Effect of a food supplement containing berberine, monacolin K, hydroxytyrosol and coenzyme Q10 on lipid levels: a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2017 May 23:11:1585-1592.
doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S128623. eCollection 2017.
Affiliations
- PMID: 28579756
- PMCID: PMC5447697
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S128623
Randomized Controlled Trial
Effect of a food supplement containing berberine, monacolin K, hydroxytyrosol and coenzyme Q10 on lipid levels: a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study
Sergio D'Addato et al. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017.
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the ability of the new food supplement, Body Lipid (BL), containing red yeast rice, berberine, coenzyme Q10 and hydroxytyrosol, to lower the LDL-C in patients with mild-to-moderate hypercholesterolemia and to assess the overall safety profile of the product.
Methods: In this multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo and active comparator (the marketed Armolipid Plus® [AM]) controlled study, 158 hypercholesterolemic patients were randomized following a 4-week dietary run-in period. After 4 weeks of treatment with a daily oral dose of the new food supplement BL, AM or placebo, plus diet, the main outcome was the decrease of LDL-C, total cholesterol (TC), and triglyceride levels.
Findings: The absolute changes of LDL-C and TC levels from baseline, at week 4 were: -39.1 mg/dL ±17.76 and -45.9 mg/dL ±21.54, respectively in the BL group; 5.7 mg/dL ±14.98 and 2.4 mg/dL ±18.43, respectively in the placebo group. Results were statistically significant. In terms of mean percentage, BL was shown to be more effective in lowering LDL-C levels as compared to placebo and the active comparator (AM), with a reduction of -26.3%, +4.2%, -18.3%, respectively. Five adverse events (AEs) were reported by five patients after the initiation of the study treatment: two in the BL group (influence and insomnia), two in the AM group (ear pain and rash), and one in the placebo group (back pain). All AEs were mild in intensity, except for back pain (severe). The case of insomnia in the BL group and the case of rash in the AM group were judged as treatment related. The safety review of the laboratory (blood and urine) analyses, vital signs and physical findings did not show any clinical effect of the study products on any of the parameters.
Implications: BL showed a good efficacy and safety profile and, for this reason, it can be considered an alternative to pharmacological treatment, for patients with mild-to-moderate hypercholesterolemia.
Keywords: berberine; coenzyme Q10; hydroxytyrosol; lipid profile; red yeast rice.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure F Focanti, F Pelacchi, E Salvatori, G Di Loreto, and A Comandini are employed by ACRAF S.p.A. Angelini Research Center RR&D. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
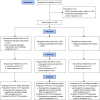
Figure 1
Consort flow diagram. Abbreviations: BL, Body Lipid; m-ITT, modified intent-to-treat; PP, per protocol.
Similar articles
- A nutraceutical approach (Armolipid Plus) to reduce total and LDL cholesterol in individuals with mild to moderate dyslipidemia: Review of the clinical evidence.
Barrios V, Escobar C, Cicero AF, Burke D, Fasching P, Banach M, Bruckert E. Barrios V, et al. Atheroscler Suppl. 2017 Feb;24:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosissup.2016.10.003. Epub 2016 Dec 18. Atheroscler Suppl. 2017. PMID: 27998714 Review. - LDL-cholesterol lowering effect of a new dietary supplement: an open label, controlled, randomized, cross-over clinical trial in patients with mild-to-moderate hypercholesterolemia.
Magno S, Ceccarini G, Pelosini C, Jaccheri R, Vitti J, Fierabracci P, Salvetti G, Airoldi G, Minale M, Saponati G, Santini F. Magno S, et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2018 May 24;17(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0775-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29793488 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Middle-Term Dietary Supplementation with Red Yeast Rice Plus Coenzyme Q10 Improves Lipid Pattern, Endothelial Reactivity and Arterial Stiffness in Moderately Hypercholesterolemic Subjects.
Cicero AF, Morbini M, Rosticci M, D''Addato S, Grandi E, Borghi C. Cicero AF, et al. Ann Nutr Metab. 2016;68(3):213-9. doi: 10.1159/000445359. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Ann Nutr Metab. 2016. PMID: 27055107 Clinical Trial. - Low Dose Monacolin K Combined with Coenzyme Q10, Grape Seed, and Olive Leaf Extracts Lowers LDL Cholesterol in Patients with Mild Dyslipidemia: A Multicenter, Randomized Controlled Trial.
Angelopoulos N, Paparodis RD, Androulakis I, Boniakos A, Argyrakopoulou G, Livadas S. Angelopoulos N, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Jun 9;15(12):2682. doi: 10.3390/nu15122682. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37375586 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Traditional Chinese lipid-lowering agent red yeast rice results in significant LDL reduction but safety is uncertain - a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Gerards MC, Terlou RJ, Yu H, Koks CH, Gerdes VE. Gerards MC, et al. Atherosclerosis. 2015 Jun;240(2):415-23. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.04.004. Epub 2015 Apr 12. Atherosclerosis. 2015. PMID: 25897793 Review.
Cited by
- Cardiovascular and Metabolic Benefits of Extra Virgin Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds: Mechanistic Insights from In Vivo Studies.
Serreli G, Boronat A, De la Torre R, Rodriguez-Moratò J, Deiana M. Serreli G, et al. Cells. 2024 Sep 16;13(18):1555. doi: 10.3390/cells13181555. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39329739 Free PMC article. Review. - The Effect of Nattokinase-Monascus Supplements on Dyslipidemia: A Four-Month Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial.
Liu X, Zeng X, Mahe J, Guo K, He P, Yang Q, Zhang Z, Li Z, Wang D, Zhang Z, Wang L, Jing L. Liu X, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Sep 30;15(19):4239. doi: 10.3390/nu15194239. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37836525 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - An open-label study on the short-term effects of a novel EFSA-compliant nutraceutical combination in mild-to-moderate hypercholesterolemia.
Minoretti P, Biagi M, Emanuele E. Minoretti P, et al. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2022 Nov-Dec;12(6):559-565. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2022.20662. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2022. PMID: 36583178 Free PMC article. - Promising Antioxidative Effect of Berberine in Cardiovascular Diseases.
An N, Zhang G, Li Y, Yuan C, Yang F, Zhang L, Gao Y, Xing Y. An N, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 7;13:865353. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.865353. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35321323 Free PMC article. Review. - Nutraceutical Combinations in Hypercholesterolemia: Evidence from Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials.
Protic O, Bonfigli AR, Antonicelli R. Protic O, et al. Nutrients. 2021 Sep 8;13(9):3128. doi: 10.3390/nu13093128. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34579005 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Furie K, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics 2008 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2008;117(4):e25–e146. - PubMed
- National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002;106(25):3143–3421. - PubMed
- Kamal-Bahl SJ, Burke T, Watson D, Wentworth C. Discontinuation of lipid modifying drugs among commercially insured United States patients in recent clinical practice. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(4):530–534. - PubMed
- Bays H. Statin safety: an overview and assessment of the data – 2005. Am J Cardiol. 2006;97(8A):6C–26C. - PubMed
- Derosa G, Romano D, D’Angelo A, Maffioli P. Berberis aristata combined with Silybum marianum on lipid profile in patients not tolerating statins at high doses. Atherosclerosis. 2015;239(1):87–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical