M, Egglefield DA, Schiff SG, Premnath P, Sneed JR. Bursky M, et al. Brain Sci. 2022 May 19;12(5):663. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12050663. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35625049 Free PMC article. Review. - The (In)flexible self: Psychopathology, mindfulness, and neuroscience.
Giommi F, Bauer PR, Berkovich-Ohana A, Barendregt H, Brown KW, Gallagher S, Nyklíček I, Ostafin B, Raffone A, Slagter HA, Trautwein FM, Vago DR. Giommi F, et al. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2023 Oct-Dec;23(4):100381. doi: 10.1016/j.ijchp.2023.100381. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36969914 Free PMC article. - Long-term mindfulness meditation increases occurrence of sensory and attention brain states.
Panitz DY, Mendelsohn A, Cabral J, Berkovich-Ohana A. Panitz DY, et al. Front Hum Neurosci. 2025 Jan 6;18:1482353. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1482353. eCollection 2024. Front Hum Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39834400 Free PMC article. - Functional connectivity changes in meditators and novices during yoga nidra practice.
Fialoke S, Tripathi V, Thakral S, Dhawan A, Majahan V, Garg R. Fialoke S, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 5;14(1):12957. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63765-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38839877 Free PMC article. - Multimodal Fingerprints of Resting State Networks as assessed by Simultaneous Trimodal MR-PET-EEG Imaging.
Shah NJ, Arrubla J, Rajkumar R, Farrher E, Mauler J, Kops ER, Tellmann L, Scheins J, Boers F, Dammers J, Sripad P, Lerche C, Langen KJ, Herzog H, Neuner I. Shah NJ, et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 25;7(1):6452. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05484-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28743861 Free PMC article.
References
- Berkovich-Ohana A., Harel M., Hahamy A., Arieli A., Malach R. Task-induced activity and resting-state fluctuations undergo similar alterations in visual and DMN areas of long-term meditators. NeuroImage. 2016;135:125–134. - PubMed
- Jang J., Jung W.H., Kang D.H., Byun M.S., Kwon S.J., Choi C.H., Kwon J.S. Increased default mode network connectivity associated with meditation. Neurosci. Lett. 2011;487:358–362. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources