A statistical test for conserved RNA structure shows lack of evidence for structure in lncRNAs - PubMed (original) (raw)
A statistical test for conserved RNA structure shows lack of evidence for structure in lncRNAs
Elena Rivas et al. Nat Methods. 2017 Jan.
Abstract
Many functional RNAs have an evolutionarily conserved secondary structure. Conservation of RNA base pairing induces pairwise covariations in sequence alignments. We developed a computational method, R-scape (RNA Structural Covariation Above Phylogenetic Expectation), that quantitatively tests whether covariation analysis supports the presence of a conserved RNA secondary structure. R-scape analysis finds no statistically significant support for proposed secondary structures of the long noncoding RNAs HOTAIR, SRA, and Xist.
Conflict of interest statement
Author information An R-scape web server is at eddylab.org/R-scape and source code can be downloaded from a link on that page. The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to E.R. (elenarivas@fas.harvard.edu).
Figures
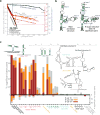
Figure 1. Independent substitutions on a tree can create confounding covariations
(a) Illustrative example showing a histogram of maximum covariance score per alignment, over 100 synthetic alignments simulated under three evolutionary models: no phylogeny/no structure constraint (red); phylogeny alone (grey); or phylogeny plus structure constraint (cyan). (b) Toy alignment (top left) with two independent substitutions (marked 1,2) on the same branch, resulting in an apparent pairwise covariation annotated by R2R (top right). R-scape simulated null alignments (bottom left) retain this confounding covariation signal, and it is judged insignificant (bottom right). (c) Toy alignment with five compensatory base pair substitutions (marked 1–5) showing a covariation pattern that is destroyed in the R-scape simulated null alignments, and thus judged significant.
Figure 2. Covariation analysis of known or proposed RNA secondary structures
(a) 5S rRNA as an example of an known structural RNA with significant covariation support. The plot (left) shows the expected null distribution (fit: black lines; data: black circles), compared to covariances observed for pairs in (blue) or not in (red) the annotated structure. (b) Covariation support for the Rfam annotated 5S rRNA structure, versus an alternative structure proposed by R-scape to include all significantly covarying pairs. Significant pairs (at E< 0.05) are highlighted in green. Coordinates are alignment column positions. Specific nucleotides are shown when their weighted frequency in the column exceeds 50%; black dots represent more variable positions. (c) On the positive y-axis, plot shows percentage of base pairs supported by covariation at three thresholds (red, E< 10–5; orange, E < 0.05; grey, E < 10). Negative y-axis shows the number of additional significantly covarying pairs not in the proposed structure. Transfer RNA (tRNA), RNase P RNA, and the purine riboswitch (leftmost) are examples of functional structural RNAs with strong statistical support; three human DNA repeat elements (rightmost) are negative controls with no known RNA secondary structure constraint.
Similar articles
- Phylogenetic Analysis with Improved Parameters Reveals Conservation in lncRNA Structures.
Tavares RCA, Pyle AM, Somarowthu S. Tavares RCA, et al. J Mol Biol. 2019 Apr 5;431(8):1592-1603. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.03.012. Epub 2019 Mar 16. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30890332 Free PMC article. - RNA covariation at helix-level resolution for the identification of evolutionarily conserved RNA structure.
Rivas E. Rivas E. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Jul 14;19(7):e1011262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011262. eCollection 2023 Jul. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37450549 Free PMC article. - Estimating the power of sequence covariation for detecting conserved RNA structure.
Rivas E, Clements J, Eddy SR. Rivas E, et al. Bioinformatics. 2020 May 1;36(10):3072-3076. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa080. Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32031582 Free PMC article. - Evolutionary conservation of RNA sequence and structure.
Rivas E. Rivas E. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021 Sep;12(5):e1649. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1649. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021. PMID: 33754485 Free PMC article. Review. - Sizing up long non-coding RNAs: do lncRNAs have secondary and tertiary structure?
Novikova IV, Hennelly SP, Sanbonmatsu KY. Novikova IV, et al. Bioarchitecture. 2012 Nov-Dec;2(6):189-99. doi: 10.4161/bioa.22592. Bioarchitecture. 2012. PMID: 23267412 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Intronic RNA secondary structural information captured for the human MYC pre-mRNA.
Eich TO, O'Leary CA, Moss WN. Eich TO, et al. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024 Oct 24;6(4):lqae143. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqae143. eCollection 2024 Sep. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39450312 Free PMC article. - Identification of 11 candidate structured noncoding RNA motifs in humans by comparative genomics.
Hou L, Xie J, Wu Y, Wang J, Duan A, Ao Y, Liu X, Yu X, Yan H, Perreault J, Li S. Hou L, et al. BMC Genomics. 2021 Mar 9;22(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07474-9. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33750298 Free PMC article. - Thirteen dubious ways to detect conserved structural RNAs.
Gao W, Yang A, Rivas E. Gao W, et al. IUBMB Life. 2023 Jun;75(6):471-492. doi: 10.1002/iub.2694. Epub 2022 Dec 10. IUBMB Life. 2023. PMID: 36495545 Free PMC article. - Zinc-finger protein CNBP alters the 3-D structure of lncRNA Braveheart in solution.
Kim DN, Thiel BC, Mrozowich T, Hennelly SP, Hofacker IL, Patel TR, Sanbonmatsu KY. Kim DN, et al. Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 9;11(1):148. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13942-4. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 31919376 Free PMC article.
References
- Holley RW, Apgar J, Everett GA, Madison JT, Marquisee M, Merrill SH, Penswick JR, Zamir A. Structure of a ribonucleic acid. Science. 1965;14:1462–1465. - PubMed
- Pace NR, Smith DK, Olsen GJ, James BD. Phylogenetic comparative analysis and the secondary structure of Ribonuclease P RNA – a review. Gene. 1989;82:65–75. - PubMed
- Michel F, Costa M, Massire C, Westhof E. Modeling RNA tertiary structure from patterns of sequence variation. Meth. Enzymol. 2000;317:491–510. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources