Microglial activation in Parkinson's disease using [18F]-FEPPA - PubMed (original) (raw)
Microglial activation in Parkinson's disease using [18F]-FEPPA
Christine Ghadery et al. J Neuroinflammation. 2017.
Abstract
Background: Neuroinflammatory processes including activated microglia have been reported to play an important role in Parkinson's disease (PD). Increased expression of translocator protein (TSPO) has been observed after brain injury and inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Positron emission tomography (PET) radioligand targeting TSPO allows for the quantification of neuroinflammation in vivo.
Methods: Based on the genotype of the rs6791 polymorphism in the TSPO gene, we included 25 mixed-affinity binders (MABs) (14 PD patients and 11 age-matched healthy controls (HC)) and 27 high-affinity binders (HABs) (16 PD patients and 11 age-matched HC) to assess regional differences in the second-generation radioligand [18F]-FEPPA between PD patients and HC. FEPPA total distribution volume (V T) values in cortical as well as subcortical brain regions were derived from a two-tissue compartment model with arterial plasma as an input function.
Results: Our results revealed a significant main effect of genotype on [18F]-FEPPA V T in every brain region, but no main effect of disease or disease × genotype interaction in any brain region. The overall percentage difference of the mean FEPPA V T between HC-MABs and HC-HABs was 32.6% (SD = 2.09) and for PD-MABs and PD-HABs was 43.1% (SD = 1.21).
Conclusions: Future investigations are needed to determine the significance of [18F]-FEPPA as a biomarker of neuroinflammation as well as the importance of the rs6971 polymorphism and its clinical consequence in PD.
Keywords: Neuroinflammation; PET; Parkinson’s disease; TSPO imaging.
Figures
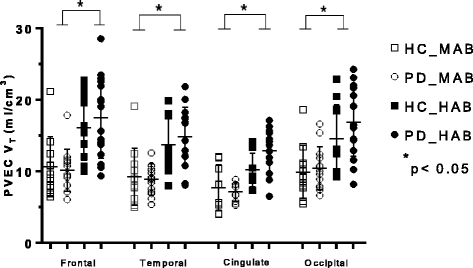
Fig. 1
Graphs of partial volume effect corrected (PVEC) total distribution volume (V T) in different brain regions. Healthy control with mixed affinity binder (HC-MAB) and healthy control with high affinity binder (HC-HAB) groups as well as Parkinson’s disease with mixed affinity binder (PD-MAB) and Parkinson’s disease with high affinity binder (PD-HAB) groups. Asterisks indicate that the HAB groups show significantly higher V T mean values compared with the MAB groups
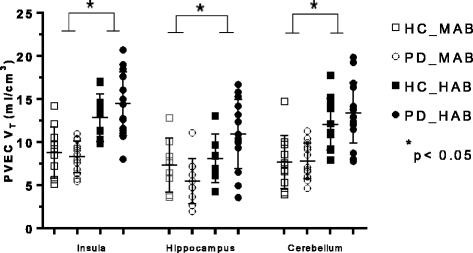
Fig. 2
Graphs of partial volume effect corrected (PVEC) total distribution volume (V T) in different brain regions. Healthy control with mixed affinity binder (HC-MAB) and healthy control with high affinity binder (HC-HAB) groups as well as Parkinson’s disease with mixed affinity binder (PD-MAB) and Parkinson’s disease with high affinity binder (PD-HAB) groups. Asterisks indicate that the HAB groups show significantly higher V T mean values compared with the MAB groups
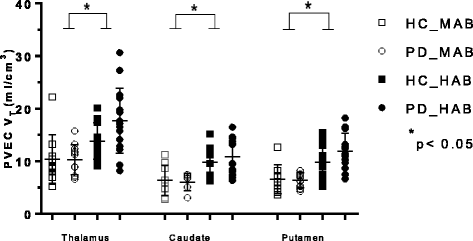
Fig. 3
Graphs of partial volume effect corrected (PVEC) total distribution volume (V T) in different brain regions. Healthy control with mixed affinity binder (HC-MAB) and healthy control with high affinity binder (HC-HAB) groups as well as Parkinson’s disease with mixed affinity binder (PD-MAB) and Parkinson’s disease with high affinity binder (PD-HAB) groups. Asterisks indicate that the HAB groups show significantly higher V T mean values compared with the MAB groups
Similar articles
- Imaging Striatal Microglial Activation in Patients with Parkinson's Disease.
Koshimori Y, Ko JH, Mizrahi R, Rusjan P, Mabrouk R, Jacobs MF, Christopher L, Hamani C, Lang AE, Wilson AA, Houle S, Strafella AP. Koshimori Y, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Sep 18;10(9):e0138721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138721. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26381267 Free PMC article. - Neuroinflammation in healthy aging: a PET study using a novel Translocator Protein 18kDa (TSPO) radioligand, [(18)F]-FEPPA.
Suridjan I, Rusjan PM, Voineskos AN, Selvanathan T, Setiawan E, Strafella AP, Wilson AA, Meyer JH, Houle S, Mizrahi R. Suridjan I, et al. Neuroimage. 2014 Jan 1;84:868-75. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.09.021. Epub 2013 Sep 21. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24064066 Free PMC article. - Quantitative imaging of neuroinflammation in human white matter: a positron emission tomography study with translocator protein 18 kDa radioligand, [18F]-FEPPA.
Suridjan I, Rusjan PM, Kenk M, Verhoeff NP, Voineskos AN, Rotenberg D, Wilson AA, Meyer JH, Houle S, Mizrahi R. Suridjan I, et al. Synapse. 2014 Nov;68(11):536-47. doi: 10.1002/syn.21765. Epub 2014 Jul 28. Synapse. 2014. PMID: 25043159 Free PMC article. - Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis of PET imaging studies.
Zhang PF, Gao F. Zhang PF, et al. J Neurol. 2022 May;269(5):2304-2314. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10877-z. Epub 2021 Nov 1. J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34724571 Review. - Neuroinflammation in the living brain of Parkinson's disease.
Ouchi Y, Yagi S, Yokokura M, Sakamoto M. Ouchi Y, et al. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009 Dec;15 Suppl 3:S200-4. doi: 10.1016/S1353-8020(09)70814-4. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009. PMID: 20082990 Review.
Cited by
- Pharmacological Targeting of Microglial Activation: New Therapeutic Approach.
Liu CY, Wang X, Liu C, Zhang HL. Liu CY, et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Nov 19;13:514. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00514. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31803024 Free PMC article. Review. - Mild Inflammatory Profile without Gliosis in the c-Rel Deficient Mouse Modeling a Late-Onset Parkinsonism.
Porrini V, Mota M, Parrella E, Bellucci A, Benarese M, Faggi L, Tonin P, Spano PF, Pizzi M. Porrini V, et al. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017 Jul 19;9:229. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00229. eCollection 2017. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28769786 Free PMC article. - Microglial signatures and their role in health and disease.
Butovsky O, Weiner HL. Butovsky O, et al. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018 Oct;19(10):622-635. doi: 10.1038/s41583-018-0057-5. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30206328 Free PMC article. Review. - How should we be using biomarkers in trials of disease modification in Parkinson's disease?
Vijiaratnam N, Foltynie T. Vijiaratnam N, et al. Brain. 2023 Dec 1;146(12):4845-4869. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad265. Brain. 2023. PMID: 37536279 Free PMC article. - Novel PET Biomarkers to Disentangle Molecular Pathways across Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases.
Wilson H, Politis M, Rabiner EA, Middleton LT. Wilson H, et al. Cells. 2020 Dec 2;9(12):2581. doi: 10.3390/cells9122581. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33276490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Mogi M, Harada M, Kondo T, Riederer P, Inagaki H, Minami M, Nagatsu T. Interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-alpha are elevated in the brain from parkinsonian patients. Neurosci Lett. 1994;180(2):147–150. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90508-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical