Third generation drug eluting stent (DES) with biodegradable polymer in diabetic patients: 5 years follow-up - PubMed (original) (raw)
Multicenter Study
doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0500-3.
Sinisa Stoikovic 2, Alexander Samol 3, Zisis Dimitriadis 4, Juan M Ruiz-Nodar 5, Ralf Birkemeyer 6, Jacques Monsegu 7, Gérard Finet 8, David Hildick-Smith 9, Damras Tresukosol 10, Enrique Garcia Novo 11, Jacques J Koolen 12, Emanuele Barbato 13 14, Gian Battista Danzi 15; NOBORI 2 investigators
Affiliations
- PMID: 28183306
- PMCID: PMC5301341
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-017-0500-3
Multicenter Study
Third generation drug eluting stent (DES) with biodegradable polymer in diabetic patients: 5 years follow-up
Marcus Wiemer et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017.
Erratum in
- Erratum to: Third generation drug eluting stent (DES) with biodegradable polymer in diabetic patients: 5 years follow-up.
Wiemer M, Stojkovic S, Samol A, Dimitriadis Z, Ruiz-Nodar JM, Birkemeyer R, Monsegu J, Finet G, Hildick-Smith D, Tresukosol D, Novo EG, Koolen JJ, Barbato E, Danzi GB; NOBORI 2 investigators. Wiemer M, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017 May 4;16(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0541-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017. PMID: 28472961 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To report the long-term safety and efficacy data of a third generation drug eluting stent (DES) with biodegradable polymer in the complex patient population of diabetes mellitus after a follow-up period of 5 years.
Background: After percutaneous coronary intervention patients with diabetes mellitus are under higher risk of death, restenosis and stent thrombosis (ST) compared to non-diabetic patients.
Methods: In 126 centers worldwide 3067 patients were enrolled in the NOBORI 2 registry, 888 patients suffered from diabetes mellitus (DM), 213 of them (14%) being insulin dependent (IDDM). Five years follow-up has been completed in this study.
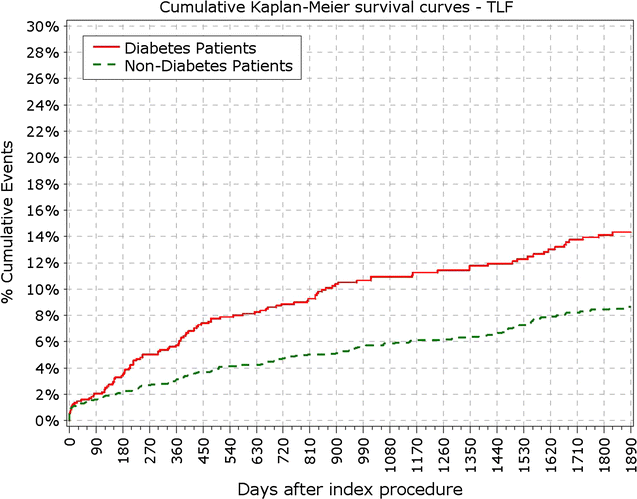
Results: At 5 years, 89.3% of the patients were available for follow-up. The reported target lesion failure (TLF) rates at 5 years were 12.39% in DM group and 7.34% in non-DM group; (p < 0.0001). In the DM group, the TLF rate in patients with IDDM was significantly higher than in the non-IDDM subgroup (17.84 vs. 10.67%; p < 0.01). The rate of ST at 5 years was not different among diabetic versus non-diabetic patients or IDDM versus NIDDM. Only 10 (<0.4%) very late stent thrombotic events beyond 12 months occurred.
Conclusions: The Nobori DES performed well in patients with DM. As expected patients with DM, particularly those with IDDM, had worse outcomes. However, the very low rate of very late stent thrombosis in IDDM patients might have significant clinical value in the treatment of these patients. Clinical trial registration ISRCTN81649913; http://www.controlled-trials.com/isrctn/search.html?srch=81649913&sort=3&dir=desc&max=10.
Figures
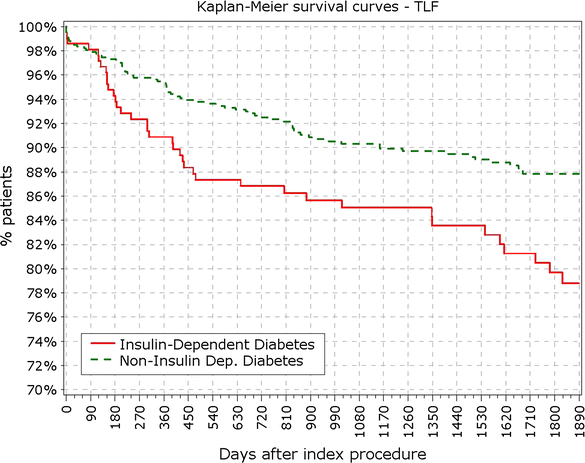
Fig. 1
Primary endpoint: TLF incidence. TLF target lesion failure
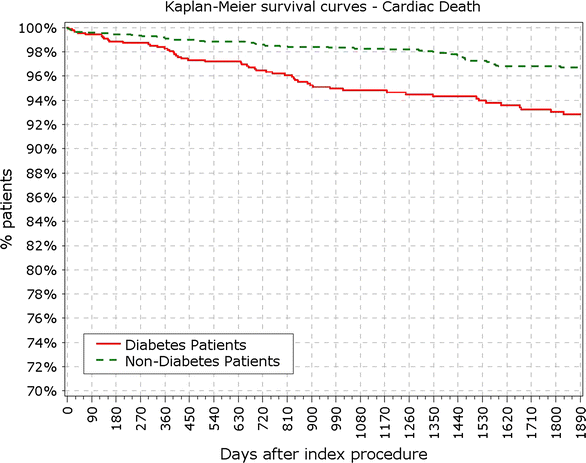
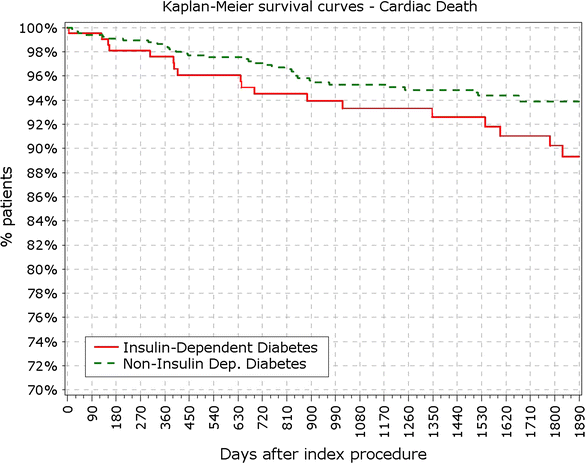
Fig. 2
Secondary endpoint: survival from cardiac death
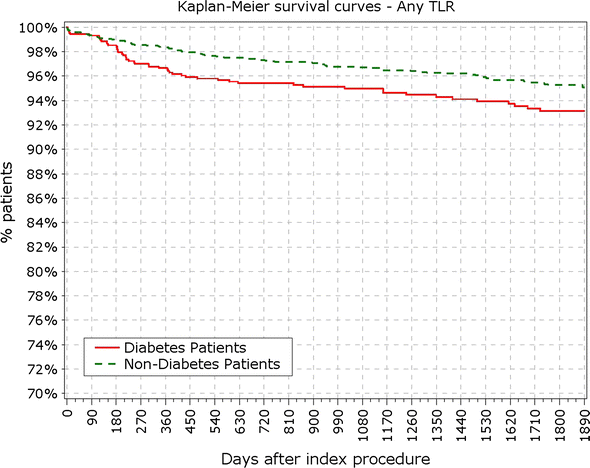
Fig. 3
Secondary endpoint: survival from TLR. TLR target lesion revascularization
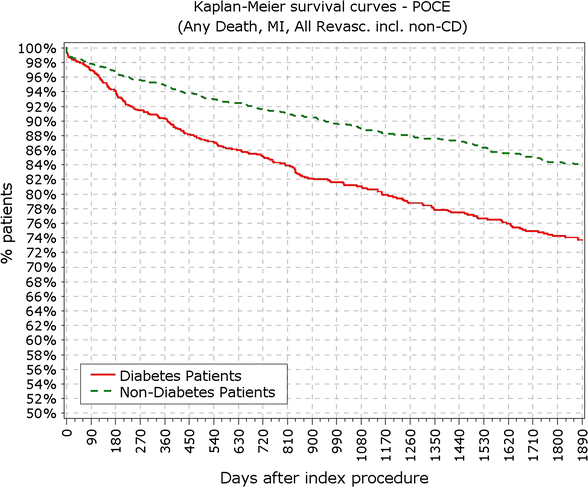
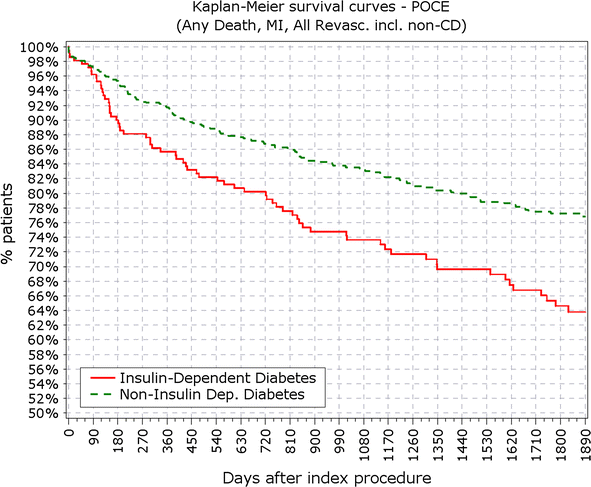
Fig. 4
Survival from patient oriented composite endpoints. POCE patient oriented composite endpoints
Fig. 5
Survival from TLF in non-IDDM versus IDDM. TLR target lesion failure
Fig. 6
Survival from cardiac death in IDDM versus non-IDDM
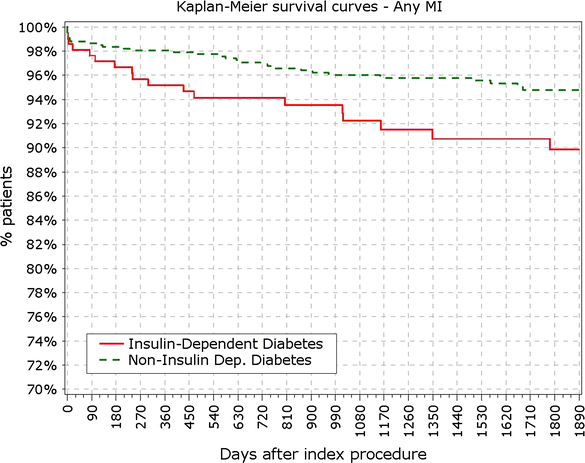
Fig. 7
Survival from myocardial infarction in IDDM versus non-IDDM
Fig. 8
Survival from POCE in IDDM versus non-IDDM
Similar articles
- Real polymer-free sirolimus- and probucol-eluting versus biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stents for obstructive coronary artery disease: DKPLUS-Wave 1, a multicenter, randomized, prospective trial.
Chen SL, Ye F, Zhang JJ, Zou JJ, Qian XS, Li F, Yang S, Ge Z, Shan SJ, Li XB, Xu T, Kan J, Lin L, Han YL. Chen SL, et al. Cardiovasc Ther. 2013 Aug;31(4):193-200. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5922.2012.00319.x. Cardiovasc Ther. 2013. PMID: 22954234 Clinical Trial. - A propensity score-matched comparison of biodegradable polymer vs second-generation durable polymer drug-eluting stents in a real-world population.
Zhao YJ, Teng M, Khoo AL, Ananthakrishna R, Yeo TC, Lim BP, Loh JP, Chan MY. Zhao YJ, et al. Cardiovasc Ther. 2018 Apr;36(2). doi: 10.1111/1755-5922.12319. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Cardiovasc Ther. 2018. PMID: 29316284 - Improved safety and reduction in stent thrombosis associated with biodegradable polymer-based biolimus-eluting stents versus durable polymer-based sirolimus-eluting stents in patients with coronary artery disease: final 5-year report of the LEADERS (Limus Eluted From A Durable Versus ERodable Stent Coating) randomized, noninferiority trial.
Serruys PW, Farooq V, Kalesan B, de Vries T, Buszman P, Linke A, Ischinger T, Klauss V, Eberli F, Wijns W, Morice MC, Di Mario C, Corti R, Antoni D, Sohn HY, Eerdmans P, Rademaker-Havinga T, van Es GA, Meier B, Jüni P, Windecker S. Serruys PW, et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013 Aug;6(8):777-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2013.04.011. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013. PMID: 23968698 Clinical Trial. - Meta-analysis of bioabsorbable versus durable polymer drug-eluting stents in 20,005 patients with coronary artery disease: an update.
Lupi A, Gabrio Secco G, Rognoni A, Lazzero M, Fattori R, Sheiban I, Sante Bongo A, Bolognese L, Agostoni P, Porto I. Lupi A, et al. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2014 May 1;83(6):E193-206. doi: 10.1002/ccd.25416. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2014. PMID: 24478247 Review. - Biodegradable versus durable polymer drug eluting stents in coronary artery disease: insights from a meta-analysis of 5,834 patients.
Lupi A, Rognoni A, Secco GG, Lazzero M, Nardi F, Fattori R, Bongo AS, Agostoni P, Sheiban I. Lupi A, et al. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014 Apr;21(4):411-24. doi: 10.1177/2047487312467745. Epub 2012 Nov 14. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 23152364 Review.
Cited by
- Biodegradable polymer drug-eluting stents versus second-generation drug-eluting stents in patients with and without diabetes mellitus: a single-center study.
Tang XF, Ma YL, Song Y, Xu JJ, Yao Y, He C, Wang HH, Jiang P, Jiang L, Liu R, Gao Z, Zhao XY, Qiao SB, Yang YJ, Gao RL, Xu B, Yuan JQ. Tang XF, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018 Aug 14;17(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0758-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 30107794 Free PMC article. - Long-term cardiovascular outcomes of biodegradable polymer drug eluting stents in patients with diabetes versus non-diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis.
Wang H, Zu Q, Tang H, Lu M, Chen R, Yang Z. Wang H, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Aug 29;22(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01962-w. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37644465 Free PMC article. Review. - Five-Year Outcomes in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus Treated With Biodegradable Polymer Sirolimus-Eluting Stents Versus Durable Polymer Everolimus-Eluting Stents.
Iglesias JF, Heg D, Roffi M, Tüller D, Lanz J, Rigamonti F, Muller O, Moarof I, Cook S, Weilenmann D, Kaiser C, Cuculi F, Valgimigli M, Jüni P, Windecker S, Pilgrim T. Iglesias JF, et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Nov 19;8(22):e013607. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.013607. Epub 2019 Nov 7. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31696762 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - CABG versus PCI in the Treatment of Unprotected Left Main Disease in Diabetics: A Literature Review.
Lambert D, Mattia A, Hsu A, Manetta F. Lambert D, et al. Int J Angiol. 2021 Nov 10;30(3):187-193. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1735517. eCollection 2021 Sep. Int J Angiol. 2021. PMID: 34776818 Free PMC article. Review. - Baseline plasma fibrinogen is associated with haemoglobin A1c and 2-year major adverse cardiovascular events following percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a single-centre, prospective cohort study.
Zhang L, Xu C, Liu J, Bai X, Li R, Wang L, Zhou J, Wu Y, Yuan Z. Zhang L, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019 Apr 23;18(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0858-5. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019. PMID: 31014348 Free PMC article.
References
- Sousa JE, Costa MA, Abizaid A, Abizaid AS, Feres F, Pinto IM, Seixas AC, Staico R, Mattos LA, Sousa AG, et al. Lack of neointimal proliferation after implantation of sirolimus-coated stents in human coronary arteries: a quantitative coronary angiography and three-dimensional intravascular ultrasound study. Circulation. 2001;103(2):192–195. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.103.2.192. - DOI - PubMed
- Finn AV, Kolodgie FD, Harnek J, Guerrero LJ, Acampado E, Tefera K, Skorija K, Weber DK, Gold HK, Virmani R. Differential response of delayed healing and persistent inflammation at sites of overlapping sirolimus- or paclitaxel-eluting stents. Circulation. 2005;112(2):270–278. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.508937. - DOI - PubMed
- Sarno G, Lagerqvist B, Nilsson J, Frobert O, Hambraeus K, Varenhorst C, Jensen UJ, Todt T, Gotberg M, James SK. Stent thrombosis in new-generation drug-eluting stents in patients with STEMI undergoing primary PCI: a report from SCAAR. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64(1):16–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.04.022. - DOI - PubMed
- Chevalier B, Silber S, Park SJ, Garcia E, Schuler G, Suryapranata H, Koolen J, Hauptmann KE, Wijns W, Morice MC, et al. Randomized comparison of the Nobori Biolimus A9-eluting coronary stent with the Taxus Liberte paclitaxel-eluting coronary stent in patients with stenosis in native coronary arteries: the NOBORI 1 trial—Phase 2. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2009;2(3):188–195. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.108.823443. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials