Residual Dizziness after Successful Repositioning Maneuver for Idiopathic Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Residual Dizziness after Successful Repositioning Maneuver for Idiopathic Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Review
Giorgia Giommetti et al. Audiol Res. 2017.
Abstract
The benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a vestibular disorder cause of vertigo. The BPPV may be corrected mechanically by repositioning maneuvers but even after successful maneuvers, some patients report residual dizziness for a certain period afterward. Early recognition and treatment might decrease the incidence of residual dizziness in patients with BPPV, especially in those patients with psychiatric comorbidities and in the elderly, lowering the risk of falling. Many pathogenetic hypotheses for residual dizziness are under debate. The purpose of this review was to identify, evaluate and review recent researches about possible causal factors involved in residual dizziness and the implications on clinical practice. A literature search was performed using different databases such as Pubmed and Scopus. The following search terms were used: residual dizziness, otolithic membrane and BPPV. The search found a total of 1192 titles, which were reduced to 963 after a procedure of de-duplication of the found titles. The research was then restricted to an interval of time comprised between 2000 and 2016 for a total of 800 titles. Among these titles, only those including the terms benign paroxysmal positional vertigo were considered eligible for this review. Only publications in English language were taken into consideration and we excluded those with not available abstract. Finally, 90 abstracts were obtained and critically evaluated by two different Authors, and additional studies were identified by hand searching from the references of artiche of interest. Only 53 were included in this work.
Keywords: Residual dizziness; benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; repositioning maneuver.
Figures
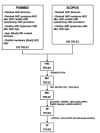
Figure 1.
Search strategy flow chart.
Similar articles
- Residual dizziness after successful repositioning maneuvers for idiopathic benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in the elderly.
Teggi R, Giordano L, Bondi S, Fabiano B, Bussi M. Teggi R, et al. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2011 Apr;268(4):507-11. doi: 10.1007/s00405-010-1422-9. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2011. PMID: 21069369 - Residual dizziness after successful repositioning treatment in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.
Seok JI, Lee HM, Yoo JH, Lee DK. Seok JI, et al. J Clin Neurol. 2008 Sep;4(3):107-10. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2008.4.3.107. Epub 2008 Sep 30. J Clin Neurol. 2008. PMID: 19513312 Free PMC article. - Risk factors for residual dizziness in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo after successful repositioning: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Ke Y, Ma X, Jing Y, Diao T, Yu L. Ke Y, et al. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Jul;279(7):3237-3256. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07288-9. Epub 2022 Feb 26. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 35218384 Review. - Clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.
Bhattacharyya N, Baugh RF, Orvidas L, Barrs D, Bronston LJ, Cass S, Chalian AA, Desmond AL, Earll JM, Fife TD, Fuller DC, Judge JO, Mann NR, Rosenfeld RM, Schuring LT, Steiner RW, Whitney SL, Haidari J; American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation. Bhattacharyya N, et al. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008 Nov;139(5 Suppl 4):S47-81. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2008.08.022. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008. PMID: 18973840 Review.
Cited by
- Acupuncture for Residual Dizziness After Successful Repositioning Maneuvers in Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: Study Protocol for a Randomized Noninferiority Trial.
Xia Y, Sun J, Dai K, Sun F, Ren Z, Cheng B. Xia Y, et al. Med Acupunct. 2024 Aug 21;36(4):227-234. doi: 10.1089/acu.2023.0135. eCollection 2024 Aug. Med Acupunct. 2024. PMID: 39309621 - Approach to residual dizziness after successfully treated benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: effect of a polyphenol compound supplementation.
Casani AP, Navari E, Albera R, Agus G, Asprella Libonati G, Chiarella G, Lombardo N, Marcelli V, Ralli G, Scotto di Santillo L, Teggi R, Viola P, Califano L. Casani AP, et al. Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Aug 1;11:117-125. doi: 10.2147/CPAA.S210763. eCollection 2019. Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31534374 Free PMC article. - Clinical Efficacy and Metabolomics Modifications Induced by Polyphenol Compound Supplementation in the Treatment of Residual Dizziness following Semont Maneuver in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) of the Posterior Semicircular Canal (PSC): Preliminary Results.
Casani AP, Albera R, Piras C, Albera A, Noto A, Ducci N, Atzori L, Lucisano S, Mussap M, Fanos V. Casani AP, et al. Metabolites. 2024 Jan 25;14(2):86. doi: 10.3390/metabo14020086. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38392978 Free PMC article. - Increased functional connectivity between default mode network and visual network potentially correlates with duration of residual dizziness in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.
Chen Z, Cai Y, Xiao L, Wei XE, Liu Y, Lin C, Liu D, Liu H, Rong L. Chen Z, et al. Front Neurol. 2024 Mar 4;15:1363869. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1363869. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38500812 Free PMC article. - Efficacy of Repositioning Therapy in Patients With Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo and Preexisting Central Neurologic Disorders.
Chen CC, Cho HS, Lee HH, Hu CJ. Chen CC, et al. Front Neurol. 2018 Jun 29;9:486. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00486. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30013505 Free PMC article.
References
- Baloh RW, Honrubia V, Jacobson K. Benign positional vertigo: clinical and oculographic features in 240 cases. Neurology 1987;37:371-8. - PubMed
- Nedels JM, Barber HO, Mcilmoyl L. Diagnoses in a dizziness unit. J Otolaryngol 1986;15:101-4. - PubMed
- Bhattacharyya N, Baugh RF, Orvidas L, et al. American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head, Neck Surgery foundation Clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2008;139:47-81. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources