Accelerated cryo-EM structure determination with parallelisation using GPUs in RELION-2 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Accelerated cryo-EM structure determination with parallelisation using GPUs in RELION-2
Dari Kimanius et al. Elife. 2016.
Abstract
By reaching near-atomic resolution for a wide range of specimens, single-particle cryo-EM structure determination is transforming structural biology. However, the necessary calculations come at large computational costs, which has introduced a bottleneck that is currently limiting throughput and the development of new methods. Here, we present an implementation of the RELION image processing software that uses graphics processors (GPUs) to address the most computationally intensive steps of its cryo-EM structure determination workflow. Both image classification and high-resolution refinement have been accelerated more than an order-of-magnitude, and template-based particle selection has been accelerated well over two orders-of-magnitude on desktop hardware. Memory requirements on GPUs have been reduced to fit widely available hardware, and we show that the use of single precision arithmetic does not adversely affect results. This enables high-resolution cryo-EM structure determination in a matter of days on a single workstation.
Keywords: GPU; biophysics; classification; cryo-EM; image reconstruction; micrograph; none; refinement; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
SHWS: Reviewing editor, eLife.
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
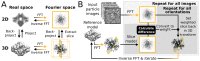
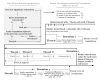
Figure 1.. High level flowchart of RELION.
(A) Operations and the real vs. Fourier spaces used during (B) image reconstruction in RELION. Micrograph input and model setup use the CPU, while most subsequent processing steps have been adapted for accelerator hardware. The highlighted orientation-dependent difference calculation is by far the most demanding task, and fully accelerated. Taking 2D slices out of (and setting them back into) the reference transforms has also been accelerated at high gain. The inverse FFT operation has not yet been accelerated, but uses the CPU. DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18722.002
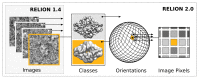
Figure 2.. Extensive task-level parallelism for accelerators.
While previously relion only exploited parallelism over images (left), in the new implementation classes and all orientations of each class are expressed as tasks that can be scheduled independently on the accelerator hardware (e.g. GPUs). Even individual pixels for each orientation can be calculated in parallel, which makes the algorithm highly suited for GPUs. DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18722.003
Figure 3.. Semi-automated particle picking in RELION-2.
The low-pass filter applied to micrographs is a novel feature in RELION, aimed at reducing the size and execution time of the highlighted inverse FFTs, which accounts for most of the computational work. In addition to the inverse FFTs, all template- and rotation-dependent parallel steps have also been accelerated on GPUs. DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18722.004
Figure 4.. RELION-2 enables desktop classification and refinement using GPUs.
EMPIAR (Iudin et al., 2016) entry 10028 was used to assess performance, using refinements of 105 k ribosomal particles in 3602-pixel images. (A) A quad-GPU workstation easily outperforms even a large cluster job in 3D classification. (B) In 2D classification, the GPU desktop performs slightly better in the first few iteration and then provides performance equivalent to the 280 CPU cores. (C) Total time for 25 iterations of 3D classification for a few different hardware configurations. (D) Additional classes are processed at reduced cost compared to CPU-only execution, due to faster execution and increased capacity for latency hiding. (E) With increasing number of classes, the time spent in non-accelerated vs accelerated execution increases. (F) The workstation also beats the cluster for single-class refinement to high resolution, despite the generally lower degree of parallelism. This is particularly striking for the finer exhaustive sampling at 3.8∘ due to the GPU’s ability to parallelise the drastically increased number of tasks. DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18722.005
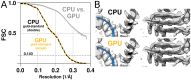
Figure 5.. The GPU reconstruction is qualitatively identical to the CPU version.
(A) A high-resolution refinement of the Plasmodium falciparum 80S ribosome using single precision GPU arithmetic achieves a gold-standard Fourier shell correlation (FSC) indistinguishable from double precision CPU-only refinement (previously deposited as EMD-2660). The FSC of full reconstructions comparing the two methods shows their agreement far exceeds the recoverable signal (grey), and as shown in Figure 5—figure supplement 1 the variation in angle assignments match the differences between CPU runs with different random seeds. (B) Partial snapshots of the final reconstruction following post-processing, superimposed on PDB ID 3J79 (Wong et al., 2014). DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18722.006
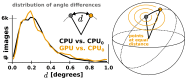
Figure 5—figure supplement 1.. The CPU and GPU implementations provide qualitatively identical distributions of image orientations.
For two CPU runs with different random seeds, 81% of images fall within 1∘, and for a GPU vs. CPU run 82%. Note that the probability of observing small angles vanishes since the number of potentially available points is proportional to the sine of the angle, which approaches zero for identical orientations. Both distributions were aligned against the reference refinement by fitting reconstructed models. DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18722.007
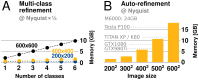
Figure 6.. GPU memory requirements.
(A) The required GPU memory scales linearly with the number of classes. (B) The maximum required GPU memory occurs for single-class refinement to the Nyquist frequency, which increases rapidly with the image size. Horizontal grey lines indicate avaliable GPU memory on different cards. DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18722.008
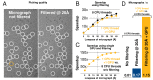
Figure 7.. Low-pass filtering and acceleration of particle picking.
(A) Ribosomal particles were auto-picked from representative 40962-pixel micrographs collected at 1.62 Å/pixel using four template classes, showing near-identical picking with and without low-pass filtering to 20 Å. The only differing particle is indicated in orange, and likely does not depict a ribosomal particle. (B–C) Despite near-identical particle selection, performance is dramatically improved. (D) Filtering alone provides almost 20-fold performance improvement on any hardware compared to previsos versions of relion, and when combined with GPU-accelerated particle picking the resulting performance gain is more than two orders of magnitude using only a single GPU (GTX 1080). DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18722.009
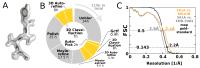
Figure 8.. High-resolution structure determination on a single desktop.
(A) The resulting 2.2 Å map (deposited as EMD-4116) shows excellent high-resolution density throughout the complex. (B) The most time-consuming steps in the image processing workflow. GPU-accelerated steps are indicated in orange. The total time of image processing was less than that of downloading the data. (C) The resolution estimate is based on the gold-standard FSC after correcting for the convolution effects of a soft solvent mask (black). The FSC between the relion map and the atomic model in PDB ID 5A1A is shown in orange. The FSC between EMD-2984 and the same atomic model is shown for comparison (dashed gray). DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18722.010
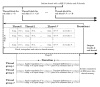
Appendix 1—figure 1.. Computational flow in difference calculation kernel.
The kernel is initiated with ceil(𝐏/P0) thread-blocks and N threads, where P is the total number of projections. The work flow of a thread-block in each iteration i is divided into two stages. In stage A the N pixels of P0 reference slices are fetched through texture memory, interpolated, and stored in shared memory. This data is then exhaustively reused in stage B, where groups of threads compute the differences to the corresponding translated image components. Individual threads within a group work with different image components, n, of each reference slice, p. Collectively all threads iterate through the N components of each reference slice, for a total of N×P0 components for each iteration i. The final result is reduced back into shared memory through atomic reduction operations. All image components are covered as i goes from 1 to ceil(C/N), where C is the total number of Fourier components. A reduced sum of differences for each pair of orientation and translation is written to global memory prior to the kernel exiting. DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18722.012
Appendix 1—figure 2.. A dedicated kernel function performs the targeted fine-grained examination of the most significantly matching regions during image alignment against a reference model.
The oversampling of each of five fitting dimensions during fine-grained search renders storage of all possible weights intractable, so input and output data are stored with explicit mapping arrays. These are read by the kernel function thread-block, rather than inferred based on block ID. This creates overhead and possible latency of global memory access, which makes this kernel even further separated from the exhaustive kernel represented in Figure 9. Here, a pixel-chunk of a single projection is reused for a number of sequential translations, arranged contiguously if possible. Invoking separate thread blocks for non-contiguous translations allows some implicit indexing of them, which affords better access patterns for SIMD instructions and reduced latency. Due to the sparseness, shared memory can also be used for in-kernel summation of all pixels of each image, which despite some some required explicit thread-level synchronisation increases throughput by avoiding the higher latency of atomic write operations during image summation in the coarse-search kernel. DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18722.013
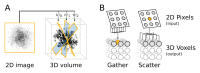
Appendix 2—figure 1.. Computational flow of fine-grained search kernel.
(A) Weighted back-projection of a 2D image into three different planes. We explored two memory access approaches (B) for this task, namely gather and scatter. In the gather approach a process (marked with orange) is assigned to individual or groups of 3D voxels. The process read from the input image and updates the data of the assigned voxel(s). DOI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18722.014
Similar articles
- A Robust Single-Particle Cryo-Electron Microscopy (cryo-EM) Processing Workflow with cryoSPARC, RELION, and Scipion.
DiIorio MC, Kulczyk AW. DiIorio MC, et al. J Vis Exp. 2022 Jan 31;(179). doi: 10.3791/63387. J Vis Exp. 2022. PMID: 35104261 - New tools for automated high-resolution cryo-EM structure determination in RELION-3.
Zivanov J, Nakane T, Forsberg BO, Kimanius D, Hagen WJ, Lindahl E, Scheres SH. Zivanov J, et al. Elife. 2018 Nov 9;7:e42166. doi: 10.7554/eLife.42166. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30412051 Free PMC article. - Sparseness and Smoothness Regularized Imaging for improving the resolution of Cryo-EM single-particle reconstruction.
Luo Z, Campos-Acevedo AA, Lv L, Wang Q, Ma J. Luo Z, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jan 12;118(2):e2013756118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2013756118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33402531 Free PMC article. - Processing of Structurally Heterogeneous Cryo-EM Data in RELION.
Scheres SH. Scheres SH. Methods Enzymol. 2016;579:125-57. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2016.04.012. Epub 2016 May 31. Methods Enzymol. 2016. PMID: 27572726 Review. - Advances in computational approaches to structure determination of alphaviruses and flaviviruses using cryo-electron microscopy.
Lata K, Charles S, Mangala Prasad V. Lata K, et al. J Struct Biol. 2023 Sep;215(3):107993. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2023.107993. Epub 2023 Jul 4. J Struct Biol. 2023. PMID: 37414374 Review.
Cited by
- Molecular basis of Coxsackievirus A10 entry using the two-in-one attachment and uncoating receptor KRM1.
Cui Y, Peng R, Song H, Tong Z, Qu X, Liu S, Zhao X, Chai Y, Wang P, Gao GF, Qi J. Cui Y, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 4;117(31):18711-18718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005341117. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32690697 Free PMC article. - HIV-1 VRC01 Germline-Targeting Immunogens Select Distinct Epitope-Specific B Cell Receptors.
Lin YR, Parks KR, Weidle C, Naidu AS, Khechaduri A, Riker AO, Takushi B, Chun JH, Borst AJ, Veesler D, Stuart A, Agrawal P, Gray M, Pancera M, Huang PS, Stamatatos L. Lin YR, et al. Immunity. 2020 Oct 13;53(4):840-851.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.09.007. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 33053332 Free PMC article. - A kinetic model for solving a combination optimization problem in ab-initio Cryo-EM 3D reconstruction.
Liu J, Lu Y, Zhu L. Liu J, et al. Brief Bioinform. 2024 Jan 22;25(2):bbad473. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad473. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38261343 Free PMC article. - A VHH single-domain platform enabling discovery and development of monospecific antibodies and modular neutralizing bispecifics against SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Yang ML, Yuan TZ, Chan KY, Ding L, Han Z, Franco H, Holliday C, Kannan S, Davidson E, Doranz BJ, Chandran K, Miller EH, Plante JA, Weaver SC, Cho E, Kailasan S, Marsalek L, Giang H, Abdiche Y, Sato AK. Yang ML, et al. Antib Ther. 2024 May 3;7(2):164-176. doi: 10.1093/abt/tbae009. eCollection 2024 Apr. Antib Ther. 2024. PMID: 38933534 Free PMC article. - Below 3 Å structure of apoferritin using a multipurpose TEM with a side entry cryoholder.
Kayama Y, Burton-Smith RN, Song C, Terahara N, Kato T, Murata K. Kayama Y, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 16;11(1):8395. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87183-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33863933 Free PMC article.
References
- Abraham MJ, Murtola T, Schulz R, Páll S, Smith JC, Hess B, Lindahl E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX. 2015;1-2:19–25. doi: 10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001. - DOI
- Chen S, McMullan G, Faruqi AR, Murshudov GN, Short JM, Scheres SH, Henderson R. High-resolution noise substitution to measure overfitting and validate resolution in 3D structure determination by single particle electron cryomicroscopy. Ultramicroscopy. 2013;135:24–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2013.06.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources