NASP: an accurate, rapid method for the identification of SNPs in WGS datasets that supports flexible input and output formats - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2016 Aug 25;2(8):e000074.
doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000074. eCollection 2016 Aug.
Darrin Lemmer 1, Jason Travis 1, James M Schupp 1, John D Gillece 1, Maliha Aziz 3, Elizabeth M Driebe 1, Kevin P Drees 4, Nathan D Hicks 5, Charles Hall Davis Williamson 2, Crystal M Hepp 2, David Earl Smith 1, Chandler Roe 1, David M Engelthaler 1, David M Wagner 2, Paul Keim 2
Affiliations
- PMID: 28348869
- PMCID: PMC5320593
- DOI: 10.1099/mgen.0.000074
NASP: an accurate, rapid method for the identification of SNPs in WGS datasets that supports flexible input and output formats
Jason W Sahl et al. Microb Genom. 2016.
Abstract
Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) of bacterial isolates has become standard practice in many laboratories. Applications for WGS analysis include phylogeography and molecular epidemiology, using single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) as the unit of evolution. NASP was developed as a reproducible method that scales well with the hundreds to thousands of WGS data typically used in comparative genomics applications. In this study, we demonstrate how NASP compares with other tools in the analysis of two real bacterial genomics datasets and one simulated dataset. Our results demonstrate that NASP produces similar, and often better, results in comparison with other pipelines, but is much more flexible in terms of data input types, job management systems, diversity of supported tools and output formats. We also demonstrate differences in results based on the choice of the reference genome and choice of inferring phylogenies from concatenated SNPs or alignments including monomorphic positions. NASP represents a source-available, version-controlled, unit-tested method and can be obtained from tgennorth.github.io/NASP.
Keywords: Phylogeography; SNPs; bioinformatics.
Figures
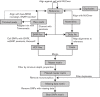
Fig. 1.
Workflow of the NASP pipeline.
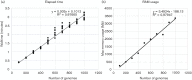
Fig. 2.
NASP benchmark comparisons of walltime (a) and RAM (b) on a set of Escherichia coli genomes. For the walltime comparisons, 3520 E. coli genomes were randomly sampled ten times at different depths and run on a server with 856 cores. Only the matrix-building step is shown, but demonstrates a linear scaling with the processing of additional genomes.
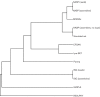
Fig. 3.
Dendrogram of tree building methods on a simulated set of mutations in the genome of Yersinia pestis Colorado 92. The topological score was generated by compare2trees (Nye et al., 2006) compared with a maximum likelihood phylogeny inferred from a set of 3501 SNPs inserted by Tree2Reads. The dendrogram was generated with the neighbor-joining method in the Phylip software package (Felsenstein, 2005).
Similar articles
- Evaluation of SNP calling methods for closely related bacterial isolates and a novel high-accuracy pipeline: BactSNP.
Yoshimura D, Kajitani R, Gotoh Y, Katahira K, Okuno M, Ogura Y, Hayashi T, Itoh T. Yoshimura D, et al. Microb Genom. 2019 May;5(5):e000261. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000261. Epub 2019 May 17. Microb Genom. 2019. PMID: 31099741 Free PMC article. - Whole genome sequencing options for bacterial strain typing and epidemiologic analysis based on single nucleotide polymorphism versus gene-by-gene-based approaches.
Schürch AC, Arredondo-Alonso S, Willems RJL, Goering RV. Schürch AC, et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018 Apr;24(4):350-354. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2017.12.016. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018. PMID: 29309930 Review. - Validation and Implementation of Clinical Laboratory Improvements Act-Compliant Whole-Genome Sequencing in the Public Health Microbiology Laboratory.
Kozyreva VK, Truong CL, Greninger AL, Crandall J, Mukhopadhyay R, Chaturvedi V. Kozyreva VK, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Aug;55(8):2502-2520. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00361-17. Epub 2017 Jun 7. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28592550 Free PMC article. - Evaluating the use of whole-genome sequencing for outbreak investigations in the lack of closely related reference genome.
Abdelbary MMH, Senn L, Moulin E, Prod'hom G, Croxatto A, Greub G, Blanc DS. Abdelbary MMH, et al. Infect Genet Evol. 2018 Apr;59:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2018.01.014. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Infect Genet Evol. 2018. PMID: 29367013 - The Evolution of Strain Typing in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex.
Merker M, Kohl TA, Niemann S, Supply P. Merker M, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1019:43-78. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-64371-7_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29116629 Review.
Cited by
- Bacterial Genome Wide Association Studies (bGWAS) and Transcriptomics Identifies Cryptic Antimicrobial Resistance Mechanisms in Acinetobacter baumannii.
Roe C, Williamson CHD, Vazquez AJ, Kyger K, Valentine M, Bowers JR, Phillips PD, Harrison V, Driebe E, Engelthaler DM, Sahl JW. Roe C, et al. Front Public Health. 2020 Sep 2;8:451. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00451. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33014966 Free PMC article. - Escherichia coli Sequence Type 410 Is Causing New International High-Risk Clones.
Roer L, Overballe-Petersen S, Hansen F, Schønning K, Wang M, Røder BL, Hansen DS, Justesen US, Andersen LP, Fulgsang-Damgaard D, Hopkins KL, Woodford N, Falgenhauer L, Chakraborty T, Samuelsen Ø, Sjöström K, Johannesen TB, Ng K, Nielsen J, Ethelberg S, Stegger M, Hammerum AM, Hasman H. Roer L, et al. mSphere. 2018 Jul 18;3(4):e00337-18. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00337-18. mSphere. 2018. PMID: 30021879 Free PMC article. - Multiple introductions and subsequent transmission of multidrug-resistant Candida auris in the USA: a molecular epidemiological survey.
Chow NA, Gade L, Tsay SV, Forsberg K, Greenko JA, Southwick KL, Barrett PM, Kerins JL, Lockhart SR, Chiller TM, Litvintseva AP; US Candida auris Investigation Team. Chow NA, et al. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018 Dec;18(12):1377-1384. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30597-8. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30293877 Free PMC article. - Salmonella in Pig Farms and on Pig Meat in Suriname.
Butaye P, Halliday-Simmonds I, Van Sauers A. Butaye P, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Dec 6;10(12):1495. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10121495. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943707 Free PMC article. - Evaluation of SNP calling methods for closely related bacterial isolates and a novel high-accuracy pipeline: BactSNP.
Yoshimura D, Kajitani R, Gotoh Y, Katahira K, Okuno M, Ogura Y, Hayashi T, Itoh T. Yoshimura D, et al. Microb Genom. 2019 May;5(5):e000261. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000261. Epub 2019 May 17. Microb Genom. 2019. PMID: 31099741 Free PMC article.
References
Data Bibliography
- Cui, Y. Sequence Read Archive. SRA010790 (2013).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous