Leptin Resistance and Lipolysis of White Adipose Tissue: An Implication to Ectopic Fat Disposition and Its Consequences - PubMed (original) (raw)
Editorial
. 2017 Nov 1;24(11):1088-1089.
doi: 10.5551/jat.ED083. Epub 2017 Aug 5.
Affiliations
- PMID: 28781341
- PMCID: PMC5684473
- DOI: 10.5551/jat.ED083
Editorial
Leptin Resistance and Lipolysis of White Adipose Tissue: An Implication to Ectopic Fat Disposition and Its Consequences
Michio Shimabukuro. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017.
No abstract available
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
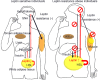
Fig. 1.
Leptin signals and lipolysis of white adipose tissue in leptin sensitive lean and leptin resistance obese individuals. (A) In leptin sensitive lean individuals, leptin constrains insulin biosynthesis and secretion in pancreatic _β_-cells and lower insulin minimizes leptin secretion and regulates lipolysis from adipose tissue via hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL). Leptin maintains hepatic insulin sensitivity via the hepatic branch of the vagus nerve (not shown) and increases glucose uptake in the skeletal muscle, heart, and brown adipose tissue (BAT) via the sympathetic nervous system (black arrows). (B) In leptin resistant obese individuals, effects of leptin, though its plasma levels are increased, is decreased in hypothalamus. Insufficiency of leptin signaling causes hyperinsulinemia in pancreatic _β_-cells, which lead to subsequent impairment of insulin secretion and diabetes mellitus. Leptin resistance increases productions of leptin in white adipose tissue, but cannot abolish fat via HSL. Combined above mechanisms, leptin resistance instigates ectopic fat disposition in the liver and the skeletal muscle, provoking insulin resistance and chronic inflammation.
References
- Friedman JM: The function of leptin in nutrition, weight, and physiology. Nutr Rev, 2002; 60: S1-14; discussion S68-84, 85-17 - PubMed
- Tartaglia LA, Dembski M, Weng X, Deng N, Culpepper J, Devos R, Richards GJ, Campfield LA, Clark FT, Deeds J, Muir C, Sanker S, Moriarty A, Moore KJ, Smutko JS, Mays GG, Wool EA, Monroe CA, Tepper RI: Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R. Cell, 1995; 83: 1263-1271 - PubMed
- Lee G-H, Proenca R, Montez JM, Carroll KM, Darvishzadeh JG, Lee JI, Friedman JM: Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Nature, 1996; 379: 632-635 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical