The chronic mild stress (CMS) model of depression: History, evaluation and usage - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The chronic mild stress (CMS) model of depression: History, evaluation and usage
Paul Willner. Neurobiol Stress. 2016.
Abstract
Now 30 years old, the chronic mild stress (CMS) model of depression has been used in >1300 published studies, with a year-on-year increase rising to >200 papers in 2015. Data from a survey of users show that while a variety of names are in use (chronic mild/unpredictable/varied stress), these describe essentially the same procedure. This paper provides an update on the validity and reliability of the CMS model, and reviews recent data on the neurobiological basis of CMS effects and the mechanisms of antidepressant action: the volume of this research may be unique in providing a comprehensive account of antidepressant action within a single model. Also discussed is the use of CMS in drug discovery, with particular reference to hippocampal and extra-hippocampal targets. The high translational potential of the CMS model means that the neurobiological mechanisms described may be of particular relevance to human depression and mechanisms of clinical antidepressant action.
Keywords: Antidepressant; Chronic mild stress; Depression; Hippocampus; Neurobiology of stress; Prefrontal cortex; Reliability; Validity.
Figures
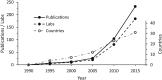
Fig. 1
Uptake of the CMS model: 1990–2015.
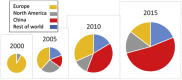
Fig. 2
Geographical origin of CMS studies. The size of the circle approximates the volume of publications in each year.
Fig. 3
Intracellular and systemic mechanisms of antidepressant action.
References
- American Psychiatric Association . American Psychiatric Association; Washington DC: 2013. DSM-5: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
- Atanasova B., El-Hage W., Chabanet C., Gaillard P., Belzung C., Camus V. Olfactory anhedonia and negative olfactory alliesthesia in depressed patients. Psychiatry Res. 2010;176:190–196. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources