Heparin prevents Zika virus induced-cytopathic effects in human neural progenitor cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.12.023. Epub 2017 Jan 5.
Lynsay Cooper 2, Alicia Rubio 1, Isabel Pagani 1, Maria Rosaria Capobianchi [ 3](#full-view-affiliation-3 ""Lazzaro Spallanzani" National Institute for Infectious Diseases, Rome, Italy."), Giuseppe Ippolito [ 3](#full-view-affiliation-3 ""Lazzaro Spallanzani" National Institute for Infectious Diseases, Rome, Italy."), Julien Pelletier 4, Maria Cecilia Z Meneghetti 5, Marcelo A Lima 6, Mark A Skidmore 7, Vania Broccoli 8, Edwin A Yates 9, Elisa Vicenzi 1
Affiliations
- PMID: 28063994
- PMCID: PMC7113768
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.12.023
Heparin prevents Zika virus induced-cytopathic effects in human neural progenitor cells
Silvia Ghezzi et al. Antiviral Res. 2017 Apr.
Abstract
The recent Zika virus (ZIKV) outbreak, which mainly affected Brazil and neighbouring states, demonstrated the paucity of information concerning the epidemiology of several flaviruses, but also highlighted the lack of available agents with which to treat such emerging diseases. Here, we show that heparin, a widely used anticoagulant, while exerting a modest inhibitory effect on Zika Virus replication, fully prevents virus-induced cell death of human neural progenitor cells (NPCs).
Keywords: Cell death; Heparin; Neural progenitor cells; Zika virus (ZIKV).
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Fig. 1
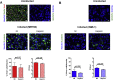
Heparin does not inhibit ZIKV infection of hNPCs. A. Infection of hNPCs with the MR766 strain with (middle two panels) and without (upper two panels) heparin treatment (100 μg/ml). To determine that the cells were bona fide hNPCs, cells were stained with Sox2 (red), Nestin (green) and Hoechst (blue). Uninfected and infected cells were fixed after 3 days with paraformaldehyde solution and stained with a mAb specific for Flavivirus E protein (green). After PBS washes, cells were washed again, mounted and examined by microscopy. Quantification of infection efficiency and viral titers released into the culture supernatant are reported in the two lower panels (left and right, respectively). Scale bar of upper left panel: 20 μm, scale bar of remaining panels: 5 μm. Bar graphs indicate the mean ± SEM of 4 independent experiments. P values were calculated by Student's paired _t_-test. B. Infection of hNPCs by the INMI-1 strain, with (middle two panels) or without (upper panel) heparin treatment (100 μg/ml). Uninfected and infected cells were fixed after 7 days with paraformaldehyde solution and stained with a mAb specific for Flavivirus E protein (green). Quantification of infection efficiency and viral titers released into the culture supernatant are reported in the lower two panels (left and right, respectively). Scale bar: 5 μm. Bar graphs indicate the mean ± SEM of 2 fields including more than 1000 cells in 3 independent experiments. P values were calculated by Student's paired _t_-test. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
Fig. 2
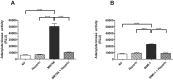
Heparin prevents virus-induced CPE. A. Supernatant of infected hNPCs with the MR766 strain was collected 3 days post infection. The results are expressed as relative luminescent unit (RLU). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. Repeated measures Anova was used with the Bonferroni correction. *Represents statistical comparison among groups (**, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05). B. Supernatant of infected hNPCs with the INMI-1 strain was collected 7 days post infection. The cell death was analyzed as reported in A. Results are expressed as relative luminescent units (RLU). Data represent the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. Repeated Measures ANOVA was used with the Bonferroni correction. *Represents statistical comparison among groups (**, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05).
Similar articles
- Heparin Protects Human Neural Progenitor Cells from Zika Virus-Induced Cell Death While Preserving Their Differentiation into Mature Neuroglial Cells.
Pagani I, Ottoboni L, Podini P, Ghezzi S, Brambilla E, Bezukladova S, Corti D, Bianchi ME, Capobianchi MR, Poli G, Panina-Bordignon P, Yates EA, Martino G, Vicenzi E. Pagani I, et al. J Virol. 2022 Oct 12;96(19):e0112222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01122-22. Epub 2022 Sep 19. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36121298 Free PMC article. - Strain-Dependent Consequences of Zika Virus Infection and Differential Impact on Neural Development.
Goodfellow FT, Willard KA, Wu X, Scoville S, Stice SL, Brindley MA. Goodfellow FT, et al. Viruses. 2018 Oct 9;10(10):550. doi: 10.3390/v10100550. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30304805 Free PMC article. - Western Zika Virus in Human Fetal Neural Progenitors Persists Long Term with Partial Cytopathic and Limited Immunogenic Effects.
Hanners NW, Eitson JL, Usui N, Richardson RB, Wexler EM, Konopka G, Schoggins JW. Hanners NW, et al. Cell Rep. 2016 Jun 14;15(11):2315-22. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.075. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27268504 Free PMC article. - The impact of Zika virus in the brain.
Russo FB, Beltrão-Braga PCB. Russo FB, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Oct 28;492(4):603-607. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.074. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28108286 Review. - Zika infection and the development of neurological defects.
Russo FB, Jungmann P, Beltrão-Braga PCB. Russo FB, et al. Cell Microbiol. 2017 Jun;19(6). doi: 10.1111/cmi.12744. Epub 2017 May 3. Cell Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28370966 Review.
Cited by
- Promising Drug Fondaparinux for the Treatment of COVID-19: an In Silico Analysis of Low Molecular Weight Heparin, Direct Oral Anticoagulant, and Antiplatelet Drug Interactions with Host Protease Furin.
Ertan-Bolelli T, Bolelli K, Elçi SD, Belen-Apak FB. Ertan-Bolelli T, et al. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024 Jun;38(3):425-432. doi: 10.1007/s10557-022-07406-z. Epub 2022 Nov 19. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. PMID: 36401727 Free PMC article. - Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Inhibitors by In Vitro Screening of Drug Libraries.
David AB, Diamant E, Dor E, Barnea A, Natan N, Levin L, Chapman S, Mimran LC, Epstein E, Zichel R, Torgeman A. David AB, et al. Molecules. 2021 May 27;26(11):3213. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113213. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34072087 Free PMC article. - Is heparan sulfate a target for inhibition of RNA virus infection?
Ling J, Li J, Khan A, Lundkvist Å, Li JP. Ling J, et al. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Apr 1;322(4):C605-C613. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00028.2022. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35196165 Free PMC article. Review. - Biological Properties of Heparins Modified with an Arylazopyrazole-Based Photoswitch.
Stolarek M, Pycior A, Bonarek P, Opydo M, Kolaczkowska E, Kamiński K, Mogielnicki A, Szczubiałka K. Stolarek M, et al. J Med Chem. 2023 Feb 9;66(3):1778-1789. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01616. Epub 2023 Jan 19. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36657057 Free PMC article. - Venous Thromboembolism and Heparin Use in COVID-19 Patients: Juggling between Pragmatic Choices, Suggestions of Medical Societies and the Lack of Guidelines.
Porfidia A, Pola R. Porfidia A, et al. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020 Jul;50(1):68-71. doi: 10.1007/s11239-020-02125-4. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020. PMID: 32367471 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
- Bell T.M., Field E.J., Narang H.K. Zika virus infection of the central nervous system of mice. Arch. Gesamte Virusforsch. 1971;35:183–193. - PubMed
- Caldwell M.A., Garcion E., terBorg M.G., He X., Svendsen C.N. Heparin stabilizes FGF-2 and modulates striatal precursor cell behavior in response to EGF. Exp. Neurol. 2004;188:408–420. - PubMed
- Cao-Lormeau V.M., Blake A., Mons S., Lastere S., Roche C., Vanhomwegen J., Dub T., Baudouin L., Teissier A., Larre P., Vial A.L., Decam C., Choumet V., Halstead S.K., Willison H.J., Musset L., Manuguerra J.C., Despres P., Fournier E., Mallet H.P., Musso D., Fontanet A., Neil J., Ghawche F. Guillain-Barre Syndrome outbreak associated with Zika virus infection in French Polynesia: a case-control study. Lancet. 2016;387:1531–1539. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical