Trends in Drug Utilization, Glycemic Control, and Rates of Severe Hypoglycemia, 2006-2013 - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2017 Apr;40(4):468-475.
doi: 10.2337/dc16-0985. Epub 2016 Sep 22.
Affiliations
- PMID: 27659408
- PMCID: PMC5360291
- DOI: 10.2337/dc16-0985
Trends in Drug Utilization, Glycemic Control, and Rates of Severe Hypoglycemia, 2006-2013
Kasia J Lipska et al. Diabetes Care. 2017 Apr.
Abstract
Objective: To examine temporal trends in utilization of glucose-lowering medications, glycemic control, and rate of severe hypoglycemia among patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM).
Research design and methods: Using claims data from 1.66 million privately insured and Medicare Advantage patients with T2DM from 2006 to 2013, we estimated the annual 1) age- and sex-standardized proportion of patients who filled each class of agents; 2) age-, sex-, race-, and region-standardized proportion with hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) <6%, 6 to <7%, 7 to <8%, 8 to <9%, ≥9%; and 3) age- and sex-standardized rate of severe hypoglycemia among those using medications. Proportions were calculated overall and stratified by age-group (18-44, 45-64, 65-74, and ≥75 years) and number of chronic comorbidities (zero, one, and two or more).
Results: From 2006 to 2013, use increased for metformin (from 47.6 to 53.5%), dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (0.5 to 14.9%), and insulin (17.1 to 23.0%) but declined for sulfonylureas (38.8 to 30.8%) and thiazolidinediones (28.5 to 5.6%; all P < 0.001). The proportion of patients with HbA1c <7% declined (from 56.4 to 54.2%; P < 0.001) and with HbA1c ≥9% increased (9.9 to 12.2%; P < 0.001). Glycemic control varied by age and was poor among 23.3% of the youngest and 6.3% of the oldest patients in 2013. The overall rate of severe hypoglycemia remained the same (1.3 per 100 person-years; P = 0.72), declined modestly among the oldest patients (from 2.9 to 2.3; P < 0.001), and remained high among those with two or more comorbidities (3.2 to 3.5; P = 0.36).
Conclusions: During the recent 8-year period, the use of glucose-lowering drugs has changed dramatically among patients with T2DM. Overall glycemic control has not improved and remains poor among nearly a quarter of the youngest patients. The overall rate of severe hypoglycemia remains largely unchanged.
© 2017 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
Figure 1
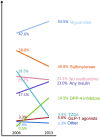
Age- and sex-standardized proportion of patients with T2DM who filled each class of glucose-lowering agents, 2006 and 2013 (see
Supplementary Table 2
for annual data). Since patients may fill more than one class in each year, percentages do not add up to 100%. Other medications were comprised of meglitinides, α-glucosidase inhibitors, SGLT-2 inhibitors, and amylin analogs. Patients with no fills for glucose-lowering medications were included in the “No medications” group.
Figure 2
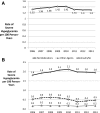
Glycemic control among patients with T2DM, 2006–2013. Estimates were standardized by age, sex, race, and region to the 2013 cohort of people included in the study.
Figure 3
Age- and sex-standardized rate of severe hypoglycemia resulting in hospital admission, observation stay, or emergency department visit per 100 person-years, 2006–2013. A: Patients with T2DM who filled at least one glucose-lowering agent. B: Patients with T2DM who filled insulin or insulin secretagogues (diamonds), other glucose-lowering agents (triangles), and no glucose-lowering agents (circles). SU, sulfonylurea.
Similar articles
- Trends in medication utilization, glycemic control and outcomes among type 2 diabetes patients in a tertiary referral center in Singapore from 2007 to 2017.
Tan YZ, Cheen MHH, Goh SY, Bee YM, Lim PS, Khee GY, Thumboo J. Tan YZ, et al. J Diabetes. 2019 Jul;11(7):573-581. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12886. Epub 2019 Jan 24. J Diabetes. 2019. PMID: 30556375 - Trends in Glucose-Lowering Drug Use, Glycemic Control, and Severe Hypoglycemia in Adults With Diabetes in Hong Kong, 2002-2016.
Yang A, Wu H, Lau ESH, Ma RCW, Kong APS, So WY, Luk AOY, Chan JCN, Chow E. Yang A, et al. Diabetes Care. 2020 Dec;43(12):2967-2974. doi: 10.2337/dc20-0260. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Diabetes Care. 2020. PMID: 33046501 - Association of Cumulative Multimorbidity, Glycemic Control, and Medication Use With Hypoglycemia-Related Emergency Department Visits and Hospitalizations Among Adults With Diabetes.
McCoy RG, Lipska KJ, Van Houten HK, Shah ND. McCoy RG, et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Jan 3;3(1):e1919099. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.19099. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 31922562 Free PMC article. - Glycemic control of type 2 diabetes mellitus across stages of renal impairment: information for primary care providers.
Tong L, Adler S. Tong L, et al. Postgrad Med. 2018 May;130(4):381-393. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2018.1457397. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Postgrad Med. 2018. PMID: 29667921 Review. - Dapagliflozin compared with other oral anti-diabetes treatments when added to metformin monotherapy: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.
Goring S, Hawkins N, Wygant G, Roudaut M, Townsend R, Wood I, Barnett AH. Goring S, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014 May;16(5):433-42. doi: 10.1111/dom.12239. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014. PMID: 24237939 Review.
Cited by
- Expert Opinion on Optimising Type 2 Diabetes Treatment Using Fixed-Ratio Combination of Basal Insulin and GLP-1 RA for Treatment Intensification and Simplification.
Haluzik M, Taybani Z, Araszkiewicz A, Cerghizan A, Mankovsky B, Zuhdi A, Malecki M. Haluzik M, et al. Diabetes Ther. 2024 Aug;15(8):1673-1685. doi: 10.1007/s13300-024-01610-w. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Diabetes Ther. 2024. PMID: 38935189 Free PMC article. Review. - Diabetes mellitus in older persons with neurocognitive disorder: overtreatment prevalence and associated structural brain MRI findings.
Putallaz P, Seematter-Bagnoud L, Draganski B, Rouaud O, Krief H, Büla CJ. Putallaz P, et al. BMC Geriatr. 2024 May 14;24(1):427. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05025-x. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38745127 Free PMC article. - Trends in diabetes prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control in French-speaking Switzerland.
Pauli A, de Mestral C, Marques-Vidal P. Pauli A, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 28;14(1):4839. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54856-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38418618 Free PMC article. - Diabetes Mellitus and Thyroid Cancers: Risky Correlation, Underlying Mechanisms and Clinical Prevention.
Wu R, Zhang J, Zou G, Li S, Wang J, Li X, Xu J. Wu R, et al. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Feb 16;17:809-823. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S450321. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 38380275 Free PMC article. Review. - Cyb5r3 activation rescues secondary failure to sulfonylurea but not β-cell dedifferentiation.
Watanabe H, Asahara SI, Son J, McKimpson WM, de Cabo R, Accili D. Watanabe H, et al. PLoS One. 2024 Feb 9;19(2):e0297555. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297555. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38335173 Free PMC article.
References
- International Hypoglycaemia Study Group. Minimizing hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015;38:1583–1591 - PubMed
- Zhuo X, Zhang P, Kahn HS, Bardenheier BH, Li R, Gregg EW. Change in medical spending attributable to diabetes: national data from 1987 to 2011. Diabetes Care 2015;38:581–587 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG021342/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG048359/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000135/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG049057/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- L30 AG045923/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG044281/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous