Glucose Self-monitoring in Non-Insulin-Treated Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in Primary Care Settings: A Randomized Trial - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
Glucose Self-monitoring in Non-Insulin-Treated Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in Primary Care Settings: A Randomized Trial
Laura A Young et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2017.
Abstract
Importance: The value of self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) levels in patients with non-insulin-treated type 2 diabetes has been debated.
Objective: To compare 3 approaches of SMBG for effects on hemoglobin A1c levels and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) among people with non-insulin-treated type 2 diabetes in primary care practice.
Design, setting, and participants: The Monitor Trial study was a pragmatic, open-label randomized trial conducted in 15 primary care practices in central North Carolina. Participants were randomized between January 2014 and July 2015. Eligible patients with type 2 non-insulin-treated diabetes were: older than 30 years, established with a primary care physician at a participating practice, had glycemic control (hemoglobin A1c) levels higher than 6.5% but lower than 9.5% within the 6 months preceding screening, as obtained from the electronic medical record, and willing to comply with the results of random assignment into a study group. Of the 1032 assessed for eligibility, 450 were randomized.
Interventions: No SMBG, once-daily SMBG, and once-daily SMBG with enhanced patient feedback including automatic tailored messages delivered via the meter.
Main outcomes and measures: Coprimary outcomes included hemoglobin A1c levels and HRQOL at 52 weeks.
Results: A total of 450 patients were randomized and 418 (92.9%) completed the final visit. There were no significant differences in hemoglobin A1c levels across all 3 groups (P = .74; estimated adjusted mean hemoglobin A1c difference, SMBG with messaging vs no SMBG, -0.09%; 95% CI, -0.31% to 0.14%; SMBG vs no SMBG, -0.05%; 95% CI, -0.27% to 0.17%). There were also no significant differences found in HRQOL. There were no notable differences in key adverse events including hypoglycemia frequency, health care utilization, or insulin initiation.
Conclusions and relevance: In patients with non-insulin-treated type 2 diabetes, we observed no clinically or statistically significant differences at 1 year in glycemic control or HRQOL between patients who performed SMBG compared with those who did not perform SMBG. The addition of this type of tailored feedback provided through messaging via a meter did not provide any advantage in glycemic control.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT02033499.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: Dr Young reports grants from Eli Lilly, grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb, grants and other from GI Dynamics, grants from PhaseBio, grants from Medtronic Minimed, grants from Sanofi, grants from Tolerex, grants from Halozyme, grants from Johnson & Johnson, grants from Andromeda, grants from Boehringer-Ingelheim, grants from GlaxoSmithKline, grants from Intarcia Therapeutics, grants from Lexicon, grants from Scion NeuroStim, grants from Orexigen, grants from Takeda, grants from Theracos, grants from Novo Nordisk, other from Dexcom, outside the submitted work; she is a member of the planning committee for Taking Control of Your Diabetes; and UNC has licensed its interest in copyright works to Telcare of a glucose messaging and treatment algorithm for the purposes of commercialization. Dr Buse reports grants, nonfinancial support, and other from Eli Lilly, grants, nonfinancial support, and other from Bristol-Myers Squibb, grants, nonfinancial support, and other from GI Dynamics, nonfinancial support and other from Elcylex, grants, nonfinancial support, and other from Merck, nonfinancial support and other from Metavention, nonfinancial support and other from vTv Pharma, grants, personal fees, nonfinancial support, and other from PhaseBio, grants, nonfinancial support, and other from AstraZeneca, nonfinancial support and other from Dance Biopharm, nonfinancial support and other from Quest, grants from Medtronic Minimed, grants, nonfinancial support, and other from Sanofi, grants from Tolerex, grants from Osiris, grants from Halozyme, grants from Johnson & Johnson, grants from Andromeda, grants from Boehringer-Ingelheim, grants from GlaxoSmithKline, grants from Astellas, grants from MacroGenics, grants from Intarcia Therapeutics, grants, nonfinancial support, and other from Lexicon, grants from Scion NeuroStim, grants, nonfinancial support, and other from Orexigen, grants, nonfinancial support, and other from Takeda, nonfinancial support and other from Adocia, grants, nonfinancial support, and other from F. Hoffman LaRoche, grants from Theracos, grants, nonfinancial support, and other from Novo Nordisk outside the submitted work; and he is or has been a member of a variety of nonprofit boards: American Diabetes Association, DiabetesSisters, Taking Control of Your Diabetes, AstraZeneca Healthcare Foundation, Bristol-Myers Squib Together on Diabetes Foundation, the National Diabetes Education Program; and UNC has licensed its interest in copyright works to Telcare of a glucose messaging and treatment algorithm for the purposes of commercialization. Dr Donahue reports UNC has licensed its interest in copyright works to Telcare of a glucose messaging and treatment algorithm for the purposes of commercialization. No other disclosures are reported.
Figures
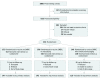
Figure 1.. The Monitor Trial CONSORT Flow Diagram
SMBG indicates self-monitoring of blood glucose.
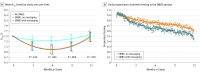
Figure 2.. Mean Hemoglobin A1c by Study Arm Over Time and Daily Proportions of Patients Testing in the SMBG Groups
A, Model-estimated mean hemoglobin A1c values obtained by fitting a quadratic polynomial regression with linear mixed models using all observed hemoglobin A1c values, including those at interim visits, but excluding any following insulin use. The model included 1875 total hemoglobin A1c measurements from 450 patients; only 10 patients contributed no interim hemoglobin A1c measurements and the median number was 4. The intervals represent pointwise 95% CIs for each group, and the P values compare the average of the SMBG groups with the no SMBG group. B, Daily proportions of patients in the SMBG groups uploading a result with the meter on each study day. Lines represent locally weighted smoothing using local quadratic polynomials across the observed proportions. SMBG Indicates self-monitoring of blood glucose.
Comment in
- The Need to Test Strategies Based on Common Sense.
Khoong EC, Ross JS. Khoong EC, et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Jul 1;177(7):929. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.1251. JAMA Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28600912 No abstract available. - Der Effekt der Blutzuckerselbstmessung bei Typ-2-Diabetes scheint nicht so gross wie oft angenommen.
Steurer J. Steurer J. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2017 Aug;106(16):893-894. doi: 10.1024/1661-8157/a002762. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2017. PMID: 28795627 German. No abstract available. - Routine Glucose Self-Monitoring Unnecessary for Non-Insulin-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.
Rosenberg K. Rosenberg K. Am J Nurs. 2017 Sep;117(9):55-56. doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000524549.73814.ca. Am J Nurs. 2017. PMID: 28837492 No abstract available. - Self-monitoring of blood glucose did not improve HbA1c or QoL at 1 year in non-insulin-treated type 2 diabetes.
Murff HJ. Murff HJ. Ann Intern Med. 2017 Oct 17;167(8):JC46. doi: 10.7326/ACPJC-2017-167-8-046. Ann Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 29049765 No abstract available. - Concerns About Conclusions of Self-monitoring of Blood Glucose.
Pimazoni-Netto A, Rodbard D. Pimazoni-Netto A, et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Dec 1;177(12):1873-1874. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.6142. JAMA Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 29204633 No abstract available. - Concerns About Conclusions of Self-monitoring of Blood Glucose-Reply.
Young LA, Buse JB, Donahue KE. Young LA, et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Dec 1;177(12):1874-1875. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.6152. JAMA Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 29204640 No abstract available. - Commentary: Glucose Self-monitoring in Non-Insulin-Treated Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in Primary Care Settings: A Randomized Trial.
Brož J, Holubová A, Vlasáková M, Mužík J, Brabec M, Rahelić D. Brož J, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Jul 12;9:389. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00389. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30050503 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Does Daily Self-Monitoring of Blood Sugar Levels Improve Blood Sugar Control and Quality of Life for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Do Not Use Insulin? – The Monitor Trial [Internet].
Young LA, Buse JB, Weaver MA, Vu MB, Mitchell CM, Blakeney T, Grimm K, Rees J, Niblock F, Donahue KE. Young LA, et al. Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2018 Mar. Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2018 Mar. PMID: 37184185 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Three approaches to glucose monitoring in non-insulin treated diabetes: a pragmatic randomized clinical trial protocol.
Young LA, Buse JB, Weaver MA, Vu MB, Reese A, Mitchell CM, Blakeney T, Grimm K, Rees J, Donahue KE. Young LA, et al. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017 May 25;17(1):369. doi: 10.1186/s12913-017-2202-7. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017. PMID: 28545493 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Implications of remote monitoring Technology in Optimizing Traditional Self-Monitoring of blood glucose in adults with T2DM in primary care.
Montero AR, Toro-Tobon D, Gann K, Nassar CM, Youssef GA, Magee MF. Montero AR, et al. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021 Nov 10;21(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00884-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021. PMID: 34758807 Free PMC article. - Feasibility and effectiveness of self-monitoring of blood glucose among insulin-dependent patients with type 2 diabetes: open randomized control trial in three rural districts in Rwanda.
Ng'ang'a L, Ngoga G, Dusabeyezu S, Hedt-Gauthier BL, Harerimana E, Niyonsenga SP, Bavuma CM, Bukhman G, Adler AJ, Kateera F, Park PH. Ng'ang'a L, et al. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Oct 8;22(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-01162-9. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 36209209 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Meta-analysis of the benefits of self-monitoring of blood glucose on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients: an update.
Poolsup N, Suksomboon N, Rattanasookchit S. Poolsup N, et al. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2009 Dec;11(12):775-84. doi: 10.1089/dia.2009.0091. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2009. PMID: 20001678
Cited by
- A qualitative study of blood glucose and side effect self-management among patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing chemotherapy for cancer.
Terao N. Terao N. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2022 Dec 6;10(2):100172. doi: 10.1016/j.apjon.2022.100172. eCollection 2023 Feb. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2022. PMID: 36632446 Free PMC article. - Clinical Team Response to the Impact of COVID-19 on Diabetes Self-Management: Findings From a Qualitative Study.
Hale L, Cameron TC, Donahue KE, Vu MB, Leeman J, Johnson A, Richman E, Rees J, Young L. Hale L, et al. Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2022 Mar 10;3:835845. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2022.835845. eCollection 2022. Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2022. PMID: 36992778 Free PMC article. - Guidelines and Recommendations for Laboratory Analysis in the Diagnosis and Management of Diabetes Mellitus.
Sacks DB, Arnold M, Bakris GL, Bruns DE, Horvath AR, Lernmark Å, Metzger BE, Nathan DM, Kirkman MS. Sacks DB, et al. Diabetes Care. 2023 Oct 1;46(10):e151-e199. doi: 10.2337/dci23-0036. Diabetes Care. 2023. PMID: 37471273 Free PMC article. Review. - Effects of intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring on blood glucose control and the production of urinary ketone bodies in pregestational diabetes mellitus.
Li SY, Guo H, Zhang Y, Li P, Zhou P, Sun LR, Li J, Chen LM. Li SY, et al. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021 Apr 9;13(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13098-021-00657-0. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021. PMID: 33836817 Free PMC article. - Effects of physician's diabetes self-management education using Japan Association of Diabetes Education and Care Diabetes Education Card System Program and a self-monitoring of blood glucose readings analyzer in individuals with type 2 diabetes: An exploratory, open-labeled, prospective randomized clinical trial.
Tanaka N, Yabe D, Murotani K, Yamaguchi Y, Fujita Y, Kubota S, Nakashima-Yasuda R, Kubota-Okamoto S, Ueno S, Yamazaki Y, Kuwata H, Watanabe K, Hyo T, Hamamoto Y, Kurose T, Higashiyama H, Seino Y, Yamada Y, Seino Y. Tanaka N, et al. J Diabetes Investig. 2021 Dec;12(12):2221-2231. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13607. Epub 2021 Jul 30. J Diabetes Investig. 2021. PMID: 34087060 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- American Diabetes Association 5. Glycemic targets. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(suppl 1):S39-S46. - PubMed
- Allemann S, Houriet C, Diem P, Stettler C. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in non-insulin treated patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009;25(12):2903-2913. - PubMed
- Clar C, Barnard K, Cummins E, Royle P, Waugh N. Aberdeen Health Technology Assessment Group . Self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes: systematic review. Health Technol Assess. 2010;14(12):1-140. - PubMed
- Farmer AJ, Perera R, Ward A, et al. . Meta-analysis of individual patient data in randomised trials of self monitoring of blood glucose in people with non-insulin treated type 2 diabetes. BMJ. 2012;344:e486-e486. - PubMed
- Malanda UL, Welschen LM, Riphagen II, Dekker JM, Nijpels G, Bot SD Self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who are not using insulin. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com.libproxy.lib.unc.edu/doi/10.1002/14651858.... Login required. Accessed April 9, 2017. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical