RNA sensors of the innate immune system and their detection of pathogens - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2017 May;69(5):297-304.
doi: 10.1002/iub.1625. Epub 2017 Apr 4.
Affiliations
- PMID: 28374903
- PMCID: PMC7165898
- DOI: 10.1002/iub.1625
Review
RNA sensors of the innate immune system and their detection of pathogens
Nanhua Chen et al. IUBMB Life. 2017 May.
Abstract
The innate immune system plays a critical role in pathogen recognition and initiation of protective immune response through the recognition of pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) by its pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). Nucleic acids including RNA and DNA have been recognized as very important PAMPs of pathogens especially for viruses. RNA are the major PAMPs of RNA viruses, to which most severe disease causing viruses belong thus posing a tougher challenge to human and animal health. Therefore, the understanding of the immune biology of RNA PRRs is critical for control of pathogen infections especially for RNA virus infections. RNA PRRs are comprised of TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, RIG-I, MDA5, NLRP3, NOD2, and some other minorities. This review introduces these RNA PRRs by describing the cellular localizations, ligand recognitions, activation mechanisms, cell signaling pathways, and recognition of pathogens; the cross-talks between various RNA PRRs are also reviewed. The deep insights of these RNA PRRs can be utilized to improve anti-viral immune response. © 2017 IUBMB Life, 69(5):297-304, 2017.
Keywords: RNA; pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs); pathogens; pattern recognition receptors (PRRs).
© 2017 International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
Figures
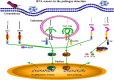
Figure 1
The RNA sensors in pathogen detection. The RNA viruses and some bacteria can be recognized by the main RNA sensors inside cells including endosomal TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, cytosolic RIG‐I, MDA5, NLRP3, and NOD2. Except NLRP3 which initiates inflammasome formation and processes cytokines for maturation, all others activate downstream NF‐κB and IRF signaling pathways, and thus cytokine gene transcription. All these RNA sensor induced signaling together combats pathogen infections.
Similar articles
- Identifying RNA Sensors in Antiviral Innate Immunity.
Zheng C, Zhang L. Zheng C, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2854:107-115. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4108-8_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39192123 - Pattern-recognition receptors in endometriosis: A narrative review.
Guo B, Chen JH, Zhang JH, Fang Y, Liu XJ, Zhang J, Zhu HQ, Zhan L. Guo B, et al. Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 23;14:1161606. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1161606. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37033937 Free PMC article. Review. - The transcriptomic expression of pattern recognition receptors: Insight into molecular recognition of various invading pathogens in Oyster Crassostrea gigas.
Wang L, Zhang H, Wang M, Zhou Z, Wang W, Liu R, Huang M, Yang C, Qiu L, Song L. Wang L, et al. Dev Comp Immunol. 2019 Feb;91:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2018.09.021. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Dev Comp Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30287242 - RIG-I and Other RNA Sensors in Antiviral Immunity.
Chow KT, Gale M Jr, Loo YM. Chow KT, et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 2018 Apr 26;36:667-694. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-042617-053309. Annu Rev Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29677479 - Master sensors of pathogenic RNA - RIG-I like receptors.
Schlee M. Schlee M. Immunobiology. 2013 Nov;218(11):1322-35. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23896194 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease Negatively Regulates the NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway and Pyroptosis by Reducing the Oligomerization and Ubiquitination of ASC.
Meng H, Zhou J, Wang M, Zheng M, Xing Y, Wang Y. Meng H, et al. Microorganisms. 2023 Nov 17;11(11):2799. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112799. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38004809 Free PMC article. - Vaccines for COVID-19: perspectives from nucleic acid vaccines to BCG as delivery vector system.
de Queiroz NMGP, Marinho FV, Chagas MA, Leite LCC, Homan EJ, de Magalhães MTQ, Oliveira SC. de Queiroz NMGP, et al. Microbes Infect. 2020 Nov-Dec;22(10):515-524. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2020.09.004. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Microbes Infect. 2020. PMID: 32961274 Free PMC article. Review. - SARS-CoV-2 vaccination diversifies the CD4+ spike-reactive T cell repertoire in patients with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Dykema AG, Zhang B, Woldemeskel BA, Garliss CC, Rashid R, Westlake T, Zhang L, Zhang J, Cheung LS, Caushi JX, Pardoll DM, Cox AL, Ji H, Smith KN, Blankson JN. Dykema AG, et al. EBioMedicine. 2022 Jun;80:104048. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104048. Epub 2022 May 6. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35533495 Free PMC article. - Finding a Toll on the Route: The Fate of Osteoclast Progenitors After Toll-Like Receptor Activation.
Souza PPC, Lerner UH. Souza PPC, et al. Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 17;10:1663. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01663. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31379855 Free PMC article. Review. - Axillary lymph node imaging in mRNA, vector-based, and mix-and-match COVID-19 vaccine recipients: ultrasound features.
Igual-Rouilleault AC, Soriano I, Elizalde A, Quan PL, Fernandez-Montero A, Sobrido C, Pina L. Igual-Rouilleault AC, et al. Eur Radiol. 2022 Oct;32(10):6598-6607. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08846-9. Epub 2022 May 13. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35554651 Free PMC article.
References
- Medzhitov, R. (2009) Approaching the asymptote: 20 years later. Immunity 30, 766–775. - PubMed
- Barbalat, R. , Ewald, S. E. , Mouchess, M. L. , and Barton, G. M. (2011) Nucleic acid recognition by the innate immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 29, 185–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous