Prospects for the Use of ATR Inhibitors to Treat Cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Prospects for the Use of ATR Inhibitors to Treat Cancer
Jill M Wagner et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2010.
Abstract
ATR is an apical kinase in one of the DNA-damage induced checkpoint pathways. Despite the development of inhibitors of kinases structurally related to ATR, as well as inhibitors of the ATR substrate Chk1, no ATR inhibitors have yet been developed. Here we review the effects of ATR downregulation in cancer cells and discuss the potential for development of ATR inhibitors for clinical use.
Keywords: ATM; ATR; Chk1; Replication checkpoint; chemotherapy.
Figures
Figure 1
Structural domains of ATR in comparison to other PIKK family members. The shaded domains share the highest degree of sequence homology. ATRIP (ATR-interacting protein), FAT (FRAP, ATM, TRRAP), PRD (PIK regulatory domain), FATC (FAT domain at the carboxyl terminus).
Figure 2
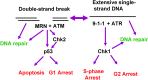
ATM and ATR signaling pathways. DNA DSBs generally activate ATM, which along with the Mre11-Rad50-NBS1 complex, can facilitate DNA repair or phosphorylate the Chk2 kinase leading to activation of p53 followed by G1 arrest or apoptosis. Alternatively, extensive regions of single-stranded DNA that result from the continued activity of helicases after replication forks are stalled (see Figure 3) activate the ATR pathway. ATR, together with the Rad9-Hus1-Rad1 complex can activate Chk1. Chk1 in turn phosphorylates Cdc25A and Cdc25C, which targets the former for degradation and the latter for sequestration, causing the cells to arrest in S or G2. Chk1 activation can also facilitate DNA repair.
Figure 3
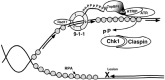
Model of the activation of ATR through Rad9 and TopBP1. See text for details. Modified from [27].
Figure 4
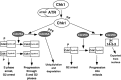
Chk1 mediates ATR-induced cell cycle arrest. ATR activates Chk1, which then phosphorylates and inactivates Cdc25A and Cdc25C. Phosphorylated Cdc25A is ubiquitylated and degraded, leaving Cdk2/cyclin complexes in their inactive form, resulting in S-phase and G2-phase arrest. Phosphorylated Cdc25C binds to 14-3-3 proteins and is exported from the nucleus, leaving Cdk1/cyclin B complexes in the inactive form, resulting in G2 arrest.
Similar articles
- Inhibition of ATR-dependent feedback activation of Chk1 sensitises cancer cells to Chk1 inhibitor monotherapy.
Massey AJ. Massey AJ. Cancer Lett. 2016 Dec 1;383(1):41-52. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.09.024. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27693461 - The ATM-Chk2 and ATR-Chk1 pathways in DNA damage signaling and cancer.
Smith J, Tho LM, Xu N, Gillespie DA. Smith J, et al. Adv Cancer Res. 2010;108:73-112. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380888-2.00003-0. Adv Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21034966 Review. - ATR/CHK1 inhibitors and cancer therapy.
Qiu Z, Oleinick NL, Zhang J. Qiu Z, et al. Radiother Oncol. 2018 Mar;126(3):450-464. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.09.043. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Radiother Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29054375 Free PMC article. Review. - Chk1- and claspin-dependent but ATR/ATM- and Rad17-independent DNA replication checkpoint response in HeLa cells.
Rodríguez-Bravo V, Guaita-Esteruelas S, Florensa R, Bachs O, Agell N. Rodríguez-Bravo V, et al. Cancer Res. 2006 Sep 1;66(17):8672-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4443. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16951182 - The ATM and Rad3-Related (ATR) Protein Kinase Pathway Is Activated by Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and Required for Efficient Viral Replication.
Edwards TG, Bloom DC, Fisher C. Edwards TG, et al. J Virol. 2018 Feb 26;92(6):e01884-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01884-17. Print 2018 Mar 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29263259 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Association of variations in the CAT and prognosis in lung cancer patients with platinum-based chemotherapy.
Liu JS, Liu JY, Xiao Q, Li XP, Chen J, Liu ZQ. Liu JS, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 9;14:1119837. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1119837. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36969849 Free PMC article. - The "extreme phenotype approach" applied to male breast cancer allows the identification of rare variants of ATR as potential breast cancer susceptibility alleles.
Chevarin M, Alcantara D, Albuisson J, Collonge-Rame MA, Populaire C, Selmani Z, Baurand A, Sawka C, Bertolone G, Callier P, Duffourd Y, Jonveaux P, Bignon YJ, Coupier I, Cornelis F, Cordier C, Mozelle-Nivoix M, Rivière JB, Kuentz P, Thauvin C, Boidot R, Ghiringhelli F, O'Driscoll M, Faivre L, Nambot S. Chevarin M, et al. Oncotarget. 2023 Feb 7;14:111-125. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28358. Oncotarget. 2023. PMID: 36749285 Free PMC article. - The Implication of Topoisomerase II Inhibitors in Synthetic Lethality for Cancer Therapy.
Matias-Barrios VM, Dong X. Matias-Barrios VM, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jan 9;16(1):94. doi: 10.3390/ph16010094. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678591 Free PMC article. Review. - Targeting of RecQ Helicases as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Ovarian Cancer.
Maity J, Horibata S, Zurcher G, Lee JM. Maity J, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 26;14(5):1219. doi: 10.3390/cancers14051219. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267530 Free PMC article. Review. - Progress towards a clinically-successful ATR inhibitor for cancer therapy.
Barnieh FM, Loadman PM, Falconer RA. Barnieh FM, et al. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021 Feb 5;2:100017. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100017. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34909652 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Zhou B.B., Elledge S.J. The DNA damage response: putting checkpoints in perspective. Nature. 2000;408:433–439. - PubMed
- Kastan M.B., Bartek J. Cell-cycle checkpoints and cancer. Nature. 2004;432:316–323. - PubMed
- Keith C.T., Schreiber S.L. PIK-Related Kinases: DNA Repair, Recombination, and Cell Cycle Checkpoints. Science. 1995;270:50–51. - PubMed
- Engelman J.A., Luo J., Cantley L.C. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006;7:606–619. - PubMed
- Bosotti R., Isacchi A., Sonnhammer E.L. FAT: a novel domain in PIK-related kinases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000;25:225–227. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous