Mechanisms of Silver Nanoparticle Release, Transformation and Toxicity: A Critical Review of Current Knowledge and Recommendations for Future Studies and Applications - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Mechanisms of Silver Nanoparticle Release, Transformation and Toxicity: A Critical Review of Current Knowledge and Recommendations for Future Studies and Applications
Bogumiła Reidy et al. Materials (Basel). 2013.
Abstract
Nanosilver, due to its small particle size and enormous specific surface area, facilitates more rapid dissolution of ions than the equivalent bulk material; potentially leading to increased toxicity of nanosilver. This, coupled with their capacity to adsorb biomolecules and interact with biological receptors can mean that nanoparticles can reach sub-cellular locations leading to potentially higher localized concentrations of ions once those particles start to dissolve or degrade in situ. Further complicating the story is the capacity for nanoparticles to generate reactive oxygen species, and to interact with, and potentially disturb the functioning of biomolecules such as proteins, enzymes and DNA. The fact that the nanoparticle size, shape, surface coating and a host of other factors contribute to these interactions, and that the particles themselves are evolving or ageing leads to further complications in terms of elucidating mechanisms of interaction and modes of action for silver nanoparticles, in contrast to dissolved silver species. This review aims to provide a critical assessment of the current understanding of silver nanoparticle toxicity, as well as to provide a set of pointers and guidelines for experimental design of future studies to assess the environmental and biological impacts of silver nanoparticles. In particular; in future we require a detailed description of the nanoparticles; their synthesis route and stabilisation mechanisms; their coating; and evolution and ageing under the exposure conditions of the assay. This would allow for comparison of data from different particles; different environmental or biological systems; and structure-activity or structure-property relationships to emerge as the basis for predictive toxicology. On the basis of currently available data; such comparisons or predictions are difficult; as the characterisation and time-resolved data is not available; and a full understanding of silver nanoparticle dissolution and ageing under different conditions is observed. Clear concerns are emerging regarding the overuse of nanosilver and the potential for bacterial resistance to develop. A significant conclusion includes the need for a risk-benefit analysis for all applications and eventually restrictions of the uses where a clear benefit cannot be demonstrated.
Keywords: agglomeration; biological impacts; coatings; cytotoxicity; dissolution; interaction with environmental components; physico-chemical characterisation.
Figures
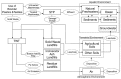
Figure 1
Overview of one model of silver flow triggered by use of biocidal plastics and textiles. Arrows represent silver flows; dashed lines indicate different environmental spheres. TWT = thermal waste treatment; STP = sewage treatment plant [13].
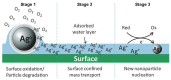
Figure 2
Proposed pathway for new particle formation from parent (nano) particles. Reprint with permission from [10]. Copyright 2011 American Chemical Society.
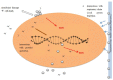
Figure 3
Schematic representation of the known mechanism(s) of antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles and released ionic silver. The numbers 1–4 correspond to the mechanisms described in the paragraphs above. Grey circles indicate silver NPs and Ag+ implies ionic silver released from the NPs.
Figure 4
Main differences between ionic, nanoparticulate and bulk silver.
Similar articles
- Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in macrophages.
Pratsinis A, Hervella P, Leroux JC, Pratsinis SE, Sotiriou GA. Pratsinis A, et al. Small. 2013 Aug 12;9(15):2576-84. doi: 10.1002/smll.201202120. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Small. 2013. PMID: 23418027 - The biological effects and possible modes of action of nanosilver.
Völker C, Oetken M, Oehlmann J. Völker C, et al. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2013;223:81-106. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5577-6_4. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23149813 Review. - Comparative cytotoxicity of nanosilver in human liver HepG2 and colon Caco2 cells in culture.
Sahu SC, Zheng J, Graham L, Chen L, Ihrie J, Yourick JJ, Sprando RL. Sahu SC, et al. J Appl Toxicol. 2014 Nov;34(11):1155-66. doi: 10.1002/jat.2994. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Appl Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24522958 - Systematic analysis of silver nanoparticle ionic dissolution by tangential flow filtration: toxicological implications.
Maurer EI, Sharma M, Schlager JJ, Hussain SM. Maurer EI, et al. Nanotoxicology. 2014 Nov;8(7):718-27. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2013.824127. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Nanotoxicology. 2014. PMID: 23848466 - Molecular toxicity mechanism of nanosilver.
McShan D, Ray PC, Yu H. McShan D, et al. J Food Drug Anal. 2014 Mar;22(1):116-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Feb 7. J Food Drug Anal. 2014. PMID: 24673909 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Nanotechnology-based antiviral therapeutics.
Chakravarty M, Vora A. Chakravarty M, et al. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021 Jun;11(3):748-787. doi: 10.1007/s13346-020-00818-0. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 32748035 Free PMC article. Review. - Remediation of Water Using a Nanofabricated Cellulose Membrane Embedded with Silver Nanoparticles.
Shad S, Lynch I, Shah SWH, Bashir N. Shad S, et al. Membranes (Basel). 2022 Oct 24;12(11):1035. doi: 10.3390/membranes12111035. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36363590 Free PMC article. - Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Mediated by Fungi: A Review.
Guilger-Casagrande M, de Lima R. Guilger-Casagrande M, et al. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019 Oct 22;7:287. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00287. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31696113 Free PMC article. Review. - Preparation and Properties of Bulk and Porous Ti-Ta-Ag Biomedical Alloys.
Adamek G, Kozlowski M, Junka A, Siwak P, Jakubowicz J. Adamek G, et al. Materials (Basel). 2022 Jun 18;15(12):4332. doi: 10.3390/ma15124332. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35744391 Free PMC article. - Application of fungal copper carbonate nanoparticles as environmental catalysts: organic dye degradation and chromate removal.
Liu F, Shah DS, Csetenyi L, Gadd GM. Liu F, et al. Microbiology (Reading). 2021 Dec;167(12):001116. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001116. Microbiology (Reading). 2021. PMID: 34882532 Free PMC article.
References
- Project on emerging nanotechnologies. [(accessed on 3 June 2013)]. Avaliable online: http://www.nanotechproject.org/inventories/consumer/
- Jonas P.R. Environmental impacts of artificial ice nucleating agents. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1979;105:728–728. doi: 10.1002/qj.49710544517. - DOI
- Wong K.K.Y., Liu X. Silver nanoparticles—The real “silver bullet” in clinical medicine? Med. Chem. Commun. 2010;1:125–131. doi: 10.1039/c0md00069h. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources