Towards Profiles of Resistance Development and Toxicity for the Small Cationic Hexapeptide RWRWRW-NH2 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Towards Profiles of Resistance Development and Toxicity for the Small Cationic Hexapeptide RWRWRW-NH2
Michaela Wenzel et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016.
Abstract
RWRWRW-NH2 (MP196) is an amphipathic hexapeptide that targets the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane and inhibits cellular respiration and cell wall synthesis. In previous studies it showed promising activity against Gram-positive bacteria and no significant cytotoxicity or hemolysis. MP196 is therefore used as lead structure for developing more potent antibiotic derivatives. Here we present a more comprehensive study on the parent peptide MP196 with regard to clinically relevant parameters. We found that MP196 acts rapidly bactericidal killing 97% of initial CFU within 10 min at two times MIC. We were unable to detect resistance in standard 24 and 48 h resistance frequency assays. However, MP196 was effective against some but not all MRSA and VISA strains. Serum binding of MP196 was intermediate and we confirmed its low toxicity against mammalian cell lines. MP196 did neither induce NFκB activation nor cause an increase in IL8 levels at 250 μg/mL, and no IgE-dependent activation of basophil granulocytes was detected at 500 μg/mL. Yet, MP196 demonstrated acute toxicity in mice upon injection into the blood stream. Phase contrast microscopy of mouse blood treated with MP196 revealed a shrinking of erythrocytes at 250 μg/mL and severe morphological changes and lysis of erythrocytes at 500 μg/mL. These data suggest that MP196 derivatization directed at further lowering hemolysis could be instrumental in overcoming acute toxicity. The assessment of hemolysis is a critical step in the evaluation of the clinical potential of promising antimicrobial peptides and should be accompanied by microscopy-based morphological analysis of blood cells.
Keywords: acute; antimicrobial cationic peptides; antimicrobial peptide; antimicrobial peptide resistance; toxicity mechanisms; toxicity tests.
Figures
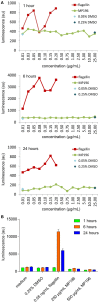
Figure 1
Activation of Nf-κB in RT4 bladder cells at concentrations up to 25 μg/mL (A) and at 250 and 500 μg/mL (B).
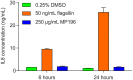
Figure 2
IL8 levels in RT4 bladder cells challenged with MP196 and in DMSO and flagellin-treated controls.
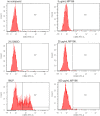
Figure 3
IgE-dependent basophil activation measured by FACS. Anti-IgE (PE) reacts with human IgE and is used for the characterization of basophilic granulocytes. Anti-gp53 (FITC) recognizes a glycoprotein expressed on activated basophils. The chemotactic peptide N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe served as positive, DMSO as negative control.
Figure 4
Phase contrast images of whole mouse blood mixed with MP196. Five percent DMSO is the maximum DMSO concentration reached by diluting MP196 from the stock solution. Scale bar represents 20 μm.
Similar articles
- Fusions of a carbohydrate binding module with the small cationic hexapeptide RWRWRW confer antimicrobial properties to cellulose-based materials.
Barbosa M, Simões H, Pinto SN, Macedo AS, Fonte P, Prazeres DMF. Barbosa M, et al. Acta Biomater. 2022 Apr 15;143:216-232. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.02.042. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35257951 - Functional structure and antimicrobial activity of persulcatusin, an antimicrobial peptide from the hard tick Ixodes persulcatus.
Miyoshi N, Saito T, Ohmura T, Kuroda K, Suita K, Ihara K, Isogai E. Miyoshi N, et al. Parasit Vectors. 2016 Feb 13;9:85. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1360-5. Parasit Vectors. 2016. PMID: 26873587 Free PMC article. - Central β-turn increases the cell selectivity of imperfectly amphipathic α-helical peptides.
Shao C, Tian H, Wang T, Wang Z, Chou S, Shan A, Cheng B. Shao C, et al. Acta Biomater. 2018 Mar 15;69:243-255. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.01.009. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29355714 - Effective antimicrobial activity of a peptide mutant Cbf-14-2 against penicillin-resistant bacteria based on its unnatural amino acids.
Kang W, Liu H, Ma L, Wang M, Wei S, Sun P, Jiang M, Guo M, Zhou C, Dou J. Kang W, et al. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017 Jul 15;105:169-177. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2017.05.030. Epub 2017 May 15. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 28522372 - In vitro activity of novel in silico-developed antimicrobial peptides against a panel of bacterial pathogens.
Romani AA, Baroni MC, Taddei S, Ghidini F, Sansoni P, Cavirani S, Cabassi CS. Romani AA, et al. J Pept Sci. 2013 Sep;19(9):554-65. doi: 10.1002/psc.2532. Epub 2013 Jul 26. J Pept Sci. 2013. PMID: 23893489
Cited by
- Achyranthes aspera Extracts as Adjuvants for the Redressal of Antibiotic Resistance.
Ahmad H, Gohar UF, Mukhtar H, Zia-Ui-Haq M, Marc RA, Irimie M, Marceanu LG, Gavris CM. Ahmad H, et al. Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 18;14(10):2219. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102219. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297652 Free PMC article. - Development of a Potent Antimicrobial Peptide With Photodynamic Activity.
Zhang D, Chen J, Jing Q, Chen Z, Ullah A, Jiang L, Zheng K, Yuan C, Huang M. Zhang D, et al. Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 1;12:624465. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.624465. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34140932 Free PMC article. - A Staphylococcus capitis strain with unusual bacteriocin production.
Szekat C, Josten M, Rickmeyer J, Crüsemann M, Bierbaum G. Szekat C, et al. Microb Biotechnol. 2023 Nov;16(11):2181-2193. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14356. Epub 2023 Oct 18. Microb Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37850940 Free PMC article. - Antimicrobial Peptides with Antibacterial Activity against Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains: Classification, Structures, and Mechanisms of Action.
Hernández-Aristizábal I, Ocampo-Ibáñez ID. Hernández-Aristizábal I, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 25;22(15):7927. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157927. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360692 Free PMC article. Review. - A flat embedding method for transmission electron microscopy reveals an unknown mechanism of tetracycline.
Wenzel M, Dekker MP, Wang B, Burggraaf MJ, Bitter W, van Weering JRT, Hamoen LW. Wenzel M, et al. Commun Biol. 2021 Mar 8;4(1):306. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01809-8. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33686188 Free PMC article.
References
- Albada H. B., Prochnow P., Bobersky S., Bandow J. E., Metzler-Nolte N. (2014). Highly active antibacterial ferrocenoylated or ruthenocenoylated Arg-Trp peptides can be discovered by an L-to-D substitution scan. Chem. Sci. 5, 4453–4459. 10.1039/C4SC01822B - DOI
- Albada H. B., Prochnow P., Bobersky S., Langklotz S., Bandow J. E., Metzler-Nolte N. (2013). Short antibacterial peptides with significantly reduced hemolytic activity can be identified by a systematic L-to-D exchange scan of their amino acid residues. ACS Comb. Sci. 15, 585–592. 10.1021/co400072q - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous