Do research papers provide enough information on design and material used in ankle foot orthoses for children with cerebral palsy? A systematic review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Do research papers provide enough information on design and material used in ankle foot orthoses for children with cerebral palsy? A systematic review
N Eddison et al. J Child Orthop. 2017.
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this article is to determine how many of the current peer-reviewed studies of ankle foot or-thoses (AFOs) on children with cerebral palsy (CP) have included adequate details of the design and material of the AFO, to enable the study to be reproduced and outcomes clearly understood.
Methods: A thorough search of studies published in English was conducted in March 2015, with no restriction on dates, within all major databases using relevant phrases. These searches were then supplemented by tracking all key references from the appropriate articles identified.
Study selection: The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) population - children with CP; (2) intervention - AFOs; and (3) outcome measure. One reviewer extracted data regarding the characteristics of the included studies, with the extracted data checked for accuracy and completeness by a second reviewer. None of the studies reviewed gave adequate details of the AFOs. Only 3.6% (n = 2) of papers tested the stiffness. Many studies (54.5%) did not describe the material used nor the material thickness (72.7 %). None of them gave any clinical justification for the chosen design of AFO.
Conclusions: There is a clear paucity of detail regarding the design and material used in AFOs on studies involving children with CP. Such a lack of detail has the potential to affect the validity of the reported outcomes, the ability to reproduce the studies and may misinform clinical practice.
Keywords: AFO, orthoses; cerebral palsy; clinical outcomes; materials testing; orthotic devices.
Figures
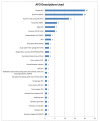
Fig. 1
The type of ankle foot orthoses (AFO) design reported in each study.
Similar articles
- The effect of tuning ankle foot orthoses-footwear combination on the gait parameters of children with cerebral palsy.
Eddison N, Chockalingam N. Eddison N, et al. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2013 Apr;37(2):95-107. doi: 10.1177/0309364612450706. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2013. PMID: 22833518 Review. - Efficacy of ankle foot orthoses types on walking in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review.
Aboutorabi A, Arazpour M, Ahmadi Bani M, Saeedi H, Head JS. Aboutorabi A, et al. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2017 Nov;60(6):393-402. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2017. PMID: 28713039 Review. - Ankle-foot orthosis adherence in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy: A scoping review.
Faux-Nightingale A, Kelemen M, Stewart C. Faux-Nightingale A, et al. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2022 Aug 1;46(4):351-356. doi: 10.1097/PXR.0000000000000095. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2022. PMID: 35315831 Review. - The Efficacy of Ankle-Foot Orthoses on Improving the Gait of Children With Diplegic Cerebral Palsy: A Multiple Outcome Analysis.
Ries AJ, Novacheck TF, Schwartz MH. Ries AJ, et al. PM R. 2015 Sep;7(9):922-929. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Mar 11. PM R. 2015. PMID: 25771349 - Efficacy of ankle-foot orthoses on gait of children with cerebral palsy: systematic review of literature.
Figueiredo EM, Ferreira GB, Maia Moreira RC, Kirkwood RN, Fetters L. Figueiredo EM, et al. Pediatr Phys Ther. 2008 Fall;20(3):207-23. doi: 10.1097/PEP.0b013e318181fb34. Pediatr Phys Ther. 2008. PMID: 18703958 Review.
Cited by
- Effects of Ankle Foot Orthoses on the Gait Patterns in Children with Spastic Bilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Scoping Review.
Ricardo D, Raposo MR, Cruz EB, Oliveira R, Carnide F, Veloso AP, João F. Ricardo D, et al. Children (Basel). 2021 Oct 10;8(10):903. doi: 10.3390/children8100903. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34682168 Free PMC article. Review. - Defining and grouping children's therapeutic footwear and criteria for their prescription: an international expert Delphi consensus study.
Hill M, Healy A, Chockalingam N. Hill M, et al. BMJ Open. 2021 Aug 9;11(8):e051381. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-051381. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34373314 Free PMC article.
References
- Armand S, Watelain E, Mercier M, Lensel G, Lepoutre FX. Identification and classification of toe-walkers based on ankle kinematics, using a data-mining method. Gait Posture 2006;23:240-248. - PubMed
- No authors listed. Prevalence and characteristics of children with cerebral palsy in Europe. Dev Med Child Neurol 2002;44:633-640. - PubMed
- Gage JR, Novacheck TF. An update on the treatment of gait problems in cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop B 2001;10:265-274. - PubMed
- No authors listed. International Organization for Standardization. ISO 8549-1:1989 prosthetics and orthotics – vocabulary. General terms for external limb prostheses and external orthoses. https://www.iso.org/standard/15800.html (date last accessed 15 May 2017).
- British Standard. BS7313. Prosthetics and orthotics. Terminology. Glossary of general terms relating to external limb prostheses and external orthoses. London: British Standards Institute; 1990.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous