Phytochemicals of Moringa oleifera: a review of their nutritional, therapeutic and industrial significance - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Phytochemicals of Moringa oleifera: a review of their nutritional, therapeutic and industrial significance
Ramesh Kumar Saini et al. 3 Biotech. 2016 Dec.
Abstract
Moringa oleifera Lam., also known as the 'drumstick tree,' is recognized as a vibrant and affordable source of phytochemicals, having potential applications in medicines, functional food preparations, water purification, and biodiesel production. The multiple biological activities including antiproliferation, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antinociceptive, antiatherosclerotic, oxidative DNA damage protective, antiperoxidative, cardioprotective, as well as folk medicinal uses of M. oleifera (MO) are attributed to the presence of functional bioactive compounds, such as phenolic acids, flavonoids, alkaloids, phytosterols, natural sugars, vitamins, minerals, and organic acids. The low molecular weight of M. oleifera cationic proteins (MOCP) extracted from the seeds is very useful and is used in water purification, because of its potent antimicrobial and coagulant properties. Also, the M. oleifera methyl esters (MOME) produced from the oil of the seeds meet the major specifications of the biodiesel standard of Germany, Europe, and United States (US). Thus, MO is emerging as one of the prominent industrial crops for sustainable biodiesel production in tropical and subtropical countries. In view of the high nutritional, nutraceutical, and industrial values, it is important to compile an updated comprehensive review on the related aspects of this multipurpose and miracle tree. Hence, the present study is focused on the nutritionally significant bioactives and medicinal and biological properties, to explore the potential applications of MO in nutritionally rich food preparations. Furthermore, water coagulation, proteins, and fatty acid methyl esters from the MO seeds are reviewed, to explore their possible industrial applications in biodiesel production and water purification. In addition, the future perspectives in these areas are suggested.
Keywords: Bioactives; Biodiesel; Drumstick tree; M. oleifera cationic proteins (MOCP); Water purification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Fig. 1
a The distribution of Moringa oleifera in the World. The image of world map was obtained from
(royalty free). b Different vegetative and reproductive parts of M. oleifera tree; i field grown tree, ii bundle of foliage, iii flowers, and iv fruit (pod)
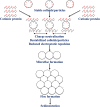
Fig. 2
Mechanism of water coagulation and sedimentation using Moringa oleifera cationic proteins (MOCP)
Similar articles
- Biological, nutritional, and therapeutic significance of Moringa oleifera Lam.
Dhakad AK, Ikram M, Sharma S, Khan S, Pandey VV, Singh A. Dhakad AK, et al. Phytother Res. 2019 Nov;33(11):2870-2903. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6475. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Phytother Res. 2019. PMID: 31453658 Review. - Bioactive components from Moringa oleifera seeds: production, functionalities and applications - a critical review.
Dzuvor CKO, Pan S, Amanze C, Amuzu P, Asakiya C, Kubi F. Dzuvor CKO, et al. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2022 Mar;42(2):271-293. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2021.1931804. Epub 2021 Jun 20. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34151645 Review. - Health Benefits of Uses and Applications of Moringa oleifera in Bakery Products.
Milla PG, Peñalver R, Nieto G. Milla PG, et al. Plants (Basel). 2021 Feb 6;10(2):318. doi: 10.3390/plants10020318. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33562157 Free PMC article. Review. - Medicinal utilization and nutritional properties of drumstick (Moringa oleifera)-A comprehensive review.
Zarina, Wani AW, Rawat M, Kaur H, Das S, Kaur T, Akram N, Faisal Z, Jan SS, Oyshe NN, Khan MR, Shah YA. Zarina, et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Apr 8;12(7):4546-4568. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4139. eCollection 2024 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39055230 Free PMC article. Review. - Research advances on the multiple uses of Moringa oleifera: A sustainable alternative for socially neglected population.
Brilhante RSN, Sales JA, Pereira VS, Castelo-Branco DSCM, Cordeiro RA, de Souza Sampaio CM, de Araújo Neto Paiva M, Santos JBFD, Sidrim JJC, Rocha MFG. Brilhante RSN, et al. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2017 Jul;10(7):621-630. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtm.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Jul 28. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2017. PMID: 28870337 Review.
Cited by
- Impact of Bioactive Compounds of Plant Leaf Powders in White Chocolate Production: Changes in Antioxidant Properties during the Technological Processes.
Poliński S, Topka P, Tańska M, Kowalska S, Czaplicki S, Szydłowska-Czerniak A. Poliński S, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Apr 10;11(4):752. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040752. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453437 Free PMC article. - An insight into the neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory effects and mechanisms of Moringa oleifera.
Azlan UK, Khairul Annuar NA, Mediani A, Aizat WM, Damanhuri HA, Tong X, Yanagisawa D, Tooyama I, Wan Ngah WZ, Jantan I, Hamezah HS. Azlan UK, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 5;13:1035220. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1035220. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36686668 Free PMC article. Review. - A 14-day repeated-dose oral toxicological evaluation of an isothiocyanate-enriched hydro-alcoholic extract from Moringa oleifera Lam. seeds in rats.
Kim Y, Jaja-Chimedza A, Merrill D, Mendes O, Raskin I. Kim Y, et al. Toxicol Rep. 2018 Mar 6;5:418-426. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.02.012. eCollection 2018. Toxicol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29854612 Free PMC article. - A comprehensive review on beneficial dietary phytochemicals in common traditional Southern African leafy vegetables.
Sivakumar D, Chen L, Sultanbawa Y. Sivakumar D, et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2018 Apr 14;6(4):714-727. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.643. eCollection 2018 Jun. Food Sci Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29983933 Free PMC article. Review. - Bioactive Components in Moringa Oleifera Leaves Protect against Chronic Disease.
Vergara-Jimenez M, Almatrafi MM, Fernandez ML. Vergara-Jimenez M, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2017 Nov 16;6(4):91. doi: 10.3390/antiox6040091. Antioxidants (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29144438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Adedapo A, Falayi O, Oyagbemi A. The anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of the methanol leaf extract of Moringa oleifera in some laboratory animals (657.19) FASEB J. 2014;28(Suppl 1):657.19.
- Akanni OE, Adedeji AL, Oloke KJ. Upregulation of TNF-α by ethanol extract of Moringa oleifera leaves in benzene-induced leukemic Wister rat: a possible mechanism of anticancer property. Cancer Res. 2014;74(Suppl 19):3792–3792. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2014-3792. - DOI
- Amaglo NK, Bennett RN, Lo Curto RB, et al. Profiling selected phytochemicals and nutrients in different tissues of the multipurpose tree Moringa oleifera L., grown in Ghana. Food Chem. 2010;122:1047–1054. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.03.073. - DOI
- Arora DS, Onsare JG. In vitro antimicrobial evaluation and phytoconstituents of Moringa oleifera pod husks. Ind Crops Prod. 2014;52:125–135. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.09.016. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources