Measuring progress and projecting attainment on the basis of past trends of the health-related Sustainable Development Goals in 188 countries: an analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Measuring progress and projecting attainment on the basis of past trends of the health-related Sustainable Development Goals in 188 countries: an analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016
GBD 2016 SDG Collaborators. Lancet. 2017.
Erratum in
- Department of Error.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] Lancet. 2017 Sep 30;390(10102):e23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32441-8. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 28935159 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Department of Error.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] Lancet. 2017 Oct 28;390(10106):e38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32650-8. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 29032990 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are grounded in the global ambition of "leaving no one behind". Understanding today's gains and gaps for the health-related SDGs is essential for decision makers as they aim to improve the health of populations. As part of the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2016 (GBD 2016), we measured 37 of the 50 health-related SDG indicators over the period 1990-2016 for 188 countries, and then on the basis of these past trends, we projected indicators to 2030.
Methods: We used standardised GBD 2016 methods to measure 37 health-related indicators from 1990 to 2016, an increase of four indicators since GBD 2015. We substantially revised the universal health coverage (UHC) measure, which focuses on coverage of essential health services, to also represent personal health-care access and quality for several non-communicable diseases. We transformed each indicator on a scale of 0-100, with 0 as the 2·5th percentile estimated between 1990 and 2030, and 100 as the 97·5th percentile during that time. An index representing all 37 health-related SDG indicators was constructed by taking the geometric mean of scaled indicators by target. On the basis of past trends, we produced projections of indicator values, using a weighted average of the indicator and country-specific annualised rates of change from 1990 to 2016 with weights for each annual rate of change based on out-of-sample validity. 24 of the currently measured health-related SDG indicators have defined SDG targets, against which we assessed attainment.
Findings: Globally, the median health-related SDG index was 56·7 (IQR 31·9-66·8) in 2016 and country-level performance markedly varied, with Singapore (86·8, 95% uncertainty interval 84·6-88·9), Iceland (86·0, 84·1-87·6), and Sweden (85·6, 81·8-87·8) having the highest levels in 2016 and Afghanistan (10·9, 9·6-11·9), the Central African Republic (11·0, 8·8-13·8), and Somalia (11·3, 9·5-13·1) recording the lowest. Between 2000 and 2016, notable improvements in the UHC index were achieved by several countries, including Cambodia, Rwanda, Equatorial Guinea, Laos, Turkey, and China; however, a number of countries, such as Lesotho and the Central African Republic, but also high-income countries, such as the USA, showed minimal gains. Based on projections of past trends, the median number of SDG targets attained in 2030 was five (IQR 2-8) of the 24 defined targets currently measured. Globally, projected target attainment considerably varied by SDG indicator, ranging from more than 60% of countries projected to reach targets for under-5 mortality, neonatal mortality, maternal mortality ratio, and malaria, to less than 5% of countries projected to achieve targets linked to 11 indicator targets, including those for childhood overweight, tuberculosis, and road injury mortality. For several of the health-related SDGs, meeting defined targets hinges upon substantially faster progress than what most countries have achieved in the past.
Interpretation: GBD 2016 provides an updated and expanded evidence base on where the world currently stands in terms of the health-related SDGs. Our improved measure of UHC offers a basis to monitor the expansion of health services necessary to meet the SDGs. Based on past rates of progress, many places are facing challenges in meeting defined health-related SDG targets, particularly among countries that are the worst off. In view of the early stages of SDG implementation, however, opportunity remains to take actions to accelerate progress, as shown by the catalytic effects of adopting the Millennium Development Goals after 2000. With the SDGs' broader, bolder development agenda, multisectoral commitments and investments are vital to make the health-related SDGs within reach of all populations.
Funding: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article published under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
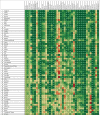
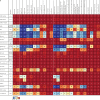
Figure 1
Performance on the health-related SDG index, MDG index, and non-MDG index, and 37 individual health-related indicators, by country, 2016 Countries are ranked by their health-related SDG index from highest to lowest in 2016. Indices and individual indicators are reported on a scale of 0 to 100, with 0 representing the worst levels from 1990 to 2030 and 100 reflecting the best during that time. Definitions of health-related SDG indicators are shown in the table. SDG=Sustainable Development Goal. MDG=Millennium Development Goal. Disaster mort=mortality due to exposure to forces of nature. MMR=maternal mortality ratio. SBA=skilled birth attendance. NN mort=neonatal mortality. Mort=mortality. Incid=incidence. NTD prev=prevalence of 15 neglected tropical diseases. NCD mort=mortality due to a subset of non-communicable diseases (cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases). FP need met, mod=family planning need met with modern contraception methods. Adol birth rate=adolescent birth rate. UHC index=universal health coverage index. Air poll mort=mortality attributable to household air pollution and ambient air pollution. WaSH mort=mortality attributable to unsafe water, sanitation, and hygiene. Poisoning mort=mortality due to unintentional poisonings. Smoking prev=prevalence of daily smoking. Vaccine cov=vaccine coverage of target populations based on national vaccine schedules. Int partner viol=prevalence of intimate partner violence. HH air poll=prevalence of household air pollution. Occ burden=disease burden attributable to occupational risks. Mean PM2.5=fine particulate matter smaller than 2·5 μm. Homicide=mortality due to interpersonal violence. Conflict mort=mortality due to conflict and terrorism. Violence prev=prevalence of physical or sexual violence. Child sex abuse=prevalence of childhood sexual abuse. Cert death reg=well-certified death registration.
Figure 1
Performance on the health-related SDG index, MDG index, and non-MDG index, and 37 individual health-related indicators, by country, 2016 Countries are ranked by their health-related SDG index from highest to lowest in 2016. Indices and individual indicators are reported on a scale of 0 to 100, with 0 representing the worst levels from 1990 to 2030 and 100 reflecting the best during that time. Definitions of health-related SDG indicators are shown in the table. SDG=Sustainable Development Goal. MDG=Millennium Development Goal. Disaster mort=mortality due to exposure to forces of nature. MMR=maternal mortality ratio. SBA=skilled birth attendance. NN mort=neonatal mortality. Mort=mortality. Incid=incidence. NTD prev=prevalence of 15 neglected tropical diseases. NCD mort=mortality due to a subset of non-communicable diseases (cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases). FP need met, mod=family planning need met with modern contraception methods. Adol birth rate=adolescent birth rate. UHC index=universal health coverage index. Air poll mort=mortality attributable to household air pollution and ambient air pollution. WaSH mort=mortality attributable to unsafe water, sanitation, and hygiene. Poisoning mort=mortality due to unintentional poisonings. Smoking prev=prevalence of daily smoking. Vaccine cov=vaccine coverage of target populations based on national vaccine schedules. Int partner viol=prevalence of intimate partner violence. HH air poll=prevalence of household air pollution. Occ burden=disease burden attributable to occupational risks. Mean PM2.5=fine particulate matter smaller than 2·5 μm. Homicide=mortality due to interpersonal violence. Conflict mort=mortality due to conflict and terrorism. Violence prev=prevalence of physical or sexual violence. Child sex abuse=prevalence of childhood sexual abuse. Cert death reg=well-certified death registration.
Figure 1
Performance on the health-related SDG index, MDG index, and non-MDG index, and 37 individual health-related indicators, by country, 2016 Countries are ranked by their health-related SDG index from highest to lowest in 2016. Indices and individual indicators are reported on a scale of 0 to 100, with 0 representing the worst levels from 1990 to 2030 and 100 reflecting the best during that time. Definitions of health-related SDG indicators are shown in the table. SDG=Sustainable Development Goal. MDG=Millennium Development Goal. Disaster mort=mortality due to exposure to forces of nature. MMR=maternal mortality ratio. SBA=skilled birth attendance. NN mort=neonatal mortality. Mort=mortality. Incid=incidence. NTD prev=prevalence of 15 neglected tropical diseases. NCD mort=mortality due to a subset of non-communicable diseases (cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases). FP need met, mod=family planning need met with modern contraception methods. Adol birth rate=adolescent birth rate. UHC index=universal health coverage index. Air poll mort=mortality attributable to household air pollution and ambient air pollution. WaSH mort=mortality attributable to unsafe water, sanitation, and hygiene. Poisoning mort=mortality due to unintentional poisonings. Smoking prev=prevalence of daily smoking. Vaccine cov=vaccine coverage of target populations based on national vaccine schedules. Int partner viol=prevalence of intimate partner violence. HH air poll=prevalence of household air pollution. Occ burden=disease burden attributable to occupational risks. Mean PM2.5=fine particulate matter smaller than 2·5 μm. Homicide=mortality due to interpersonal violence. Conflict mort=mortality due to conflict and terrorism. Violence prev=prevalence of physical or sexual violence. Child sex abuse=prevalence of childhood sexual abuse. Cert death reg=well-certified death registration.
Figure 1
Performance on the health-related SDG index, MDG index, and non-MDG index, and 37 individual health-related indicators, by country, 2016 Countries are ranked by their health-related SDG index from highest to lowest in 2016. Indices and individual indicators are reported on a scale of 0 to 100, with 0 representing the worst levels from 1990 to 2030 and 100 reflecting the best during that time. Definitions of health-related SDG indicators are shown in the table. SDG=Sustainable Development Goal. MDG=Millennium Development Goal. Disaster mort=mortality due to exposure to forces of nature. MMR=maternal mortality ratio. SBA=skilled birth attendance. NN mort=neonatal mortality. Mort=mortality. Incid=incidence. NTD prev=prevalence of 15 neglected tropical diseases. NCD mort=mortality due to a subset of non-communicable diseases (cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases). FP need met, mod=family planning need met with modern contraception methods. Adol birth rate=adolescent birth rate. UHC index=universal health coverage index. Air poll mort=mortality attributable to household air pollution and ambient air pollution. WaSH mort=mortality attributable to unsafe water, sanitation, and hygiene. Poisoning mort=mortality due to unintentional poisonings. Smoking prev=prevalence of daily smoking. Vaccine cov=vaccine coverage of target populations based on national vaccine schedules. Int partner viol=prevalence of intimate partner violence. HH air poll=prevalence of household air pollution. Occ burden=disease burden attributable to occupational risks. Mean PM2.5=fine particulate matter smaller than 2·5 μm. Homicide=mortality due to interpersonal violence. Conflict mort=mortality due to conflict and terrorism. Violence prev=prevalence of physical or sexual violence. Child sex abuse=prevalence of childhood sexual abuse. Cert death reg=well-certified death registration.
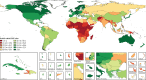
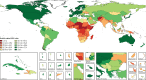
Figure 2
Map of the health-related SDG index, by decile, in 2016 Deciles ranged from less than 22·4 (first decile) to at least 75·1 (tenth decile) in 2016. SDG=Sustainable Development Goal. ATG=Antigua and Barbuda. VCT=Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. LCA=Saint Lucia. TTO=Trinidad and Tobago. Isl=Islands. FSM=Federated States of Micronesia. TLS=Timor-Leste.
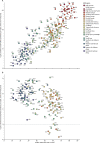
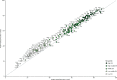
Figure 3
Comparing the health-related SDG index in 2016 to cumulative total health expenditure per capita (A) and cumulative development assistance for health per capita (B), from 2010–14, by GBD region The health-related SDG index is reported on a scale of 0–100, with 0 representing the worst levels from 1990 to 2030 and 100 reflecting the best during that time. Total health expenditure includes development assistance for health and government, out-of-pocket, and pre-paid private health spending. Of the 188 countries in this analysis, 184 had estimates of total health expenditure per capita; North Korea, Palestine, Taiwan (Province of China), and Zimbabwe were excluded due to missing data on national health expenditure. 130 countries were recipients of development assistance for health from 2010 to 2014. Countries are abbreviated according to the ISO3 code. GBD=Global Burden of Disease. SDG=Sustainable Development Goal.
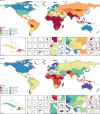
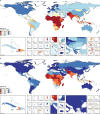
Figure 4
Map of the UHC index, by decile, in 2000 (A) and 2016 (B) Deciles were based on the distribution of UHC index values in 2016 and then were applied for 2000. Deciles ranged from less than 43·2 (first decile) to at least 79·8 (tenth decile) in 2016. UHC=universal health coverage. ATG=Antigua and Barbuda. VCT=Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. LCA=Saint Lucia. TTO=Trinidad and Tobago. Isl=Islands. FSM=Federated States of Micronesia. TLS=Timor-Leste.
Figure 5
Comparing the health-related SDG index in 2016 and, based on past trends, the projected health-related SDG index in 2030, by country The health-related SDG index is reported on a scale of 0–100, with 0 representing the worst levels from 1990 to 2030 and 100 reflecting the best during that time. The dashed line shows the equivalence line, such that values that fall on this line are equivalent for both the health-related SDG index in 2016 and, based on past trends, the projected health-related SDG index in 2030. Countries are abbreviated according to the ISO3 code. SDI=Socio-demographic Index. SDG=Sustainable Development Goal.
Figure 6
Map of the projected health-related SDG index based on past trends, by decile, in 2030 Deciles were based on the distribution of the health-related SDG index values in 2016 and then were applied for the projected SDG index in 2030. Deciles ranged from less than 22·4 (first decile) to at least 75·1 (tenth decile) in 2016. Projections were based on past trends and rates of change observed from 1990 to 2016. SDG=Sustainable Development Goal. ATG=Antigua and Barbuda. VCT=Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. LCA=Saint Lucia. TTO=Trinidad and Tobago. Isl=Islands. FSM=Federated States of Micronesia. TLS=Timor-Leste.
Figure 7
Percentage of countries attaining health-related SDG indicator targets in 2016 and projected to attain in 2030 based on past trends, according to defined SDG targets (A), and defined and conservative SDG targets (B), by indicator, across all countries and by GBD super-region and SDI quintile All projections were based on past trends and rates of change observed from 1990 to 2016. Of the 37 health-related indicators measured in this study, 24 had defined targets linked to each indicator. Definitions of health-related SDG indicators and defined targets associated with them are shown in the table. SDG target 3.6 aims to reduce road injury mortality by 50% between 2015 and 2020, and thus projected attainment for this indicator is based on estimates from 2015 to 2020 rather than 2015 to 2030. For (B), conservative targets were defined as an 80% reduction for elimination targets from 2015 to 2030, and ≥90% by 2030 for universal access or coverage. Under the conservative scenario (B), targets with specific values to meet by 2030 or with specified relative reductions remained as originally defined. SDG=Sustainable Development Goal. SDI=Socio-demographic Index. MMR=maternal mortality ratio. SBA=skilled birth attendance. Under-5 mort=under-5 mortality. NN mort=neonatal mortality. Mort=mortality. Incid=incidence. NTD prev=prevalence of 15 neglected tropical diseases. NCD mort=mortality due to a subset of non-communicable diseases (cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases). FP need met, mod=family planning need met with modern contraception methods. UHC index=universal health coverage index. Vaccine cov=vaccine coverage of target populations based on national vaccine schedules. Int partner viol=prevalence of intimate partner violence. HH air poll=prevalence of household air pollution. Child sex abuse=prevalence of childhood sexual abuse. Cert death reg=well-certified death registration.
Figure 7
Percentage of countries attaining health-related SDG indicator targets in 2016 and projected to attain in 2030 based on past trends, according to defined SDG targets (A), and defined and conservative SDG targets (B), by indicator, across all countries and by GBD super-region and SDI quintile All projections were based on past trends and rates of change observed from 1990 to 2016. Of the 37 health-related indicators measured in this study, 24 had defined targets linked to each indicator. Definitions of health-related SDG indicators and defined targets associated with them are shown in the table. SDG target 3.6 aims to reduce road injury mortality by 50% between 2015 and 2020, and thus projected attainment for this indicator is based on estimates from 2015 to 2020 rather than 2015 to 2030. For (B), conservative targets were defined as an 80% reduction for elimination targets from 2015 to 2030, and ≥90% by 2030 for universal access or coverage. Under the conservative scenario (B), targets with specific values to meet by 2030 or with specified relative reductions remained as originally defined. SDG=Sustainable Development Goal. SDI=Socio-demographic Index. MMR=maternal mortality ratio. SBA=skilled birth attendance. Under-5 mort=under-5 mortality. NN mort=neonatal mortality. Mort=mortality. Incid=incidence. NTD prev=prevalence of 15 neglected tropical diseases. NCD mort=mortality due to a subset of non-communicable diseases (cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases). FP need met, mod=family planning need met with modern contraception methods. UHC index=universal health coverage index. Vaccine cov=vaccine coverage of target populations based on national vaccine schedules. Int partner viol=prevalence of intimate partner violence. HH air poll=prevalence of household air pollution. Child sex abuse=prevalence of childhood sexual abuse. Cert death reg=well-certified death registration.
Figure 8
Map of the number of health-related SDG indicator targets, based on past trends, projected to be attained in 2030 according to defined SDG targets (A), and conservative and defined SDG targets (B) All projections were based on past trends and rates of change observed from 1990 to 2016. Of the 37 health-related indicators measured in this study, 24 had defined targets linked to each indicator. Definitions of health-related SDG indicators and defined targets associated with them are shown in the table. SDG target 3.6 aims to reduce road injury mortality by 50% between 2015 and 2020, and thus projected attainment for this indicator is based on estimates from 2015 to 2020 rather than 2015 to 2030. For (B), conservative targets were defined as an 80% reduction for elimination targets from 2015 to 2030, and ≥90% by 2030 for universal access or coverage. For the conservative scenario (B), targets with specific values to meet by 2030 or with specified relative reductions remained as originally defined. SDG=Sustainable Development Goal. ATG=Antigua and Barbuda. VCT=Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. LCA=Saint Lucia. TTO=Trinidad and Tobago. Isl=Islands. FSM=Federated States of Micronesia. TLS=Timor-Leste.
Figure 9
Median and IQR of the absolute difference between projected rates of change from 2016 to 2030 based on past trends and required rate of change needed meet defined SDG targets, by indicator, across all countries (A), high SDI quintile (B), high-middle SDI quintile (C), middle SDI quintile (D), low-middle SDI quintile (E), and low SDI quintile (F) Black stripes represent median absolute change and boxes represent IQR. Health-related indicators are colour-coded according to the health-related goals they represent. All projections were based on past trends and rates of change observed from 1990 to 2016. Of the 37 health-related indicators measured in this study, 24 had defined targets linked to each indicator. Here we present on 23 of these indicators as SDG indicator 17.19.2c, well-certified death registration, had 27 countries with 0% in 2016 and were projected to be the same in 2030. Annualised rates of change observed and required for this indicator were calculated as infinite (and thus implausible). SDG target 3·6 aims to reduce road injury mortality by 50% between 2015 and 2020, and thus annualised rates of change calculated for this indicator are based on estimates from 2015 to 2020 rather than 2015 to 2030. Definitions of health-related SDG indicators and targets associated with them are shown in the table. SDI=Socio-demographic Index. SDG=Sustainable Development Goal. MMR=maternal mortality ratio. SBA=skilled birth attendance. Mort=mortality. Incid=incidence. NN mort=Neonatal mortality. NTD prev=prevalence of 15 neglected tropical diseases. NCD mort=mortality due to a subset of non-communicable diseases (cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases). Suicide mort=mortality due to self-harm. FP need met, mod=family planning need met with modern contraception methods. UHC index=universal health coverage index. Vaccine cov=vaccine coverage of target populations based on national vaccine schedules. Int partner viol=intimate partner violence. HH air poll=household air pollution. Child sex abuse=childhood sexual abuse.
Comment in
- Political determinants of Sustainable Development Goals.
Gianella C, de Assis Machado MR, Gloppen S. Gianella C, et al. Lancet. 2017 Dec 9;390(10112):2545-2546. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33082-9. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 29231829 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Measuring the health-related Sustainable Development Goals in 188 countries: a baseline analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015.
GBD 2015 SDG Collaborators. GBD 2015 SDG Collaborators. Lancet. 2016 Oct 8;388(10053):1813-1850. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31467-2. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Lancet. 2016. PMID: 27665228 Free PMC article. - Measuring universal health coverage based on an index of effective coverage of health services in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.
GBD 2019 Universal Health Coverage Collaborators. GBD 2019 Universal Health Coverage Collaborators. Lancet. 2020 Oct 17;396(10258):1250-1284. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30750-9. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32861314 Free PMC article. - Progressing towards the 2030 health-related SDGs in ASEAN: A systematic analysis.
Si Y, Guo L, Chen S, Zhang X, Dai X, Wang D, Liu Y, Tran BX, Pronyk PM, Tang S. Si Y, et al. PLoS Med. 2025 Apr 21;22(4):e1004551. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004551. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Med. 2025. PMID: 40258012 Free PMC article. - Mapping under-5 and neonatal mortality in Africa, 2000-15: a baseline analysis for the Sustainable Development Goals.
Golding N, Burstein R, Longbottom J, Browne AJ, Fullman N, Osgood-Zimmerman A, Earl L, Bhatt S, Cameron E, Casey DC, Dwyer-Lindgren L, Farag TH, Flaxman AD, Fraser MS, Gething PW, Gibson HS, Graetz N, Krause LK, Kulikoff XR, Lim SS, Mappin B, Morozoff C, Reiner RC Jr, Sligar A, Smith DL, Wang H, Weiss DJ, Murray CJL, Moyes CL, Hay SI. Golding N, et al. Lancet. 2017 Nov 11;390(10108):2171-2182. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31758-0. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 28958464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- District-level monitoring of universal health coverage, India.
Mukherji A, Rao M, Desai S, Subramanian SV, Kang G, Patel V. Mukherji A, et al. Bull World Health Organ. 2024 Sep 1;102(9):630-638B. doi: 10.2471/BLT.23.290854. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Bull World Health Organ. 2024. PMID: 39219770 Free PMC article. - Suicide mortality among older adults in Brazil between 2000 and 2019 - estimates from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.
Pires AM, Reis JGM, Garcia FM, Veloso GA, Melo APS, Naghavi M, Passos VMA. Pires AM, et al. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2022 Jan 28;55(suppl 1):e0322. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0322-2021. eCollection 2022. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2022. PMID: 35107540 Free PMC article. - Solving the problem of access to cardiovascular medicines: revolving fund pharmacy models in rural western Kenya.
Tran DN, Manji I, Njuguna B, Kamano J, Laktabai J, Tonui E, Vedanthan R, Pastakia S. Tran DN, et al. BMJ Glob Health. 2020 Nov;5(11):e003116. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-003116. BMJ Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 33214173 Free PMC article. - Estimates of life expectancy and premature mortality among multidimensional poor and non-poor in India.
Das J, Mohanty SK. Das J, et al. BMC Public Health. 2024 Dec 20;24(1):3546. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20966-z. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39702024 Free PMC article. - Changes and heterogeneity in quality-amenable excess mortality in Mexico: a systematic analysis for the years 2012, 2018, and 2021.
Vargas SC, Rios-Zertuche D, Bauhoff S. Vargas SC, et al. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2025 Mar 29;45:101061. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2025.101061. eCollection 2025 May. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2025. PMID: 40230879 Free PMC article.
References
- UN . Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. United Nations; New York, NY, USA: 2015.
- High-Level Political Forum (HLPF) 2017 HLPF Thematic Review of SDG3: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. 2017. https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/14367SDG3format-... (accessed June 15, 2017).
- UN . The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2017. United Nations; New York, NY, USA: 2017.
- McIntyre D, McKee M, Balabanova D, Atim C, Reddy KS, Patcharanarumol W. Open letter on the SDGs: a robust measure for universal health coverage is essential. Lancet. 2016;388:2871–2872. - PubMed
- United Nations Statistical Commission . Report of the inter-agency and expert group on Sustainable Development Goal Indicators. UN Statistical Commission; New York, NY, USA: 2017.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH110163/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG047845/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- D43 TW009775/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U147585819/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 201900/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- SPHSU13/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A620_1014/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HD087993/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- SCAF/15/02/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585824/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AI112339/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 201900/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12017/13/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585827/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AI096299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD084233/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M015084/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SPHSU15/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- U54 HG007479/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K013351/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12011/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AI124389/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12017/15/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0400491/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CDF-2011-04-048/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous