Radiation-related lymphopenia is associated with spleen irradiation dose during radiotherapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma - PubMed (original) (raw)
Radiation-related lymphopenia is associated with spleen irradiation dose during radiotherapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Jing Liu et al. Radiat Oncol. 2017.
Abstract
Background: The decrease in peripheral blood lymphocytes induced by radiation lessens the antitumour effect of the immune response, which might cause immunosuppression. We aimed to investigate the correlation between the decrease in peripheral blood lymphocytes during radiotherapy (RT) and the spleen irradiation dose in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: The subjects were 59 patients with HCC who had received RT from 2005 to 2014. The Min ALC (minimum value of absolute counts for peripheral blood lymphocytes) was collected from the routine workup for each patient prior to RT and weekly during RT. Spleen dose-volume variables, including the percentage of the organ volume receiving ≥ n Gy (Vn) and the mean spleen dose (MSD), were calculated using Eclipse treatment planning. Potential associations between dosimetric variables and the Min ALC were assessed by multiple linear regression analysis.
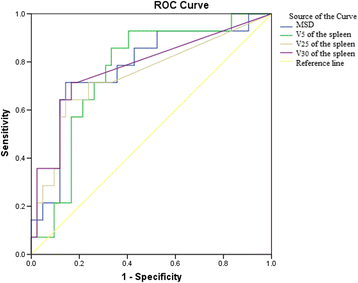
Results: Peripheral lymphocytes decreased during RT (P < 0.001). The Min ALC correlated with the MSD (P = 0.005), spleen V5 (P = 0.001), spleen V25 (P = 0.026) and spleen V30 (P = 0.018). Controlling for the Karnofsky performance status (KPS), sex, age, Child-Pugh grade, total dose and tumour stage, a multiple linear regression model with bootstrap analysis of 1000 replicates showed that only the spleen V5 was correlated with the decrease in the Min ALC (P < 0.05). According to the receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, the predictive cutoff values of the MSD, V5, V25 and V30 of the spleen for the Min ALC were 227.72 cGy, 17.84, 0.98 and 0.42%, respectively (P = 0.002, P = 0.004, P = 0.007 and P = 0.002, respectively). Furthermore, an MSD ≥ 227.72 cGy (OR = 14.39; 95% CI, 12.18 to 16.60) and V5 (OR = 7.99; 95% CI, 6.91 to 9.07) of the spleen significantly predicted the Min ALC.
Conclusions: Higher spleen irradiation doses were significantly correlated with lower Min ALC during RT for HCC. V5 should be limited in clinical practice. Maximum sparing for spleen irradiation during RT is recommended to preserve peripheral blood lymphocytes, which may decrease immunosuppression.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Lymphopenia; Radiotherapy; Spleen dosimetric indicators.
Figures
Fig. 1
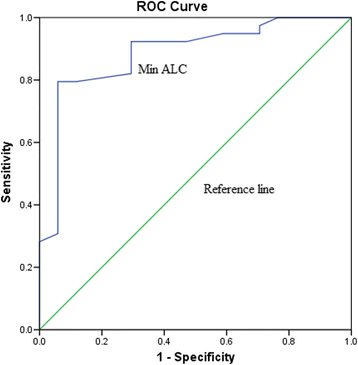
Determination of the cutoff value for the minimum absolute lymphocytes (Min ALC) in predicting the one-year survival in HCC patients who undergo radiotherapy
Fig. 2
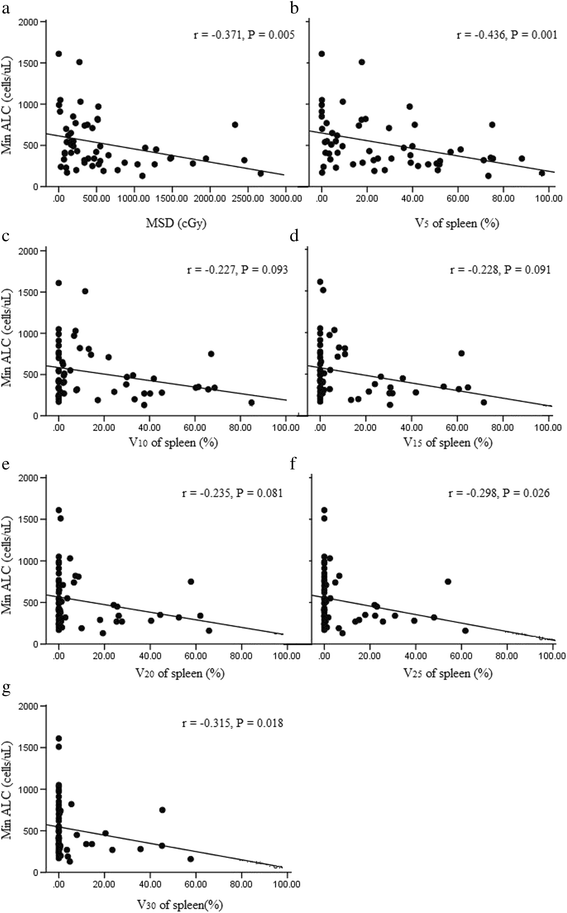
Correlation between the peripheral minimum absolute lymphocytes (Min ALC) during radiotherapy treatment with the mean dose of spleen (MSD) (a), spleen V5 (the percentage of spleen volume receiving ≥ 5 Gy) (b), V10 (c), V15 (d), V20 (e), V25 (f) and V30 (g). Spearman correlation coefficients (r) and corresponding P values are shown
Fig. 3
ROC curve analysis for determining the cutoff value of spleen dosimetric variables in predicting the minimum absolute lymphocytes (Min ALC)
Similar articles
- The relationship between splenic dose and radiation-induced lymphopenia.
Ma Y, Kong Y, Zhang S, Peng Y, Xu M, Zhang J, Xu H, Hong Z, Xing P, Qian J, Zhang L. Ma Y, et al. J Radiat Res. 2024 May 23;65(3):337-349. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrae023. J Radiat Res. 2024. PMID: 38718391 Free PMC article. - Normal Tissue Complication Probability Modeling of Severe Radiation-Induced Lymphopenia Using Blood Dose for Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
Kim S, Byun HK, Shin J, Lee IJ, Sung W. Kim S, et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024 Jul 1;119(3):1011-1020. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.11.060. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024. PMID: 38056776 - Investigation of dosimetric variations of liver radiotherapy using deformable registration of planning CT and cone-beam CT.
Huang P, Yu G, Chen J, Ma C, Qin S, Yin Y, Liang Y, Li H, Li D. Huang P, et al. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2017 Jan;18(1):66-75. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12008. Epub 2016 Dec 5. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28291931 Free PMC article. - Lymphocyte-Sparing Radiotherapy: The Rationale for Protecting Lymphocyte-rich Organs When Combining Radiotherapy With Immunotherapy.
Lambin P, Lieverse RIY, Eckert F, Marcus D, Oberije C, van der Wiel AMA, Guha C, Dubois LJ, Deasy JO. Lambin P, et al. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2020 Apr;30(2):187-193. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2019.12.003. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32381298 Free PMC article. Review. - Cardiac conduction system as a new organ at risk in radiotherapy.
Domanský M, Kubeš J. Domanský M, et al. Klin Onkol. 2024;38(1):10-19. doi: 10.48095/ccko202410. Klin Onkol. 2024. PMID: 39183546 Review. English.
Cited by
- Patient-Specific Lymphocyte Loss Kinetics as Biomarker of Spleen Dose in Patients Undergoing Radiation Therapy for Upper Abdominal Malignancies.
Yalamanchali A, Zhang H, Huang KC, Mohan R, Lin SH, Zhu C, Grossman SA, Jin JY, Ellsworth SG. Yalamanchali A, et al. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2020 Aug 10;6(1):100545. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2020.08.002. eCollection 2021 Jan-Feb. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33665481 Free PMC article. - Prediction of Severe Lymphopenia During Chemoradiation Therapy for Esophageal Cancer: Development and Validation of a Pretreatment Nomogram.
van Rossum PSN, Deng W, Routman DM, Liu AY, Xu C, Shiraishi Y, Peters M, Merrell KW, Hallemeier CL, Mohan R, Lin SH. van Rossum PSN, et al. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2020 Jan-Feb;10(1):e16-e26. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2019.07.010. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31369887 Free PMC article. - Excessive splenic volume is an unfavorable prognostic factor in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy.
Guo J, Wang L, Wang X, Li L, Lü Y, Wang C, Hao C, Zhang J. Guo J, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Dec 4;99(49):e23321. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023321. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33285708 Free PMC article. - Dosimetric analysis of lymphopenia during chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer.
Newman NB, Anderson JL, Sherry AD, Osmundson EC. Newman NB, et al. J Thorac Dis. 2020 May;12(5):2395-2405. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2020.03.93. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 32642145 Free PMC article. - Proton therapy reduces the likelihood of high-grade radiation-induced lymphopenia in glioblastoma patients: phase II randomized study of protons vs photons.
Mohan R, Liu AY, Brown PD, Mahajan A, Dinh J, Chung C, McAvoy S, McAleer MF, Lin SH, Li J, Ghia AJ, Zhu C, Sulman EP, de Groot JF, Heimberger AB, McGovern SL, Grassberger C, Shih H, Ellsworth S, Grosshans DR. Mohan R, et al. Neuro Oncol. 2021 Feb 25;23(2):284-294. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noaa182. Neuro Oncol. 2021. PMID: 32750703 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Cho Y, Miyamoto M, Kato K, Fukunaga A, Shichinohe T, Kawarada Y, et al. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells cooperate to improve prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63:1555–9. - PubMed
- Lissoni P, Meregalli S, Bonetto E, Mancuso M, Brivio F, Colciago M, et al. Radiotherapy-induced lymphocytopenia: changes in total lymphocyte count and in lymphocyte subpopulations under pelvic irradiation in gynecologic neoplasms. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2005;19:153–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical