Roles of sigma-1 receptors on mitochondrial functions relevant to neurodegenerative diseases - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Roles of sigma-1 receptors on mitochondrial functions relevant to neurodegenerative diseases
Tzu-Yu Weng et al. J Biomed Sci. 2017.
Abstract
The sigma-1 receptor (Sig-1R) is a chaperone that resides mainly at the mitochondrion-associated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane (called the MAMs) and acts as a dynamic pluripotent modulator in living systems. At the MAM, the Sig-1R is known to play a role in regulating the Ca2+ signaling between ER and mitochondria and in maintaining the structural integrity of the MAM. The MAM serves as bridges between ER and mitochondria regulating multiple functions such as Ca2+ transfer, energy exchange, lipid synthesis and transports, and protein folding that are pivotal to cell survival and defense. Recently, emerging evidences indicate that the MAM is critical in maintaining neuronal homeostasis. Thus, given the specific localization of the Sig-1R at the MAM, we highlight and propose that the direct or indirect regulations of the Sig-1R on mitochondrial functions may relate to neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), Huntington's disease (HD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). In addition, the promising use of Sig-1R ligands to rescue mitochondrial dysfunction-induced neurodegeneration is addressed.
Keywords: Mitochondria; Mitochondrion-associated ER membrane (MAM); Neurodegenerative disorders; Sigma-1 receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
Tzu-Yu Weng (tyweng@gate.sinica.edu.tw), postdoc fellow, Academia Sinica, Taiwan. Shang-Yi Anne Tsai (stsai@nih.gov), Scientific Review Officer, NIDA Division of Extramural Research, and Tsung-Ping Su (TSU@intra.nida.nih.gov), Chief, Cellular Pathobiology Section, Integrative Neuroscience Branch, Intramural Research Program, NIDA, NIH, Baltimore, Maryland.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have read the manuscript and agreed to the publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Fig. 1
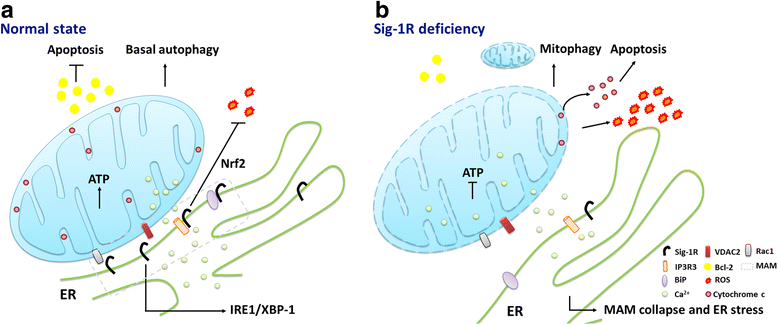
The putative model of Sig-1R at the MAM. a In the normal state, the Sig-1R interacts with BiP. Upon agonist stimulation or the decline of ER Ca2+, the Sig-1R dissociates from BiP to stabilize the IP3R3 for Ca2+ signaling from ER into mitochondria and to regulate the IRE1-dependent pathway to counteract the ER stress. The Sig-1R protects against apoptosis and ROS via the Bcl-2- or Nrf2-dependent pathways. Sig-1Rs can also associate with VDAC2 or Rac1. b The depletion of Sig-1R leads to an abnormal Ca2+ signaling between ER and mitochondria and the disruption of the ATP production. Enhanced ROS production, increased cytochrome c release, or reduced Bcl-2 can cause ER stress that leads to the collapse of the MAM and consequently enhanced autophagy or apoptotic cell death
Similar articles
- The Role of Sigma-1 Receptor, an Intracellular Chaperone in Neurodegenerative Diseases.
Penke B, Fulop L, Szucs M, Frecska E. Penke B, et al. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(1):97-116. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170529104323. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28554311 Free PMC article. Review. - At the Crossing of ER Stress and MAMs: A Key Role of Sigma-1 Receptor?
Delprat B, Crouzier L, Su TP, Maurice T. Delprat B, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1131:699-718. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-12457-1_28. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31646531 Review. - The sigma-1 receptor chaperone as an inter-organelle signaling modulator.
Su TP, Hayashi T, Maurice T, Buch S, Ruoho AE. Su TP, et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2010 Dec;31(12):557-66. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2010.08.007. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20869780 Free PMC article. - Role of Sigma-1 Receptor in Cocaine Abuse and Neurodegenerative Disease.
Cai Y, Yang L, Niu F, Liao K, Buch S. Cai Y, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;964:163-175. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50174-1_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28315271 Review. - Sigma-1 receptor chaperones at the ER-mitochondrion interface regulate Ca(2+) signaling and cell survival.
Hayashi T, Su TP. Hayashi T, et al. Cell. 2007 Nov 2;131(3):596-610. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.036. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17981125
Cited by
- Modulation of the Blood-Brain Barrier by Sigma-1R Activation.
Brailoiu E, Barr JL, Wittorf HN, Inan S, Unterwald EM, Brailoiu GC. Brailoiu E, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 9;25(10):5147. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105147. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791182 Free PMC article. - N, N-Dimethyltryptamine, a natural hallucinogen, ameliorates Alzheimer's disease by restoring neuronal Sigma-1 receptor-mediated endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria crosstalk.
Cheng D, Lei ZG, Chu K, Lam OJH, Chiang CY, Zhang ZJ. Cheng D, et al. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 May 1;16(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01462-3. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38693554 Free PMC article. - Putative Roles and Therapeutic Potential of the Chaperone System in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Multiple Sclerosis.
Noori L, Saqagandomabadi V, Di Felice V, David S, Caruso Bavisotto C, Bucchieri F, Cappello F, Conway de Macario E, Macario AJL, Scalia F. Noori L, et al. Cells. 2024 Jan 24;13(3):217. doi: 10.3390/cells13030217. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38334609 Free PMC article. Review. - Sigma-1 receptor activation mediates the sustained antidepressant effect of ketamine in mice via increasing BDNF levels.
Ma H, Li JF, Qiao X, Zhang Y, Hou XJ, Chang HX, Chen HL, Zhang Y, Li YF. Ma H, et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Apr;45(4):704-713. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01201-8. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38097715 - A Comprehensive Review of the Current Status of the Cellular Neurobiology of Psychedelics.
Banushi B, Polito V. Banushi B, et al. Biology (Basel). 2023 Oct 28;12(11):1380. doi: 10.3390/biology12111380. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37997979 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous