Effect of screening for type 2 diabetes on risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality: a controlled trial among 139,075 individuals diagnosed with diabetes in Denmark between 2001 and 2009 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Controlled Clinical Trial
. 2017 Nov;60(11):2192-2199.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4299-y. Epub 2017 Aug 23.
Affiliations
- PMID: 28831539
- PMCID: PMC6108415
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-017-4299-y
Controlled Clinical Trial
Effect of screening for type 2 diabetes on risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality: a controlled trial among 139,075 individuals diagnosed with diabetes in Denmark between 2001 and 2009
Rebecca K Simmons et al. Diabetologia. 2017 Nov.
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: There is continuing debate about the net benefits of population screening for type 2 diabetes. We compared the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality among incident cases of type 2 diabetes in a screened group with those in an unscreened group.
Methods: In this register-based non-randomised controlled trial, eligible individuals were all men and women aged 40-69 years without known diabetes, registered with a general practice in Denmark (n = 1,912,392). Between 2001 and 2006, 153,107 individuals registered with 181 practices participating in the Anglo-Danish-Dutch Study of Intensive Treatment in People with Screen-Detected Diabetes in Primary Care (ADDITION)-Denmark study were sent a diabetes-risk-score questionnaire. Individuals at moderate-to-high risk were invited to visit their family doctor for assessment of diabetes status and cardiovascular risk (screening group). The 1,759,285 individuals registered with all other practices in Denmark constituted the retrospectively constructed no-screening (control) group. In this post hoc analysis, we identified individuals from the screening and no-screening groups who were diagnosed with diabetes between 2001 and 2009 (n = 139,075), and compared risk of CVD and mortality in these groups between 2001 and 2012.
Results: In the screening group, 27,177/153,107 (18%) individuals attended for screening, of whom 1533 were diagnosed with diabetes. Between 2001 and 2009, 13,992 people were newly diagnosed with diabetes in the screening group (including those diagnosed by screening) and 125,083 in the no-screening group. Between 2001 and 2012, the risks of CVD and mortality were lower among individuals with diabetes in the screening group compared with individuals with diabetes in the no-screening (control) group (CVD HR 0.84, 95% CI 0.80, 0.89; mortality HR 0.79, 95% CI 0.74, 0.84).
Conclusions/interpretation: A single round of diabetes screening and cardiovascular risk assessment in middle-aged Danish adults in general practice was associated with a significant reduction in risk of all-cause mortality and CVD events in those diagnosed with diabetes.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; General practice; Mortality; Population; Screening; Trial; Type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Data availability
The data used in this paper are a combination of data obtained from the ADDITION study and data from the national Danish Registers at Statistics Denmark (DST). The ADDITION study data were obtained after a written application to the data owner, A. Sandbæk (Institute of Public Health, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark; annelli.sandbaek@ph.au.dk). Data from DST were made available following an application to DST (www.dst.dk/en/TilSalg/Forskningsservice). Data from ADDITION and DST were merged by DST and analyses were performed via a secure virtual private network (VPN) connection. In accordance with the Danish Act on Processing of Personal Data, future interested researchers must perform the steps mentioned above to obtain access to the data.
Duality of interest
RKS is supported by the Danish Diabetes Academy under a Visiting Professorship. The Danish Diabetes Academy is funded by the Novo Nordisk Foundation. RKS is further supported by the Aarhus Institute of Advanced Studies. SJG’s research programme is supported by MRC Epidemiology Unit core funding (MC_UU_12015/4). SJG is an NIHR Senior Investigator and a member of the NIHR School for Primary Care Research. SJG receives an honorarium and reimbursement of travel expenses from Eli Lilly associated with membership of an independent data monitoring committee for a randomised trial of a medication to lower glucose. SJG received an honorarium from Janssen for speaking at an educational meeting in 2015. TL holds shares in Novo Nordisk A/S. TL reports receiving a fee for attending an international board meeting for Astra Zeneca on early detection and treatment of diabetes in 2015. AS reports receiving lecture fees for providing continuing medical education to general practitioners.
Contribution statement
RKS and AS had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. RKS conducted and is responsible for the data analysis.
RKS and AS act as guarantors for this paper. AS and TL designed the ADDITION-Denmark study, and are principal investigators for the trial. SJG conceived the study question for this paper. SJG, TL, AS and RKS developed the study proposal. AS and RKS participated in the acquisition of the data from Statistics Denmark. RKS analysed the data and drafted the report. RKS, SJG, TL and AS participated in the interpretation of the data, the critical revision of the report for important intellectual content and gave final approval for this version to be published. RKS, TL and AS provided administrative, technical and material support for the study.
Figures
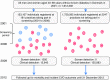
Fig. 1
Visual representation of sampling frame. The ‘S’ in a blue circle denotes individuals detected by the ADDITION stepwise screening programme. The ‘C’ in a red circle denotes individuals with clinically diagnosed diabetes
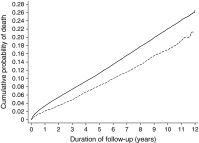
Fig. 2
Cumulative incidence of all-cause mortality in individuals with diabetes in the screening and no-screening groups (2001 to 2012). The model is unadjusted. Solid line, no-screening (control) group; dashed line, screening group
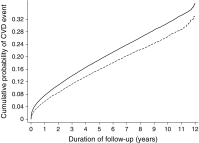
Fig. 3
Cumulative incidence of a composite CVD event among individuals with diabetes in the screening and no-screening groups (2001 to 2012). The model is unadjusted. Solid line, no-screening (control) group; dashed line, screening group
Comment in
- Does the evidence support population-wide screening for type 2 diabetes? No.
Shaw JE. Shaw JE. Diabetologia. 2017 Nov;60(11):2153-2156. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4393-1. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Diabetologia. 2017. PMID: 28831520 - Should we screen for type 2 diabetes among asymptomatic individuals? Yes.
Simmons D, Zgibor JC. Simmons D, et al. Diabetologia. 2017 Nov;60(11):2148-2152. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4397-x. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Diabetologia. 2017. PMID: 28831523
Similar articles
- Effect of population screening for type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors on mortality rate and cardiovascular events: a controlled trial among 1,912,392 Danish adults.
Simmons RK, Griffin SJ, Witte DR, Borch-Johnsen K, Lauritzen T, Sandbæk A. Simmons RK, et al. Diabetologia. 2017 Nov;60(11):2183-2191. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4323-2. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Diabetologia. 2017. PMID: 28831535 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Effect of screening for type 2 diabetes on healthcare costs: a register-based study among 139,075 individuals diagnosed with diabetes in Denmark between 2001 and 2009.
Sortsø C, Komkova A, Sandbæk A, Griffin SJ, Emneus M, Lauritzen T, Simmons RK. Sortsø C, et al. Diabetologia. 2018 Jun;61(6):1306-1314. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4594-2. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 29549417 Clinical Trial. - Screening for Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Evidence Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].
Jonas DE, Crotty K, Yun JDY, Middleton JC, Feltner C, Taylor-Phillips S, Barclay C, Dotson A, Baker C, Balio CP, Voisin CE, Harris RP. Jonas DE, et al. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2021 Aug. Report No.: 21-05276-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2021 Aug. Report No.: 21-05276-EF-1. PMID: 34554661 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Use of cardiovascular imaging in risk restratification of the diabetic patient.
Bellinge JW, Lee SC, Schultz CJ. Bellinge JW, et al. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2021 Apr 1;28(2):122-133. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000611. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2021. PMID: 33394721 Review.
Cited by
- Assessing Elevated Blood Glucose Levels Through Blood Glucose Evaluation and Monitoring Using Machine Learning and Wearable Photoplethysmography Sensors: Algorithm Development and Validation.
Shi B, Dhaliwal SS, Soo M, Chan C, Wong J, Lam NWC, Zhou E, Paitimusa V, Loke KY, Chin J, Chua MT, Liaw KCS, Lim AWH, Insyirah FF, Yen SC, Tay A, Ang SB. Shi B, et al. JMIR AI. 2023 Oct 27;2:e48340. doi: 10.2196/48340. JMIR AI. 2023. PMID: 38875549 Free PMC article. - Feasibility of a Type 2 Diabetes Prevention Program at Nationwide Level in General Practice: A Pilot Study in Italy.
La Grotta R, Pellegrini V, Prattichizzo F, Amata O, Panella L, Frizziero A, Visconti M, Averame G, Brasesco PC, Calabrese I, Vaccaro O, Ceriello A. La Grotta R, et al. J Clin Med. 2024 Feb 16;13(4):1127. doi: 10.3390/jcm13041127. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38398440 Free PMC article. - A follow-up cohort study on the risk of prediabetes, comparing women with previous preeclamptic or normotensive pregnancies.
Möller LB, Bladh MK, Brismar K, Palm K, Andolf EG. Möller LB, et al. Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 30;13(1):16427. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43014-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37777568 Free PMC article. - Life expectancy associated with different ages at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes in high-income countries: 23 million person-years of observation.
Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023 Oct;11(10):731-742. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(23)00223-1. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37708900 Free PMC article. - Improving Diabetes Screening in the Primary Care Clinic.
Tseng E, Hsu YJ, Nigrin C, Clark JM, Marsteller JA, Maruthur NM. Tseng E, et al. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2023 Dec;49(12):698-705. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjq.2023.07.009. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2023. PMID: 37704484
References
- Herman WH, Ye W, Griffin SJ, et al. Early detection and treatment of type 2 diabetes reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality: a simulation of the results of the Anglo-Danish-Dutch study of intensive treatment in people with screen-detected diabetes in primary care (ADDITION-Europe) Diabetes Care. 2015;38:1449–1455. doi: 10.2337/dc14-2459. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical