Assessment of the Anti-Hyperglycaemic, Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activities of the Methanol Extract of Moringa Oleifera in Diabetes-Induced Nephrotoxic Male Wistar Rats - PubMed (original) (raw)
Assessment of the Anti-Hyperglycaemic, Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activities of the Methanol Extract of Moringa Oleifera in Diabetes-Induced Nephrotoxic Male Wistar Rats
Elizabeth I Omodanisi et al. Molecules. 2017.
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus is an endocrine disease of multiple aetiologies in insulin secretion. A deficiency in insulin results in hyperglycemia with metabolic disturbances of biomolecules. Moringa oleifera (MO) is endemic in the tropics with a variety of ethnomedicinal importance. The leaf of this plant has been reported to possess antioxidant and medicinal properties that may be helpful in the treatment and management of diabetes and its associated complications. Diabetes was induced intraperitoneally in rats by a single dose of streptozotocin (55 mg/kg) and treated with methanolic extract of Moringa oleifera (250 mg/kg b.wt) for six weeks. Forty-eight (48) adult male Wistar strain rats were randomly divided into four groups: normal control (NC), Moringa oleifera treated control rats (NC + MO), diabetic rats (DM) and Moringa oleifera treated diabetic rats (DM + MO). Estimation of antioxidant capacity, total polyphenols, flavonoids and flavonols content of Moringa oleifera extract was performed and serum biochemical markers were evaluated. Antioxidants such as catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities, glutathione (GSH) and inflammatory biomarkers were determined in the kidney. Results showed high antioxidant capacities of MO extract and improved serum biochemical markers, whilst lipid peroxidation (MDA) levels were reduced in non-diabetic and diabetic rats after MO treatment when compared to normal control. Subsequent administration of MO led to an increased concentration of serum albumin, globulin and total protein with a decrease in the level of MDA, and improvements in CAT, SOD, GSH, GPx, (tumour necrosis factor-alpha)TNF-α and (interleukin-6)IL-6. MO contains potent phytochemical constituents that offer protective action against diabetic-induced renal damage, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammation and could therefore play a role in reducing diabetic complications, particularly in developing countries such as in Africa where the majority cannot afford orthodox medicine.
Keywords: Moringa oleifera; antioxidant; diabetes; flavonoids; hyperglycemia; inflammatory; methanolic extract; nephrotoxicity; phytochemical; streptozotocin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
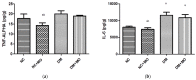
Figure 1
Effect of Moringa oleifera on (a) tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and (b) interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the kidneys. NC (Normal control), NC + MO (_Moringa oleifera_-treated control rats), DM (Diabetic rats) and DM + MO (_Moringa oleifera_-treated diabetic rats). Values are presented as mean (SD). a p < 0.05 values are significant compared with non- diabetic control. b p < 0.05 values are significant compared with diabetic control.
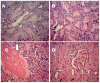
Figure 2
Effect of Moringa oleifera on the kidney sections (hematoxylin and eosin stained X 400). (A) NC (Normal control) (B) NC + MO (_Moringa oleifera_-treated control rats) (C) DM (Diabetic rats) and (D) DM + MO (_Moringa oleifera_-treated diabetic rats).
Similar articles
- Evaluation of antidiabetic and antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera in experimental diabetes.
Gupta R, Mathur M, Bajaj VK, Katariya P, Yadav S, Kamal R, Gupta RS. Gupta R, et al. J Diabetes. 2012 Jun;4(2):164-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-0407.2011.00173.x. J Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22103446 - Retinoprotective effects of Moringa oleifera via antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-angiogenic mechanisms in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Kumar Gupta S, Kumar B, Srinivasan BP, Nag TC, Srivastava S, Saxena R, Aggarwal A. Kumar Gupta S, et al. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2013 May;29(4):419-26. doi: 10.1089/jop.2012.0089. Epub 2012 Dec 10. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23215831 - Preliminary phytochemical screening, antioxidant and antihyperglycaemic activity of Moringa oleifera leaf extracts.
Aa AB, Om J, Ts E, Ga A. Aa AB, et al. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2017 Nov;30(6):2217-2222. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 29175792 - Health benefits and phenolic compounds of Moringa oleifera leaves: A comprehensive review.
Hassan MA, Xu T, Tian Y, Zhong Y, Ali FAZ, Yang X, Lu B. Hassan MA, et al. Phytomedicine. 2021 Dec;93:153771. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153771. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34700271 Review. - Review of the Safety and Efficacy of Moringa oleifera.
Stohs SJ, Hartman MJ. Stohs SJ, et al. Phytother Res. 2015 Jun;29(6):796-804. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5325. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Phytother Res. 2015. PMID: 25808883 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Moringa oleifera seeds mitigate myocardial injury and prevent ventricular failure induced by myocardial infarction.
Li YJ, Ji QQ, Wang Z, Shen LH, He B. Li YJ, et al. Am J Transl Res. 2020 Aug 15;12(8):4511-4521. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32913524 Free PMC article. - An In Vitro Evaluation of the Molecular Mechanisms of Action of Medical Plants from the Lamiaceae Family as Effective Sources of Active Compounds against Human Cancer Cell Lines.
Sitarek P, Merecz-Sadowska A, Śliwiński T, Zajdel R, Kowalczyk T. Sitarek P, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 13;12(10):2957. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102957. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33066157 Free PMC article. Review. - Moringa Oleifera Alleviates Homocysteine-Induced Alzheimer's Disease-Like Pathology and Cognitive Impairments.
Mahaman YAR, Huang F, Wu M, Wang Y, Wei Z, Bao J, Salissou MTM, Ke D, Wang Q, Liu R, Wang JZ, Zhang B, Chen D, Wang X. Mahaman YAR, et al. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;63(3):1141-1159. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180091. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 29710724 Free PMC article. - Amorphous Pterostilbene Delivery Systems Preparation-Innovative Approach to Preparation Optimization.
Rosiak N, Tykarska E, Cielecka-Piontek J. Rosiak N, et al. Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 13;15(4):1231. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041231. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111715 Free PMC article. - A Critical Review on Polyphenols and Health Benefits of Black Soybeans.
Ganesan K, Xu B. Ganesan K, et al. Nutrients. 2017 May 4;9(5):455. doi: 10.3390/nu9050455. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28471393 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous