Urinothorax: a systematic review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Urinothorax: a systematic review
María E Toubes et al. J Thorac Dis. 2017 May.
Abstract
Background: The characteristics of patients with urinothorax (UT) are poorly defined.
Methods: A systematic review was performed searching for studies reporting clinical findings, pleural fluid (PF) characteristics, and the most effective treatment of UT. Case descriptions and retrospective studies were included.
Results: The review included 78 studies with a total of 88 patients. Median age was 45 years, male/female ratio was 1.6:1 and in 76% of cases the etiology was trauma. Pleural effusion (PE) was predominantly unilateral (87%) and occupied over 2/3 of the hemithorax in most cases (64.4%). PF was straw-colored (72.7%) or hematic (27.3%) with urine-like odor in all cases. PF was transudate in 56.2% of cases (18/32) and among 14 exudates (43.8%), 3 were concordant exudates, 1 protein-discordant and 10 LDH-discordant, with lymphocyte (44.4%) and neutrophil (38.5%) predominance. The PF/serum (PF/S) creatinine ratio was >1 in all cases except one (97.9%). The diagnosis was established on the basis of PF/S creatinine ratio >1 (56.6%), urinary tract contrast extravasation (12%), abnormal computed tomography (8.4%), laparotomy findings (6%), and association of obstructive uropathy with PE (6%). The outcome was favorable (74/77; 96.1%) when treatment was direct towards the uropathy (alone or associated with thoracentesis/thoracic drainage). Outcome was unfavorable in the 15 patients who were only treated with thoracentesis/thoracic drainage.
Conclusions: UT is usually traumatic, unilateral, and PF does not have a specific pattern or cellularity predominance, with a PF/S creatinine ratio almost always >1. Treatment should include the uropathy, with or without PF evacuation.
Keywords: Pleural effusion (PE); pleural fluid (PF); urinothorax (UT); urothorax.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
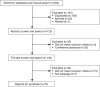
Figure 1
PRISMA flowchart of evidence synthesis. PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses.
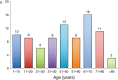
Figure 2
Age group distribution of patients with urinothorax.
Similar articles
- Characteristics of patients with pseudochylothorax-a systematic review.
Lama A, Ferreiro L, Toubes ME, Golpe A, Gude F, Álvarez-Dobaño JM, González-Barcala FJ, San José E, Rodríguez-Núñez N, Rábade C, Rodríguez-García C, Valdés L. Lama A, et al. J Thorac Dis. 2016 Aug;8(8):2093-101. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.07.84. J Thorac Dis. 2016. PMID: 27621864 Free PMC article. - The Urinothorax: A Comprehensive Review With Case Series.
Austin A, Jogani SN, Brasher PB, Argula RG, Huggins JT, Chopra A. Austin A, et al. Am J Med Sci. 2017 Jul;354(1):44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2017.03.034. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Am J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28755732 Review. - Pleural Effusion Secondary to Obstructive Uropathy: A Case of Urinothorax.
Freitas A, Coelho T, Beça S, Gregório T. Freitas A, et al. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2020 Sep 16;7(12):001865. doi: 10.12890/2020_001865. eCollection 2020. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 33312995 Free PMC article. - Urinothorax: presentation of a new case as pleural exudate.
Mora RB, Silvente CM, Nieto JM, Cuervo MA. Mora RB, et al. South Med J. 2010 Sep;103(9):931-3. doi: 10.1097/SMJ.0b013e3181e9a38a. South Med J. 2010. PMID: 20689489 - Urinothorax: a new approach.
Garcia-Pachon E, Romero S. Garcia-Pachon E, et al. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2006 Jul;12(4):259-63. doi: 10.1097/01.mcp.0000230628.65515.86. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2006. PMID: 16825877 Review.
Cited by
- Clinical overview of the physiology and pathophysiology of pleural fluid movement: a narrative review.
Ferreiro L, Toubes ME, Suárez-Antelo J, Rodríguez-Núñez N, Valdés L. Ferreiro L, et al. ERJ Open Res. 2024 Sep 30;10(5):00050-2024. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00050-2024. eCollection 2024 Sep. ERJ Open Res. 2024. PMID: 39351376 Free PMC article. Review. - A rare case of infected urinothorax.
Glozman T, Kooner S, Kostowniak C, Pacheco R, Zhang Y, Dumas CL, Chopra A. Glozman T, et al. Respir Med Case Rep. 2024 Jan 24;47:101989. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2024.101989. eCollection 2024. Respir Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38318225 Free PMC article. - Urinothorax and pseudo-azotemia following total abdominal hysterectomy: a case report.
Mikhail E, Seri A, Ralston K, Valvani A, Kalynych Z. Mikhail E, et al. AME Case Rep. 2023 Dec 18;8:25. doi: 10.21037/acr-23-146. eCollection 2024. AME Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 38236466 Free PMC article. - Tension urinothorax as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest: a case report.
Wanchu A, Verma A, Jaiswal S, Khatai AA, Prasad N. Wanchu A, et al. World J Emerg Med. 2023;14(6):499-501. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.097. World J Emerg Med. 2023. PMID: 37969212 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources