Association Between Excessive Daytime Sleepiness and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Population-based Study in China - PubMed (original) (raw)
Association Between Excessive Daytime Sleepiness and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Population-based Study in China
Sicheng Wu et al. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017.
Abstract
Background/aims: Several studies have demonstrated that sleep problems are associated with functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs): irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), functional dyspepsia, etc, but the relationship between excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) and FGIDs has not been systematically studied in the general population. This study aims to explore the relationship between EDS and specific types of FGIDs and the effect of the number of FGIDs on EDS.
Methods: A sample of 3600 individuals (aged 18-80 years) was selected from 5 regions in China using a randomized, stratified, multi-stage sampling method. EDS was measured by the Epworth Sleepiness Scale, while gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and other FGIDs were assessed by Reflux Disease Questionnaire and the Rome II diagnostic criteria, respectively.
Results: The survey was completed by 2906 individuals (response rate: 80.72%), and 644 individuals (22.16%) had EDS. EDS was significantly associated with ulcer-like dyspepsia (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.08-5.79), diarrhea-predominant IBS (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.09-3.66), alternating IBS (OR, 2.32; 95% CI, 1.30-4.13), functional constipation (OR, 1.68; 95% CI, 1.20-2.35), and GERD (OR, 1.72; 95% CI, 1.08-2.72). Risk of EDS increased along with the increasing numbers of FGIDs: with 1 FGID (OR, 1.72; 95% CI, 1.37-2.15); with 2 FGIDs (OR, 2.43; 95% CI, 1.63-3.62); and with 3 or more FGIDs (OR, 3.26; 95% CI, 1.37-7.78).
Conclusions: FGIDs, such as ulcer-like dyspepsia, diarrhea-predominant IBS, alternating IBS, functional constipation, and GERD, were significantly associated with EDS. Those who suffered from more kinds of FGIDs were more susceptible to EDS.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Excessive somnolence disorders; Functional gastrointestinal disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None.
Figures
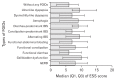
Figure
Median (Q1, Q3) of Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) score in different types of functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs). IBS, irritable bowel syndrome; GERD, gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Similar articles
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease, functional dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome: common overlapping gastrointestinal disorders.
de Bortoli N, Tolone S, Frazzoni M, Martinucci I, Sgherri G, Albano E, Ceccarelli L, Stasi C, Bellini M, Savarino V, Savarino EV, Marchi S. de Bortoli N, et al. Ann Gastroenterol. 2018 Nov-Dec;31(6):639-648. doi: 10.20524/aog.2018.0314. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Ann Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30386113 Free PMC article. Review. - The epidemiology and quality of life of functional gastrointestinal disorders according to Rome III vs Rome IV criteria: A cross-sectional study in primary care.
Chuah KH, Beh KH, Mahamad Rappek NA, Mahadeva S. Chuah KH, et al. J Dig Dis. 2021 Mar;22(3):159-166. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12975. J Dig Dis. 2021. PMID: 33595169 - Prevalence and Associated Dietary Factors of Rome IV Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Rural Western Honduras.
Norwood DA, Dominguez LB, Paredes AA, Montalvan EE, Rodriguez Murillo A, Dougherty MK, Palsson OS, Dominguez RL, Morgan DR. Norwood DA, et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2021 Sep;66(9):3086-3095. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06639-y. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Dig Dis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33089482 - Nationwide Multicenter Study for Overlaps of Common Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Korean Patients With Constipation.
Park KS, Jee SR, Lee BE, Hong KS, Shin JE, Na SY, Kwon JG, Choi SC, Kim YS, Lee HS, Lee TH, Kim KO, Choi J, Moon HS, Kim YS, Park MI, Park SJ, Park SY, Hong SN; Constipation Research Group of Korean Society of Neurogastroenterology and Motility. Park KS, et al. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017 Oct 30;23(4):569-577. doi: 10.5056/jnm17033. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017. PMID: 28992677 Free PMC article. - What Is New in Rome IV.
Schmulson MJ, Drossman DA. Schmulson MJ, et al. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017 Apr 30;23(2):151-163. doi: 10.5056/jnm16214. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017. PMID: 28274109 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Indirect effect of sleep on abdominal pain through daytime dysfunction in adults with irritable bowel syndrome.
Yang PL, Burr RL, Buchanan DT, Pike KC, Kamp KJ, Heitkemper MM. Yang PL, et al. J Clin Sleep Med. 2020 Oct 15;16(10):1701-1710. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.8658. J Clin Sleep Med. 2020. PMID: 32620184 Free PMC article. - Sleep Quality and Insomnia Are Associated With Quality of Life in Functional Dyspepsia.
Wuestenberghs F, Melchior C, Desprez C, Leroi AM, Netchitailo M, Gourcerol G. Wuestenberghs F, et al. Front Neurosci. 2022 Feb 8;16:829916. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.829916. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35210990 Free PMC article. - Importance of sleep quality in functional abdominal pain disorder in pediatric patients.
Kim HJ. Kim HJ. Sleep Biol Rhythms. 2021 Jul 23;20(1):81-85. doi: 10.1007/s41105-021-00342-9. eCollection 2022 Jan. Sleep Biol Rhythms. 2021. PMID: 38469067 Free PMC article. - Sleep Deficiency Is Associated With Exacerbation of Symptoms and Impairment of Anorectal and Autonomic Functions in Patients With Functional Constipation.
Liu J, Wang W, Tian J, Lv C, Fu Y, Fass R, Song G, Yu Y. Liu J, et al. Front Neurosci. 2022 Jul 7;16:912442. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.912442. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35873821 Free PMC article. - Prevalence and Risk Factors of Functional Constipation According to the Rome Criteria in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Chen Z, Peng Y, Shi Q, Chen Y, Cao L, Jia J, Liu C, Zhang J. Chen Z, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 16;9:815156. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.815156. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35252254 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources