Insights from 100 Years of Research with Probiotic E. Coli - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Insights from 100 Years of Research with Probiotic E. Coli
Trudy M Wassenaar. Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 2016.
Abstract
A century ago, Alfred Nissle discovered that intentional intake of particular strains of Escherichia coli could treat patients suffering from infectious diseases. Since then, one of these strains became the most frequently used probiotic E. coli in research and was applied to a variety of human conditions. Here, properties of that E. coli Nissle 1917 strain are compared with other commercially available E. coli probiotic strains, with emphasis on their human applications. A literature search formed the basis of a summary of research findings reported for the probiotics Mutaflor, Symbioflor 2, and Colinfant. The closest relatives of the strains in these products are presented, and their genetic content, including the presence of virulence, genes is discussed. A similarity to pathogenic strains causing urinary tract infections is noticeable. Historic trends in research of probiotics treatment for particular human conditions are identified. The future of probiotic E. coli may lay in what Alfred Nissle originally discovered: to treat gastrointestinal infections, which nowadays are often caused by antibiotic-resistant pathogens.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; Nissle; Symbioflor; applications; human studies; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The author works as a consultant for SymbioPharm GmbH.
Figures
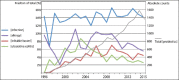
Fig. 1.
Trends in publication frequency over time for four keywords combined with “probiotics”
Similar articles
- A Toxic Friend: Genotoxic and Mutagenic Activity of the Probiotic Strain Escherichia coli Nissle 1917.
Nougayrède JP, Chagneau CV, Motta JP, Bossuet-Greif N, Belloy M, Taieb F, Gratadoux JJ, Thomas M, Langella P, Oswald E. Nougayrède JP, et al. mSphere. 2021 Aug 25;6(4):e0062421. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00624-21. Epub 2021 Aug 11. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34378987 Free PMC article. - K5 Capsule and Lipopolysaccharide Are Important in Resistance to T4 Phage Attack in Probiotic E. coli Strain Nissle 1917.
Soundararajan M, von Bünau R, Oelschlaeger TA. Soundararajan M, et al. Front Microbiol. 2019 Nov 29;10:2783. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02783. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31849915 Free PMC article. - In vitro analysis of the bactericidal activity of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 against pediatric uropathogens.
Storm DW, Koff SA, Horvath DJ Jr, Li B, Justice SS. Storm DW, et al. J Urol. 2011 Oct;186(4 Suppl):1678-83. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.04.021. Epub 2011 Aug 19. J Urol. 2011. PMID: 21855931 - Clinical use of E. coli Nissle 1917 in inflammatory bowel disease.
Schultz M. Schultz M. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008 Jul;14(7):1012-8. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20377. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008. PMID: 18240278 Review. - Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (Mutaflor): new insights into an old probiotic bacterium.
Jacobi CA, Malfertheiner P. Jacobi CA, et al. Dig Dis. 2011;29(6):600-7. doi: 10.1159/000333307. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Dig Dis. 2011. PMID: 22179217 Review.
Cited by
- Colicin FY inhibits pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica in mice.
Bosák J, Micenková L, Hrala M, Pomorská K, Kunova Bosakova M, Krejci P, Göpfert E, Faldyna M, Šmajs D. Bosák J, et al. Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 16;8(1):12242. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30729-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30115964 Free PMC article. - Evolutionary genomic analyses of canine E. coli infections identify a relic capsular locus associated with resistance to multiple classes of antimicrobials.
Ceres K, Zehr JD, Murrell C, Millet JK, Sun Q, McQueary HC, Horton A, Cazer C, Sams K, Reboul G, Andreopoulos WB, Mitchell PK, Anderson R, Franklin-Guild R, Cronk BD, Stanhope BJ, Burbick CR, Wolking R, Peak L, Zhang Y, McDowall R, Krishnamurthy A, Slavic D, Sekhon Pk, Tyson GH, Ceric O, Stanhope MJ, Goodman LB. Ceres K, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Aug 21;90(8):e0035424. doi: 10.1128/aem.00354-24. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39012166 Free PMC article. - Effects of E scherichia coli Nissle 1917 on the Porcine Gut Microbiota, Intestinal Epithelium and Immune System in Early Life.
Geervliet M, de Vries H, Jansen CA, Rutten VPMG, van Hees H, Wen C, Skovgaard K, Antonello G, Savelkoul HFJ, Smidt H, Tijhaar E, Wells JM. Geervliet M, et al. Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 25;13:842437. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.842437. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35283814 Free PMC article. - Robust performance of a live bacterial therapeutic chassis lacking the colibactin gene cluster.
Kalantari A, James MJ, Renaud LA, Perreault M, Monahan CE, McDonald MN, Hava DL, Isabella VM. Kalantari A, et al. PLoS One. 2023 Feb 2;18(2):e0280499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280499. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36730255 Free PMC article. - Potentiation of curing by a broad-host-range self-transmissible vector for displacing resistance plasmids to tackle AMR.
Lazdins A, Maurya AP, Miller CE, Kamruzzaman M, Liu S, Stephens ER, Lloyd GS, Haratianfar M, Chamberlain M, Haines AS, Kreft JU, Webber MA, Iredell J, Thomas CM. Lazdins A, et al. PLoS One. 2020 Jan 15;15(1):e0225202. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225202. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31940351 Free PMC article.
References
- Tannock GW. (1995). Normal Microflora. An Introduction to Microbes Inhabiting the Human Body, Chapman and Hall, London, UK
Publication types
Grants and funding
Founding sources
SymbioPharm GmbH provided financial support to write this review; however, it had no influence on the content of the article.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources