Parental Reports of Prodromal Psychopathology in Pediatric Bipolar Disorder - PubMed (original) (raw)
Parental Reports of Prodromal Psychopathology in Pediatric Bipolar Disorder
Mariely Hernandez et al. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017 Apr.
Abstract
Objectives: Early psychopathology in children diagnosed with Bipolar Disorder (BD) remains poorly characterized. Parental retrospective reports provide helpful details on the earliest manifestations and their evolution over time. These symptoms occur early in the course of BD, often before a formal diagnosis is made and/or treatment is implemented, and are of great importance to early recognition and prevention.
Methods: Parents of pre-pubertal children and adolescents with DSM-IV diagnoses of BD attending an outpatient mood disorders clinic provided retrospective ratings of 37 symptoms of child psychopathology. Stability and comorbidity of diagnoses were evaluated, and severity of symptoms for each subject was assessed by identifying the earliest occurrence of the reported symptoms causing impairment.
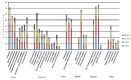
Results: Severe mood instability, temper tantrums, anxiety symptoms, sleep disturbances and aggression were among the most common signs of psychopathology reported in children diagnosed with BD before puberty. Symptoms were already apparent in the first three years in 28%, and formal diagnoses were made before the age of 8 y in the majority of cases.
Conclusions: Retrospective parental reports of early symptoms of psychopathology in pre-pubertal children with BD revealed a very early occurrence of affective precursors (irritability and mood dysregulation) and clinical risk factors like impulsive aggression and anxiety that can precede the syndromal onset of mania by several years. These findings support previous reports suggesting a progression of symptoms from abnormal, non-specific presentations to sub-threshold and finally syndromal BD. The importance of early identification and intervention is discussed.
Keywords: Adolescent; bipolar disorder; children; onset; parents; prodromes; psychopathology.
Figures
Fig. (1)
Frequencies of psychiatric symptoms by age in Bipolar patients (n=83).
Similar articles
- Is there progression from irritability/dyscontrol to major depressive and manic symptoms? A retrospective community survey of parents of bipolar children.
Fergus EL, Miller RB, Luckenbaugh DA, Leverich GS, Findling RL, Speer AM, Post RM. Fergus EL, et al. J Affect Disord. 2003 Oct;77(1):71-8. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0327(02)00176-3. J Affect Disord. 2003. PMID: 14550937 - Pediatric bipolar disorder: phenomenology and course of illness.
Faedda GL, Baldessarini RJ, Glovinsky IP, Austin NB. Faedda GL, et al. Bipolar Disord. 2004 Aug;6(4):305-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5618.2004.00128.x. Bipolar Disord. 2004. PMID: 15225148 - [Predicting bipolar disorder: what can we learn from prospective cohort studies?].
Geoffroy PA, Leboyer M, Scott J. Geoffroy PA, et al. Encephale. 2015 Feb;41(1):10-6. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2013.05.004. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Encephale. 2015. PMID: 24094986 Review. French. - Familial transmission of parental mood disorders: unipolar and bipolar disorders in offspring.
Oquendo MA, Ellis SP, Chesin MS, Birmaher B, Zelazny J, Tin A, Melhem N, Burke AK, Kolko D, Greenhill L, Stanley B, Brodsky BS, Mann JJ, Brent DA. Oquendo MA, et al. Bipolar Disord. 2013 Nov;15(7):764-73. doi: 10.1111/bdi.12107. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Bipolar Disord. 2013. PMID: 23909952 Free PMC article. - Symptoms and signs of the initial prodrome of bipolar disorder: a systematic review.
Skjelstad DV, Malt UF, Holte A. Skjelstad DV, et al. J Affect Disord. 2010 Oct;126(1-2):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2009.10.003. Epub 2009 Nov 1. J Affect Disord. 2010. PMID: 19883943 Review.
Cited by
- Developmental pathways from preschool temper tantrums to later psychopathology.
Hoyniak CP, Donohue MR, Quiñones-Camacho LE, Vogel AC, Perino MT, Hennefield L, Tillman R, Barch DM, Luby JL. Hoyniak CP, et al. Dev Psychopathol. 2023 Oct;35(4):1643-1655. doi: 10.1017/S0954579422000359. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Dev Psychopathol. 2023. PMID: 35440360 Free PMC article. - Sleep Deprivation and Insomnia in Adolescence: Implications for Mental Health.
Uccella S, Cordani R, Salfi F, Gorgoni M, Scarpelli S, Gemignani A, Geoffroy PA, De Gennaro L, Palagini L, Ferrara M, Nobili L. Uccella S, et al. Brain Sci. 2023 Mar 28;13(4):569. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13040569. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37190534 Free PMC article. Review. - Demographic and Clinical Characteristics, Including Subsyndromal Symptoms Across Bipolar-Spectrum Disorders in Adolescents.
Salazar de Pablo G, Guinart D, Cornblatt BA, Auther AM, Carrión RE, Carbon M, Jiménez-Fernández S, Vernal DL, Walitza S, Gerstenberg M, Saba R, Lo Cascio N, Brandizzi M, Arango C, Moreno C, Van Meter A, Correll CU. Salazar de Pablo G, et al. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2020 May;30(4):222-234. doi: 10.1089/cap.2019.0138. Epub 2020 Feb 21. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32083495 Free PMC article. - Sleep and Daytime Complaints During Manic and Depressive Episodes in Children and Adolescents With Bipolar Disorder.
Lopes MC, Boarati MA, Fu-I L. Lopes MC, et al. Front Psychiatry. 2020 Jan 23;10:1021. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.01021. eCollection 2019. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32038338 Free PMC article. - The relationship between sleep and depression and bipolar disorder in children and young people.
Comsa M, Anderson KN, Sharma A, Yadav VC, Watson S. Comsa M, et al. BJPsych Open. 2022 Jan 14;8(1):e27. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2021.1076. BJPsych Open. 2022. PMID: 35027099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Merikangas K.R., Akiskal H.S., Angst J., Greenberg P.E., Hirschfeld R.M., Petukhova M., Kessler R.C. Lifetime and 12-month prevalence of bipolar spectrum disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey replication. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 2007;64(5):543–552. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.64.5.543]. [PMID: 17485606]. - PMC - PubMed
- Van Meter A.R., Moreira A.L., Youngstrom E.A. Meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies of pediatric bipolar disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2011;72(9):1250–1256. [http://dx.doi.org/10.4088/ JCP.10m06290]. [PMID: 21672501]. - PubMed
- Leverich G.S., Post R.M., Keck P.E., Jr, Altshuler L.L., Frye M.A., Kupka R.W., Nolen W.A., Suppes T., McElroy S.L., Grunze H., Denicoff K., Moravec M.K., Luckenbaugh D. The poor prognosis of childhood-onset bipolar disorder. J. Pediatr. 2007;150(5):485–490. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2006.10. 070]. [PMID: 17452221]. - PubMed
- Perlis R.H., Dennehy E.B., Miklowitz D.J., Delbello M.P., Ostacher M., Calabrese J.R., Ametrano R.M., Wisniewski S.R., Bowden C.L., Thase M.E., Nierenberg A.A., Sachs G. Retrospective age at onset of bipolar disorder and outcome during two-year follow-up: results from the STEP-BD study. Bipolar Disord. 2009;11(4):391–400. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-5618.2009.00686.x]. [PMID: 19500092]. - PMC - PubMed
- Birmaher B., Axelson D., Goldstein B., Strober M., Gill M.K., Hunt J., Houck P., Ha W., Iyengar S., Kim E., Yen S., Hower H., Esposito-Smythers C., Goldstein T., Ryan N., Keller M. Four-year longitudinal course of children and adolescents with bipolar spectrum disorders: the Course and Outcome of Bipolar Youth (COBY) study. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2009;166(7):795–804. [http:// dx.doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.08101569]. [PMID: 19448190]. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical