Modification of platinum sensitivity by KEAP1/NRF2 signals in non-small cell lung cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Modification of platinum sensitivity by KEAP1/NRF2 signals in non-small cell lung cancer
Yijun Tian et al. J Hematol Oncol. 2016.
Abstract
Background: The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of platinum-based drugs on nuclear-factor erythroid2 like 2 (NRF2) signaling in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines with or without Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) mutations and to determine the role of NRF2 and KEAP1 on platinum-based drug treatment.
Methods: We used real-time PCR to assess relative mRNA expression and used western blotting and immunofluorescence assays to assess protein expression. Small interfering RNA and shuttle plasmids were used to modulate the expression of NRF2, wild-type KEAP1, and mutant KEAP1. Drug sensitivity to platinum-based drugs was evaluated with Cell Count Kit-8.
Results: We found that platinum-based therapies modified the NRF2 signaling pathway differently in KEAP1-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines compared with wild-type KEAP1 cell lines. The reactive degree of NRF2 signaling also varies between nedaplatin and cisplatin. The modification of NRF2 or KEAP1 expression in NSCLC cell lines disrupted downstream gene expression and cell sensitivity to platinum-based drugs. Finally, gene expression data retrieved from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) consortium indicated that KEAP1 mutation significantly affects NRF2 signaling activity in patients with NSCLC.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that NRF2 signaling plays an indispensable role in NSCLC cell sensitivity to platinum-based treatments and provides a rationale for using NRF2 as a specific biomarker for predicting which patients will be most likely to benefit from platinum-based treatment.
Keywords: Cisplatin; GCLM; HO1; KEAP1; NQO1; NRF2; Nedaplatin; Non-small cell lung cancer.
Figures
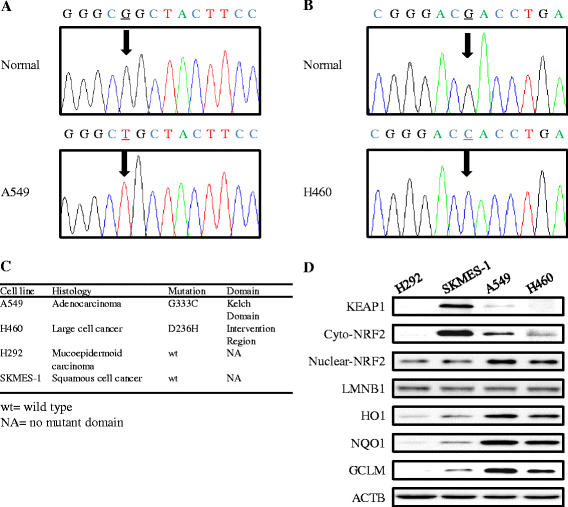
Fig. 1
Identification of KEAP1 mutations and basal expression levels of NRF2-regulated genes in NSCLC. Sequencing of the KEAP1 gene led to the identification of G333C mutation in A549 cells (a) and the D236H mutation in H460 cells (b). The arrow indicates the mutant peak. c Characteristics of the four NSCLC cell lines and a description of the KEAP1 mutations. NA, no mutant domain. d Basal expression of KEAP1, NRF2, and NRF2-regulated genes in the four NSCLC cell lines
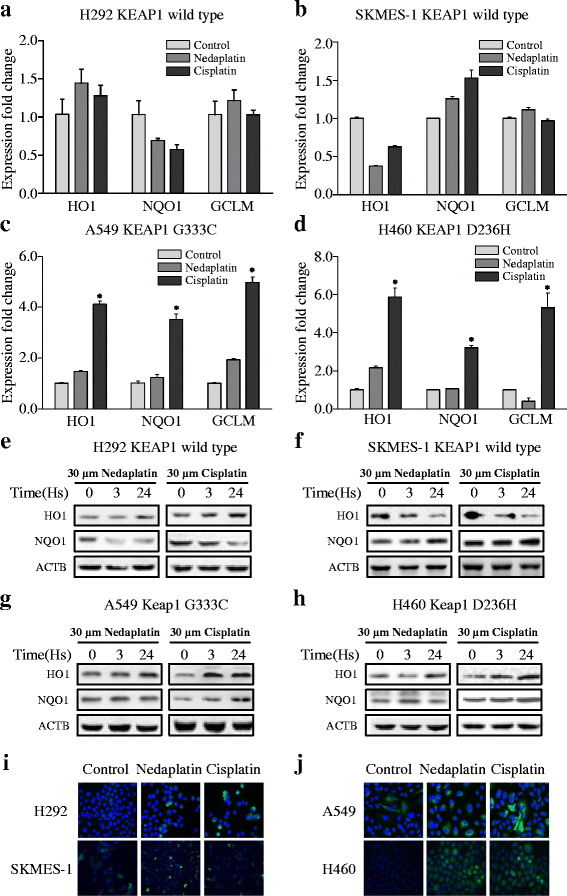
Fig. 2
Comparison of NRF2-regulated gene expression in NSCLC cells exposed to platinum-based drugs. a, b The levels of HO1, NQO1, and GCLM mRNA expression in H292 and SKMES-1 cells exposed to 30 μM nedaplatin or cisplatin for 24 h. c, d The expression levels of HO1, NQO1, and GCLM mRNA in A549 and SKMES-1 cells exposed to 30 μM nedaplatin or cisplatin for 24 h. Comparison was conducted between 24-h points and control group by using Student’s tests. The results are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.01, **p < 0.05. e, f The levels of HO1, NQO1, and GCLM protein expression in H292 and SKMES-1 cells exposed to 30 μM nedaplatin or cisplatin for 3 or 24 h. g, h The levels of HO1, NQO1, and GCLM protein expression in A549 and H460 cells exposed to 30 μM nedaplatin or cisplatin for 3 or 24 h. i Immunofluorescence staining of HO1 in H292 (upper panel) and SKMES-1 (lower panel) cells exposed to 30 μM nedaplatin or cisplatin over a 24-h treatment period. j Immunofluorescence staining of HO1 in H460 (upper panel) and A549 (lower panel) exposed to 30 μM nedaplatin or cisplatin over a 24-h treatment period
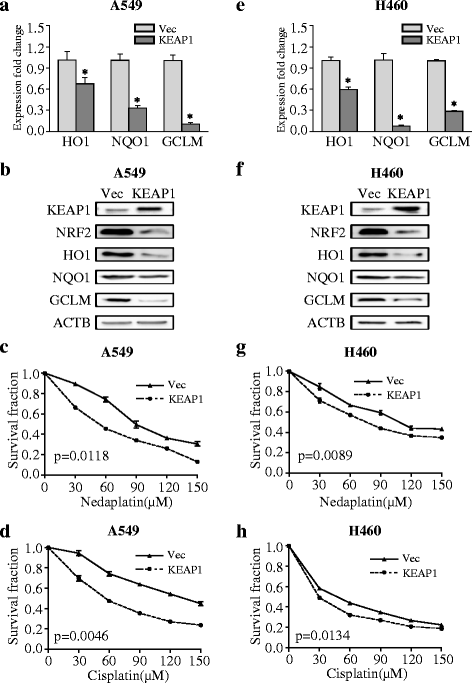
Fig. 3
KEAP1 overexpression inhibits NRF2 signaling and increases chemosensitivity to nedaplatin or cisplatin in KEAP1-mutant cells. a, b mRNA and protein levels of NRF2-regulated genes in A549 cells overexpressing wild-type KEAP1. c, d KEAP1 overexpression modified the sensitivity of A549 cells to platinum-based drugs. e, f mRNA and protein levels of NRF2 downstream genes in H460 cells overexpressing wild-type KEAP1. g, h KEAP1 overexpression modified the sensitivity of H460 cells to platinum-based drugs. The results are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.001, **p < 0.05. Vec vector
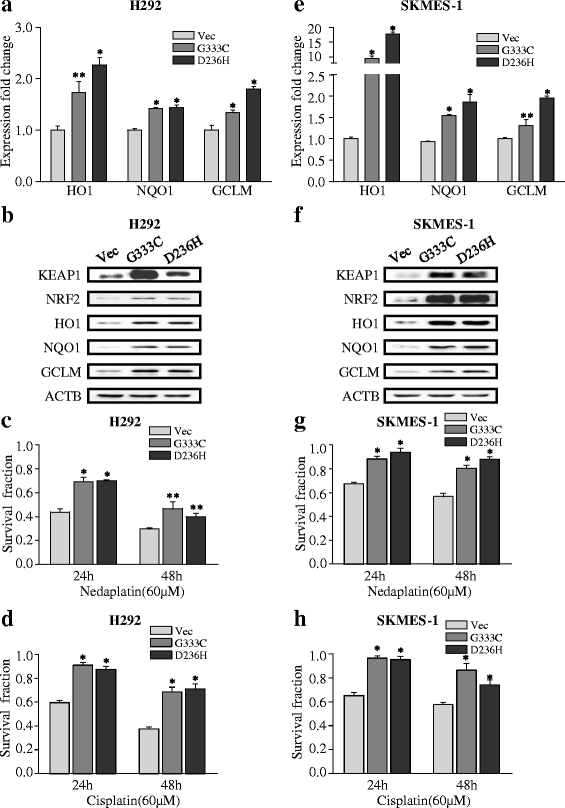
Fig. 4
KEAP1 mutations activate NRF2 signaling and confer chemo-resistance. a, b KEAP1 with the G333C or D236H mutations induced the expression of NRF2 downstream target genes at the mRNA and protein levels in H292 cells. c, d KEAP1 with the G333C or D236H mutations increased cell survival in H292 cells exposed to 60-μm platinum-based drugs. e, f KEAP1 with the G333C or D236H mutation induced the expression of NRF2-associated genes at the mRNA and protein levels in SKMES-1 cells. g, h KEAP1 with the G333C or D236H mutation increased cell survival in SKMES-1 cells exposed to 60-μm platinum-based drugs. The results are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.001, **p < 0.05. Vec vector
Fig. 5
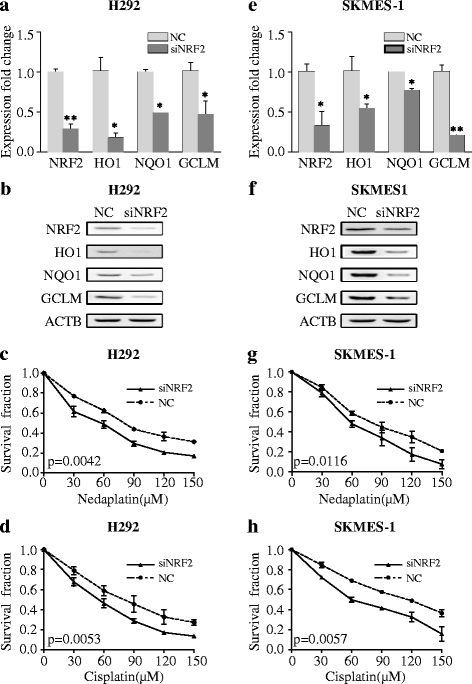
siRNA inhibited NRF2 signaling and increased chemosensitivity to platinum-based drugs. a, b siRNA knockdown of NRF2 reduced the expression of NRF2 and NRF2-regulated genes at the mRNA and protein levels in H292 cells. c, d siRNA increased the sensitivity of H292 cells to platinum-based drugs. e, f siRNA targeting NRF2 reduced the expression of NRF2 and NRF2-associated genes at the mRNA and protein levels in SKMES-1 cells. g, h siRNA knockdown of NRF2 increased platinum sensitivity in SKMES-1 cells. The results are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.001, **p < 0.05. Vec vector
Fig. 6
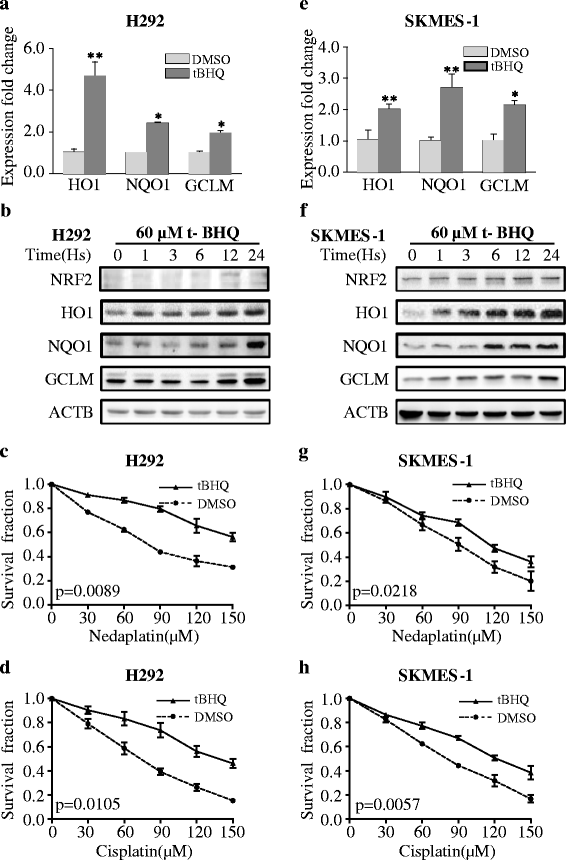
t-BHQ activated NRF2 signaling and conferred chemo-resistance to platinum-based drugs. a, b t-BHQ induced the expression of NRF2 and NRF2-regulated genes at the mRNA and protein levels in H292 cells. c, d t-BHQ conferred chemo-resistance to platinum-based drugs in H292 cells. e, f t-BHQ induced the expression of NRF2 and NRF2-regulated genes at the mRNA and protein levels in SKMES-1 cells. g, h t-BHQ conferred chemo-resistance to platinum-based drugs in SKMES-1 cells. The results are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.001, **p < 0.05. Vec vector
Fig. 7
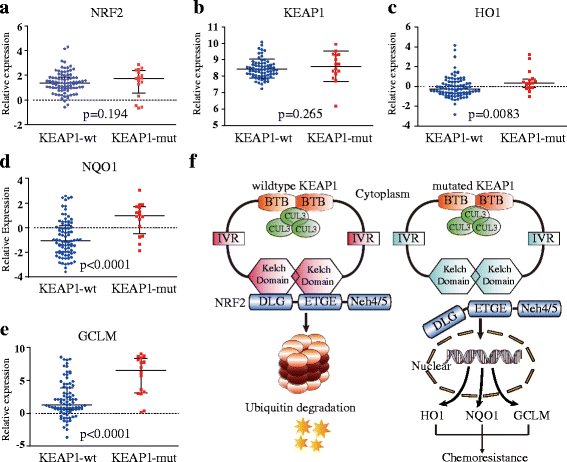
Comparison of NRF2-associated genes mRNA between KEAP1-wt and KEAP1-mut cases in squamous lung cancer. a NRF2 mRNA expression levels in KEAP1-wt and KEAP1-mut cases. b KEAP1 mRNA expression levels in KEAP1-wt and KEAP1-mut cases. c HO1 mRNA levels between KEAP1-wt and KEAP1-mut cases. d NQO1 mRNA levels in KEAP1-wt and KEAP1-mut cases. e GCLM mRNA expression levels in KEAP1-wt and KEAP1-mut cases. f Schematic diagram of wild-type (left) and mutant KEAP1 protein (right) function. Mutant KEAP1 was predicted to exhibit an attenuated unity. The increased nuclear accumulation and transcriptional activity of NRF2 upregulate the expression of cytoprotective genes such as HO1, NQO1, and GCLM, thereby leading to cancer cell chemo-resistance. BTB, broad complex, tramtrack, and Bric à brac, IVR intervention region, wt wild type, mut mutation. The results are presented as the median ± quartile
Similar articles
- Molecular mechanisms for the regulation of Nrf2-mediated cell proliferation in non-small-cell lung cancers.
Yamadori T, Ishii Y, Homma S, Morishima Y, Kurishima K, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Minami Y, Noguchi M, Hizawa N. Yamadori T, et al. Oncogene. 2012 Nov 8;31(45):4768-77. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.628. Epub 2012 Jan 16. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22249257 - Nrf2 and Keap1 abnormalities in non-small cell lung carcinoma and association with clinicopathologic features.
Solis LM, Behrens C, Dong W, Suraokar M, Ozburn NC, Moran CA, Corvalan AH, Biswal S, Swisher SG, Bekele BN, Minna JD, Stewart DJ, Wistuba II. Solis LM, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jul 15;16(14):3743-53. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3352. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20534738 Free PMC article. - Keap1-Nrf2 Interaction Suppresses Cell Motility in Lung Adenocarcinomas by Targeting the S100P Protein.
Chien MH, Lee WJ, Hsieh FK, Li CF, Cheng TY, Wang MY, Chen JS, Chow JM, Jan YH, Hsiao M, Hua KT, Kuo ML. Chien MH, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Oct 15;21(20):4719-32. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2880. Epub 2015 Jun 15. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26078391 - Emerging roles of Nrf2 signal in non-small cell lung cancer.
Tian Y, Liu Q, He X, Yuan X, Chen Y, Chu Q, Wu K. Tian Y, et al. J Hematol Oncol. 2016 Feb 27;9:14. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0246-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26922479 Free PMC article. Review. - Battles against aberrant KEAP1-NRF2 signaling in lung cancer: intertwined metabolic and immune networks.
Xu K, Ma J, Hall SRR, Peng RW, Yang H, Yao F. Xu K, et al. Theranostics. 2023 Jan 1;13(2):704-723. doi: 10.7150/thno.80184. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 36632216 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A Critical Review of the Impact of SMARCA4 Mutations on Survival Outcomes in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.
Manolakos P, Boccuto L, Ivankovic DS. Manolakos P, et al. J Pers Med. 2024 Jun 26;14(7):684. doi: 10.3390/jpm14070684. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39063938 Free PMC article. Review. - Arginine deprivation enriches lung cancer proteomes with cysteine by inducing arginine-to-cysteine substitutants.
Yang C, Pataskar A, Feng X, Montenegro Navarro J, Paniagua I, Jacobs JJL, Zaal EA, Berkers CR, Bleijerveld OB, Agami R. Yang C, et al. Mol Cell. 2024 May 16;84(10):1904-1916.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.04.012. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38759626 Free PMC article. - Cancer-associated fibroblasts secrete FGF5 to inhibit ferroptosis to decrease cisplatin sensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through binding to FGFR2.
Liu F, Tang L, Liu H, Chen Y, Xiao T, Gu W, Yang H, Wang H, Chen P. Liu F, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2024 Apr 18;15(4):279. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06671-0. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38637504 Free PMC article. - Suppression of A-to-I RNA-editing enzyme ADAR1 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to oxidative stress through regulating Keap1/Nrf2 pathway.
Wang H, Wei X, Liu L, Zhang J, Li H. Wang H, et al. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Mar 11;13(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00494-7. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38468359 Free PMC article. - Clinicopathologic and Genomic Factors Impacting Efficacy of First-Line Chemoimmunotherapy in Advanced NSCLC.
Alessi JV, Elkrief A, Ricciuti B, Wang X, Cortellini A, Vaz VR, Lamberti G, Frias RL, Venkatraman D, Fulgenzi CAM, Pecci F, Recondo G, Di Federico A, Barrichello A, Park H, Nishino M, Hambelton GM, Egger JV, Ladanyi M, Digumarthy S, Johnson BE, Christiani DC, Lin X, Gainor JF, Lin JJ, Pinato DJ, Schoenfeld AJ, Awad MM. Alessi JV, et al. J Thorac Oncol. 2023 Jun;18(6):731-743. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2023.01.091. Epub 2023 Feb 10. J Thorac Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36775193 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous