Basic fibroblast growth factor as a potential biomarker for diagnosing malignant tumor metastasis in women - PubMed (original) (raw)
Basic fibroblast growth factor as a potential biomarker for diagnosing malignant tumor metastasis in women
Man Liu et al. Oncol Lett. 2017 Aug.
Abstract
Previous studies have reported that basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) is associated with tumor genesis, growth and prognosis. The present study was conducted to detect the levels of bFGF expression in women with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), colon cancer, breast cancer and melanoma, and analyze its association with the clinicopathological characteristics of malignant tumors. The tumor tissues were obtained from 508 female patients with malignant tumors between March 2008 and May 2015 (103 NSCLC, 147 colon cancer, 206 breast cancer and 52 melanoma). Histological examination was performed on paraffin-embedded tissues. The immunohistochemical peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin method was used to detect bFGF protein expression in the tissues. The level of bFGF protein expression was significantly increased in patients with NSCLC with poor differentiation and lymph node metastasis compared with patients with moderately/well differentiated NSCLC without lymph node metastasis. Increased levels of bFGF protein expression were observed in patients with colon cancer with lymph node metastasis compared with patients without lymph node metastasis, and in patients with breast cancer with tumor-node-metastasis stage III-IV and lymph node metastasis compared with patients in stage I-II and without lymph node metastasis. The rate of positive bFGF staining in patients with melanoma with lymph node metastasis was significantly higher compared with patients without lymph node metastasis. These results suggested that bFGF may be associated with the process of malignant tumor genesis and growth, and the expression of bFGF protein may be a potential and effective biomarker for diagnosing malignant tumor metastasis in females. The present study may also provide theoretical bases for the clinical application of bFGF monoclonal antibody in molecular targeted therapies in tumors.
Keywords: basic fibroblast growth factor; breast cancer; colon cancer; malignant tumor; melanoma; non-small cell lung cancer.
Figures
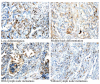
Figure 1.
Representative image of immunohistochemical staining of basic fibroblastic growth factor in tumor tissues obtained from patients with non-small cell lung cancer (magnification, ×100).
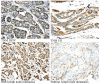
Figure 2.
Representative image of immunohistochemical staining of basic fibroblastic growth factor in tumor tissues obtained from patients with colon cancer (magnification, ×100).
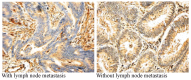
Figure 3.
Representative image of immunohistochemical staining of basic fibroblastic growth factor in in tumor tissues obtained from patients with breast cancer. TNM, tumor-node-metastasis (magnification, ×100).
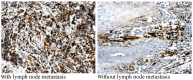
Figure 4.
Representative image of immunohistochemical staining of basic fibroblastic growth factor in in tumor tissues obtained from patients with melanoma (magnification, ×100).
Similar articles
- Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels, as prognostic indicators in NSCLC.
Iwasaki A, Kuwahara M, Yoshinaga Y, Shirakusa T. Iwasaki A, et al. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004 Mar;25(3):443-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2003.11.031. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004. PMID: 15019676 - NQO1 protein expression predicts poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancers.
Li Z, Zhang Y, Jin T, Men J, Lin Z, Qi P, Piao Y, Yan G. Li Z, et al. BMC Cancer. 2015 Mar 31;15:207. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1227-8. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25880877 Free PMC article. - Angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: the prognostic impact of neoangiogenesis and the cytokines VEGF and bFGF in tumours and blood.
Bremnes RM, Camps C, Sirera R. Bremnes RM, et al. Lung Cancer. 2006 Feb;51(2):143-58. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2005.09.005. Epub 2005 Dec 19. Lung Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16360975 Review. - Progress in investigating the relationship between Schlafen5 genes and malignant tumors.
Tu T, Yuan Y, Liu X, Liang X, Yang X, Yang Y. Tu T, et al. Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 11;13:1248825. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1248825. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37771431 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Impact of radiotherapy on the immune landscape in oesophageal adenocarcinoma.
Donlon NE, Davern M, O'Connell F, Sheppard A, Heeran A, Bhardwaj A, Butler C, Narayanasamy R, Donohoe C, Phelan JJ, Lynam-Lennon N, Dunne MR, Maher S, O'Sullivan J, Reynolds JV, Lysaght J. Donlon NE, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Jun 7;28(21):2302-2319. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i21.2302. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35800186 Free PMC article. - Role of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor in Cancer: Biological Activity, Targeted Therapies, and Prognostic Value.
Ardizzone A, Bova V, Casili G, Repici A, Lanza M, Giuffrida R, Colarossi C, Mare M, Cuzzocrea S, Esposito E, Paterniti I. Ardizzone A, et al. Cells. 2023 Mar 24;12(7):1002. doi: 10.3390/cells12071002. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048074 Free PMC article. Review. - Construction of a Novel Bispecific Antibody to Enhance Antitumor Activity against Lung Cancer.
Yin W, Zhu J, Gonzalez-Rivas D, Okumura M, Rocco G, Pass H, Jiang G, Yang Y. Yin W, et al. Adv Mater. 2018 Dec;30(51):e1805437. doi: 10.1002/adma.201805437. Epub 2018 Oct 21. Adv Mater. 2018. PMID: 30345557 Free PMC article. - Understanding the role of endothelial cells in brain tumor formation and metastasis: a proposition to be explored for better therapy.
Agnihotri TG, Salave S, Shinde T, Srikanth I, Gyanani V, Haley JC, Jain A. Agnihotri TG, et al. J Natl Cancer Cent. 2023 Aug 6;3(3):222-235. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2023.08.001. eCollection 2023 Sep. J Natl Cancer Cent. 2023. PMID: 39035200 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Chao Y, Li CP, Chau GY, Chen CP, King KL, Lui WY, Yen SH, Chang FY, Chan WK, Lee SD. Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, and angiogenin in patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma after surgery. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003;10:355–362. doi: 10.1245/ASO.2003.10.002. - DOI - PubMed
- Gospodarowicz D. Fibroblast growth factor. Chemical structure and biologic function. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 1990;257:231–248. - PubMed
- Wei X. Research advances of basic fibroblast growth factor in tissue repair. Orthop J Chin. 2011;19:1108–1110.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources