The Influence of Methylsulfonylmethane on Inflammation-Associated Cytokine Release before and following Strenuous Exercise - PubMed (original) (raw)
The Influence of Methylsulfonylmethane on Inflammation-Associated Cytokine Release before and following Strenuous Exercise
Mariè van der Merwe et al. J Sports Med (Hindawi Publ Corp). 2016.
Abstract
Background. Inflammation is associated with strenuous exercise and methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. Methods. Physically active men were supplemented with either placebo or MSM (3 grams per day) for 28 days before performing 100 repetitions of eccentric knee extension exercise. Ex vivo and in vitro testing consisted of evaluating cytokine production in blood (whole blood and isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs)) exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS), before and through 72 hours after exercise, while in vivo testing included the evaluation of cytokines before and through 72 hours after exercise. Results. LPS stimulation of whole blood after MSM supplementation resulted in decreased induction of IL-1_β_, with no effect on IL-6, TNF-α, or IL-8. After exercise, there was a reduced response to LPS in the placebo, but MSM resulted in robust release of IL-6 and TNF-α. A small decrease in resting levels of proinflammatory cytokines was noted with MSM, while an acute postexercise increase in IL-10 was observed with MSM. Conclusion. Strenuous exercise causes a robust inflammatory reaction that precludes the cells from efficiently responding to additional stimuli. MSM appears to dampen the release of inflammatory molecules in response to exercise, resulting in a less incendiary environment, allowing cells to still have the capacity to mount an appropriate response to an additional stimulus after exercise.
Figures
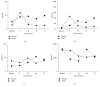
Figure 1
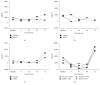
Reduced induction of inflammatory cytokines with MSM supplementation immediately after exercise. IL-β (a), IL-6 (b), TNF-α (c), and IL-8 (d) concentrations (pg/mL) were determined in whole blood ex vivo cultures from blood collected at baseline (24 h before exercise), immediately after exercise (Time 0), and then at 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h after exercise. Results represent mean (n = 2, placebo; n = 3, MSM).
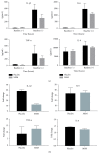
Figure 2
MSM reduces LPS-induced IL-1_β_ secretion. Cytokine secretion was determined after LPS stimulation of ex vivo whole blood cultures and measured by Luminex multiplex bead assay. (a) In the absence of exercise, LPS induces robust release of IL-1_β_, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-8. (b) Data from (a) are expressed as fold change from unstimulated samples. Results represent mean ± SEM (n = 2, placebo; n = 3, MSM).
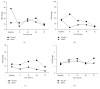
Figure 3
Exercise alters cytokine response to LPS. IL-1_β_ (a), IL-6 (b), TNF-α (c), and IL-8 (d) induced by LPS, with MSM supplementation allowing for more efficient release of IL-6 and TNF-α after exercise. Data are represented as fold change from unstimulated samples. Results represent mean ± SEM (n = 2, placebo; n = 3, MSM).
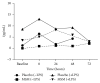
Figure 4
Induction of IL-10 by exercise and LPS in ex vivo cultures. Results represent mean ± SEM (n = 2, placebo; n = 3, MSM).
Figure 5
IL-1_β_ (a), IL-6 (b), TNF-α (c), and IL-10 (d) release from in vitro LPS-stimulated PBMCs isolated from blood collected before (baseline) or after (0 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h) exercise. Results represent mean ± SEM (n = 2, placebo; n = 3, MSM).
Similar articles
- Influence of methylsulfonylmethane on markers of exercise recovery and performance in healthy men: a pilot study.
Kalman DS, Feldman S, Scheinberg AR, Krieger DR, Bloomer RJ. Kalman DS, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2012 Sep 27;9(1):46. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-9-46. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2012. PMID: 23013531 Free PMC article. - Exercise reduced pentraxin 3 levels produced by endotoxin-stimulated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in obese individuals.
Slusher AL, Shibata Y, Whitehurst M, Maharaj A, Quiles JM, Huang CJ. Slusher AL, et al. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Jun;242(12):1279-1286. doi: 10.1177/1535370217706963. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28440716 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Systemic inflammatory response to exhaustive exercise. Cytokine kinetics.
Suzuki K, Nakaji S, Yamada M, Totsuka M, Sato K, Sugawara K. Suzuki K, et al. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2002;8:6-48. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12690937 Review. - Acute fish oil supplementation modulates the inflammatory response after strenuous exercise in obese men: A cross-over study.
Peres A, Dorneles GP, Boeira MCR, Schipper LL, Beretta Â, Vilela T, Andrade VM, Romão PRT. Peres A, et al. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2018 Oct;137:5-11. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2018.07.017. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2018. PMID: 30293597 - The cytokine response to strenuous exercise.
Pedersen BK, Ostrowski K, Rohde T, Bruunsgaard H. Pedersen BK, et al. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1998 May;76(5):505-11. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-76-5-505. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9839076 Review.
Cited by
- N-Acetylcysteine and Other Sulfur-Donors as a Preventative and Adjunct Therapy for COVID-19.
du Preez HN, Aldous C, Kruger HG, Johnson L. du Preez HN, et al. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2022 Aug 10;2022:4555490. doi: 10.1155/2022/4555490. eCollection 2022. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35992575 Free PMC article. Review. - Randomized, Placebo-controlled Study of a Nutraceutical Based on Hyaluronic Acid, L-carnosine, and Methylsulfonylmethane in Facial Skin Aesthetics and Well-being.
Guaitolini E, Cavezzi A, Cocchi S, Colucci R, Urso SU, Quinzi V. Guaitolini E, et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2019 Apr;12(4):40-45. Epub 2019 Apr 1. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 31119010 Free PMC article. - Effects of methylsulfonylmethane and neutralizing anti-IL-10 antibody supplementation during a mild Eimeria challenge infection in broiler chickens.
Rasheed MSA, Tiwari UP, Jespersen JC, Bauer LL, Dilger RN. Rasheed MSA, et al. Poult Sci. 2020 Dec;99(12):6559-6568. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.09.046. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 33248571 Free PMC article. - Non-toxic sulfur inhibits LPS-induced inflammation by regulating TLR-4 and JAK2/STAT3 through IL-6 signaling.
Kang DY, Sp N, Jo ES, Rugamba A, Kim HD, Kim IH, Park JC, Bae SW, Jang KJ, Yang YM. Kang DY, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jul;24(1):485. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12124. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33907855 Free PMC article. - Methylsulfonylmethane: Applications and Safety of a Novel Dietary Supplement.
Butawan M, Benjamin RL, Bloomer RJ. Butawan M, et al. Nutrients. 2017 Mar 16;9(3):290. doi: 10.3390/nu9030290. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28300758 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources