Comparison of anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Ginger powder and Ibuprofen in postsurgical pain model: A randomized, double-blind, case-control clinical trial - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparison of anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Ginger powder and Ibuprofen in postsurgical pain model: A randomized, double-blind, case-control clinical trial
Farshid Rayati et al. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2017 Jan-Feb.
Abstract
Background: Ginger has been used as an herbal drug for a long time for the treatment of chronic inflammatory conditions.
Materials and methods: This randomized, double-blind clinical trial was conducted on 67 healthy adults with at least one impacted lower third molar. Participants were randomly allocated into three groups: Ibuprofen, Ginger, and placebo. Evaluation of inflammation was done by measuring cheek swelling, mouth opening ability, serum C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, and visual analog scale (for pain scoring). The number and the time of using rescue medication were recorded too.
Results: Sixty patients completed the study. In all three groups, there was a significant increase in the mean cheek swelling measures, compared with the baseline, until day 5. The reduction in mouth opening ability was significant in all three groups, compared with the baseline, until day 5. There was no significant difference between ibuprofenand ginger groups in pain scores in all follow-up days. Number of required rescue medication on the day of surgery was significantly more in the placebo group. No significant or strong correlations were found between CRP levels and clinical findings.
Conclusion: Within the limitations of this study, it can ban be concluded that gingerpowder is as effective as ibuprofenin the management of postsurgical sequelae. Furthermore, CRP levels alone are not suggested for the assessment of anti-inflammatory effects of drugs.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; Ginger; Ibuprofen; surgery; third molar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, financial or non-financial in this article.
Figures
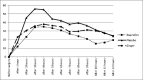
Figure 1
Median pain score (mm) of three study groups on the day of surgery (day 0).
Similar articles
- Effectiveness of ginger on pain following periodontal surgery - A randomized cross-over clinical trial.
Menon P, Perayil J, Fenol A, Rajan Peter M, Lakshmi P, Suresh R. Menon P, et al. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2021 Jan-Mar;12(1):65-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jaim.2020.05.003. Epub 2020 Jul 2. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 32624375 Free PMC article. - A single-tablet fixed-dose combination of racemic ibuprofen/paracetamol in the management of moderate to severe postoperative dental pain in adult and adolescent patients: a multicenter, two-stage, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, factorial study.
Mehlisch DR, Aspley S, Daniels SE, Southerden KA, Christensen KS. Mehlisch DR, et al. Clin Ther. 2010 Jun;32(6):1033-49. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.06.002. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20637958 Clinical Trial. - Comparative Analgesic Effects of Ibuprofen, Celecoxib and Tramadol after third Molar Surgery: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled Trial.
Akinbade AO, Ndukwe KC, Owotade FJ. Akinbade AO, et al. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018 Nov 1;19(11):1334-1340. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018. PMID: 30602637 Clinical Trial. - C-reactive protein estimation: a quantitative analysis for three nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: a randomized control trial.
Salgia G, Kulkarni DG, Shetty L. Salgia G, et al. Indian J Dent Res. 2015 Jan-Feb;26(1):43-7. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.156797. Indian J Dent Res. 2015. PMID: 25961614 Clinical Trial. - Ibuprofen as a pre-emptive analgesic is as effective as rofecoxib for mandibular third molar surgery.
Morse Z, Tump A, Kevelham E. Morse Z, et al. Odontology. 2006 Sep;94(1):59-63. doi: 10.1007/s10266-006-0062-4. Odontology. 2006. PMID: 16998619 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
- The "root" causes behind the anti-inflammatory actions of ginger compounds in immune cells.
Pázmándi K, Szöllősi AG, Fekete T. Pázmándi K, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 28;15:1400956. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1400956. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39007134 Free PMC article. Review. - The antioxidant activity, preliminary phytochemical screening of Zingiber zerumbet and antimicrobial efficacy against selective endodontic bacteria.
Assiry AA, Ahmed N, Almuaddi A, Saif A, Alshahrani MA, Mohamed RN, Karobari MI. Assiry AA, et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Jun 1;11(8):4853-4860. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3462. eCollection 2023 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37576053 Free PMC article. - Effectiveness of ginger on pain following periodontal surgery - A randomized cross-over clinical trial.
Menon P, Perayil J, Fenol A, Rajan Peter M, Lakshmi P, Suresh R. Menon P, et al. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2021 Jan-Mar;12(1):65-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jaim.2020.05.003. Epub 2020 Jul 2. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 32624375 Free PMC article. - Comparison of safety and analgesic efficacy of diclofenac sodium with etodolac after surgical extraction of third molars: a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, parallel-group study.
Vaghela JH, Shah JH, Patel JH, Purohit BM. Vaghela JH, et al. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2020 Feb;20(1):19-27. doi: 10.17245/jdapm.2020.20.1.19. Epub 2020 Feb 28. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2020. PMID: 32158956 Free PMC article. - Is Ginger Effective in Reducing Post-tonsillectomy Morbidity? A Prospective Randomised Clinical Trial.
Koçak İ, Yücepur C, Gökler O. Koçak İ, et al. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Mar;11(1):65-70. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2017.00374. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 28877566 Free PMC article.
References
- Grzanna R, Lindmark L, Frondoza CG. Ginger – An herbal medicinal product with broad anti-inflammatory actions. J Med Food. 2005;8:125–32. - PubMed
- Ali BH, Blunden G, Tanira MO, Nemmar A. Some phytochemical, pharmacological and toxicological properties of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe): A review of recent research. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008;46:409–20. - PubMed
- Chrubasik S, Pittler MH, Roufogalis BD. Zingiberis rhizoma: A comprehensive review on the ginger effect and efficacy profiles. Phytomedicine. 2005;12:684–701. - PubMed
- Ojewole JA. Analgesic, antiinflammatory and hypoglycaemic effects of ethanol extract of Zingiber officinale (Roscoe) rhizomes (Zingiberaceae) in mice and rats. Phytother Res. 2006;20:764–72. - PubMed
- Aimbire F, Penna SC, Rodrigues M, Rodrigues KC, Lopes-Martins RA, Sertié JA. Effect of hydroalcoholic extract of Zingiber officinalis rhizomes on LPS-induced rat airway hyperreactivity and lung inflammation. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2007;77:129–38. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous