Diabetes mellitus and oxidative stress-A concise review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Diabetes mellitus and oxidative stress-A concise review
Ullah Asmat et al. Saudi Pharm J. 2016 Sep.
Abstract
Human body is continuously exposed to different types of agents that results in the production of reactive species called as free radicals (ROS/RNS) which by the transfer of their free unpaired electron causes the oxidation of cellular machinery. In order to encounter the deleterious effects of such species, body has got endogenous antioxidant systems or it obtains exogenous antioxidants from diet that neutralizes such species and keeps the homeostasis of body. Any imbalance between the RS and antioxidants leads to produce a condition known as "oxidative stress" that results in the development of pathological condition among which one is diabetes. Most of the studies reveal the inference of oxidative stress in diabetes pathogenesis by the alteration in enzymatic systems, lipid peroxidation, impaired Glutathione metabolism and decreased Vitamin C levels. Lipids, proteins, DNA damage, Glutathione, catalane and superoxide dismutase are various biomarkers of oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus. Oxidative stress induced complications of diabetes may include stroke, neuropathy, retinopathy and nephropathy. The basic aim of this review was to summarize the basics of oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus.
Figures
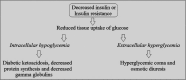
Figure 1
Pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus.
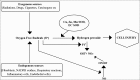
Figure 2
Free radicals induced cell injury.
Similar articles
- Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer.
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M. Valko M, et al. Chem Biol Interact. 2006 Mar 10;160(1):1-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2005.12.009. Epub 2006 Jan 23. Chem Biol Interact. 2006. PMID: 16430879 Review. - Vitamin D status and oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus.
Lee WC, Mokhtar SS, Munisamy S, Yahaya S, Rasool AHG. Lee WC, et al. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2018 May 30;64(7):60-69. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2018. PMID: 29974854 Review. - Diabetes, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: a review.
Maritim AC, Sanders RA, Watkins JB 3rd. Maritim AC, et al. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2003;17(1):24-38. doi: 10.1002/jbt.10058. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2003. PMID: 12616644 Review. - Effects of antioxidants in diabetes-induced oxidative stress in the glomeruli of diabetic rats.
Koya D, Hayashi K, Kitada M, Kashiwagi A, Kikkawa R, Haneda M. Koya D, et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003 Aug;14(8 Suppl 3):S250-3. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000077412.07578.44. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003. PMID: 12874441 - The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in diabetic complications.
Matough FA, Budin SB, Hamid ZA, Alwahaibi N, Mohamed J. Matough FA, et al. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2012 Feb;12(1):5-18. doi: 10.12816/0003082. Epub 2012 Feb 7. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2012. PMID: 22375253 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Natural products for the treatment and management of diabetes mellitus in Zimbabwe-a review.
Usai R, Majoni S, Rwere F. Usai R, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 24;13:980819. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.980819. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091798 Free PMC article. Review. - Cyclosorus terminans Extract Ameliorates Insulin Resistance and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Induced Obese Rats.
Songtrai S, Pratchayasakul W, Arunsak B, Chunchai T, Kongkaew A, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC, Kaewsuwan S. Songtrai S, et al. Nutrients. 2022 Nov 19;14(22):4895. doi: 10.3390/nu14224895. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36432581 Free PMC article. - Antidiabetic activity of aqueous stem bark extract of Annickia polycarpa in alloxan-induced diabetic mice.
Lartey NL, Asare-Anane H, Ofori EK, Antwi S, Asiedu-Larbi J, Ayertey F, Okine LKN. Lartey NL, et al. J Tradit Complement Med. 2020 Feb 5;11(2):109-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2020.02.001. eCollection 2021 Mar. J Tradit Complement Med. 2020. PMID: 33728270 Free PMC article. - Diabetes and Cancer: Metabolic Association, Therapeutic Challenges, and the Role of Natural Products.
Talib WH, Mahmod AI, Abuarab SF, Hasen E, Munaim AA, Haif SK, Ayyash AM, Khater S, Al-Yasari IH, Kury LTA. Talib WH, et al. Molecules. 2021 Apr 10;26(8):2179. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082179. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33920079 Free PMC article. Review. - Natural Functional Beverages as an Approach to Manage Diabetes.
Carvalho F, Lahlou RA, Pires P, Salgado M, Silva LR. Carvalho F, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 30;24(23):16977. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316977. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069300 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Al Homsi M.F., Lukic M.L. Department of Pathology and Medical Microbiology (Immunology Unit), Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, UAE University; Al Ain, United Arab Emirates: 1992. An Update on the pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus.
- American Diabetes Association Diagnosis and classification of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(1):S5–S10. - PubMed
- Asfandiyarova N., Kolcheva N., Ryazantsev I., Ryazantsev V. Risk factors for stroke in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2007;3:57–60. - PubMed
- Ayepola, O.R., Brooks, N.L., Oguntibeju, O.O. 2014. Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Complications: The Role of Antioxidant Vitamins and Flavonoids. <http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/57282>. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources