Laparoscopic Nissen (total) versus anterior 180° fundoplication for gastro-esophageal reflux disease: A meta-analysis and systematic review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Meta-Analysis
Laparoscopic Nissen (total) versus anterior 180° fundoplication for gastro-esophageal reflux disease: A meta-analysis and systematic review
Xing Du et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Sep.
Abstract
Background: Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication (LNF) has been the gold standard for the surgical management of Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD). Laparoscopic anterior 180° fundoplication (180° LAF) is reported to reduce the incidence of postoperative complications while obtaining similar control of reflux. The present meta-analysis was conducted to confirm the value of the 2 techniques.
Methods: PubMed, Medline, Embase, Cochrane Library, Springerlink, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure Platform databases were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing LNF and 180° LAF. Data regarding the benefits and adverse results of 2 techniques were extracted and compared using a meta-analysis.
Results: Six eligible RCTs comparing LNF (n = 266) and 180° LAF (n = 265) were identified. There were no significant differences between LNF and 180° LAF with regard to operating time, perioperative complications, length of hospital stay, patient satisfaction, willingness to undergo surgery again, quality of life, postoperative heartburn, proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use, postoperative DeMeester scores, postoperative lower esophageal sphincter (LES) pressure, postoperative gas-bloating, unable to belch, diarrhea, or overall reoperation. LNF was associated with a higher prevalence of postoperative dysphagia compared with 180° LAF, while 180° LAF was followed by more reoperation for recurrent reflux symptoms.
Conclusion: LNF and 180° LAF are equally effective in controlling reflux symptoms and obtain a comparable prevalence of patient satisfaction. 180° LAF can reduce the incidence of postoperative dysphagia while this is offset by a higher risk of reoperation for recurrent symptoms. The risk of recurrent symptoms should need to be balanced against the risk of dysphagia when surgeons choose surgical procedures for each individual with GERD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
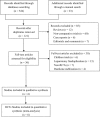
Figure 1
A flowchart showing the process and result of trials screening. RCTs = randomized controlled trials.
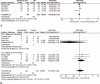
Figure 2
Meta-analysis of patient satisfaction (A) and postoperative heartburn (B) after LNF and180° LAF. LAF = laparoscopic anterior 180° fundoplication, LNF = laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication.
Figure 3
Meta-analysis of postoperative DeMeester scores (A), LES pressure (B), and esophagitis (C) after LNF and 180° LAF. LAF = laparoscopic anterior 180° fundoplication, LES = lower esophageal sphincter, LNF = laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication.
Figure 4
Meta-analysis of prevalence of postoperative dysphagia after LNF and 180° LAF. LAF = laparoscopic anterior 180° fundoplication, LNF = laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication.
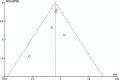
Figure 5
Funnel plot regarding postoperative dysphagia.
Similar articles
- Laparoscopic Nissen Versus Toupet Fundoplication for Short- and Long-Term Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.
Li G, Jiang N, Chendaer N, Hao Y, Zhang W, Peng C. Li G, et al. Surg Innov. 2023 Dec;30(6):745-757. doi: 10.1177/15533506231165829. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Surg Innov. 2023. PMID: 36998190 Free PMC article. - Laparoscopic anterior versus posterior fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.
Broeders JA, Roks DJ, Ahmed Ali U, Draaisma WA, Smout AJ, Hazebroek EJ. Broeders JA, et al. Ann Surg. 2011 Jul;254(1):39-47. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31821d4ba0. Ann Surg. 2011. PMID: 21543968 - Systematic review and meta-analysis of laparoscopic Nissen (posterior total) versus Toupet (posterior partial) fundoplication for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease.
Broeders JA, Mauritz FA, Ahmed Ali U, Draaisma WA, Ruurda JP, Gooszen HG, Smout AJ, Broeders IA, Hazebroek EJ. Broeders JA, et al. Br J Surg. 2010 Sep;97(9):1318-30. doi: 10.1002/bjs.7174. Br J Surg. 2010. PMID: 20641062 - LINX® magnetic esophageal sphincter augmentation versus Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Skubleny D, Switzer NJ, Dang J, Gill RS, Shi X, de Gara C, Birch DW, Wong C, Hutter MM, Karmali S. Skubleny D, et al. Surg Endosc. 2017 Aug;31(8):3078-3084. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-5370-3. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Surg Endosc. 2017. PMID: 27981382
Cited by
- Single incision laparoscopic fundoplication: A systematic review of the literature.
Perivoliotis K, Sarakatsianou C, Tepetes K, Baloyiannis I. Perivoliotis K, et al. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2019 Mar 27;11(3):179-190. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v11.i3.179. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2019. PMID: 31057702 Free PMC article. - The learning curve for transoral incisionless fundoplication.
Dbouk M, Brewer Gutierrez OI, Kannadath BS, Camilion JV, Ngamruengphong S, Kumbhari V, Khashab M, Murray M, Janu P, Ihde G, Chang K, Thosani N, Canto MI. Dbouk M, et al. Endosc Int Open. 2021 Nov 12;9(11):E1785-E1791. doi: 10.1055/a-1547-6599. eCollection 2021 Nov. Endosc Int Open. 2021. PMID: 34790546 Free PMC article. - Fundoplication significantly improves objective and subjective reflux outcomes-a meta-analysis.
Tadé Y, Newman D, Walters RW, Nandipati KC. Tadé Y, et al. Surg Endosc. 2025 May 29. doi: 10.1007/s00464-025-11856-5. Online ahead of print. Surg Endosc. 2025. PMID: 40442360 - 'Critical circle of fundoplication' - A key concept towards creating identical, replicable and consistent fundoplication wraps.
Jani K. Jani K. J Minim Access Surg. 2023 Jul-Sep;19(3):355-360. doi: 10.4103/jmas.jmas_173_22. J Minim Access Surg. 2023. PMID: 36695240 Free PMC article. - Current Status of Anti-Reflux Surgery as a Treatment for GERD.
Lee J, Lee I, Oh Y, Kim JW, Kwon Y, Alromi A, Eledreesi M, Khalid A, Aljarbou W, Park S. Lee J, et al. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Mar 21;60(3):518. doi: 10.3390/medicina60030518. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38541244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Herregods TV, Bredenoord AJ, Smout AJ. Pathophysiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease: new understanding in a new era. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2015;27:1202–13. - PubMed
- Hummel K, Richards W. Endoscopic treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Clin North Am 2015;95:653–67. - PubMed
- Dallemagne B, Weerts JM, Jehaes C, et al. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: preliminary report. Surg Laparosc Endosc 1991;1:138–43. - PubMed
- Yates RB, Oelschlager BK. Surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Clin North Am 2015;95:527–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical