Dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A pooled analysis of safety data from phase IIb/III clinical trials - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2018 Mar;20(3):620-628.
doi: 10.1111/dom.13124. Epub 2017 Oct 26.
Affiliations
- PMID: 28950419
- PMCID: PMC5836959
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.13124
Review
Dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A pooled analysis of safety data from phase IIb/III clinical trials
Serge Jabbour et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Mar.
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the safety and tolerability of dapagliflozin, a highly selective sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: Data were pooled from 13 placebo-controlled trials of up to 24 weeks' duration (dapagliflozin, n = 2360; placebo, n = 2295). Larger placebo-/comparator-controlled pools of 21 (≤208 weeks; dapagliflozin, n = 5936; control, n = 3403) and 30 trials (≥12 weeks; dapagliflozin, n = 9195; control, n = 4629) assessed the rare adverse events (AEs) of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and lower limb amputation, respectively.
Results: Over 24 weeks, the overall incidence of AEs and serious AEs (SAEs) was similar for dapagliflozin and placebo: 60.0% vs 55.7% and 5.1% vs 5.4%, respectively. Rates of hypoglycaemia, volume depletion AEs, urinary tract infections (UTIs) and fractures were balanced between the groups. Genital infections were more frequent with dapagliflozin (5.5%) vs placebo (0.6%) and renal function AEs occurred in 3.2% vs 1.8% of patients (the most common renal AE was decreased creatinine clearance: 1.1% vs 0.7%). In the 21-study pool, 1 SAE of DKA and 3 AEs of ketonuria/metabolic acidosis occurred with dapagliflozin vs none with control; estimated combined incidence for these events was 0.03% (95% confidence interval 0.010-0.089). In the 30-study pool, lower limb amputation occurred in 8 (0.1%) and 7 (0.2%) patients receiving dapagliflozin and control, respectively.
Conclusion: The overall incidence rates of AEs and SAEs were similar in the dapagliflozin and placebo/control groups, including the incidence of hypoglycaemia, volume depletion, fractures, UTIs, amputations and DKA. Genital infections were more frequent with dapagliflozin than placebo.
Keywords: SGLT2 inhibitor; antidiabetic drug; dapagliflozin; type 2 diabetes.
© 2017 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
S. J. is a consultant for AstraZeneca, Janssen and Eli Lilly. J. S. has attended advisory boards and/or speaker's bureaus for Takeda, Bayer, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Berlin‐Chemie, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, Roche, Ipsen, Pfizer, Janssen and LifeScan, and has received project‐specific research support from AstraZeneca, Takeda, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Amgen, GlaxoSmithKline, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Ipsen, Pfizer, Janssen, Servier, Eli Lilly, Apitope, Intarcia and Roche. A.S. has attended advisory boards and/or speaker's bureaus for AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Boehringer Ingelheim and Janssen, and has received research support from Novo Nordisk. C. J. B. received grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Sanofi and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Johnson & Johnson, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novo Nordisk, Elcelyx and Poxel, outside of the submitted work. C. K. and A. M. L. are employees and stockholders of AstraZeneca.
Figures
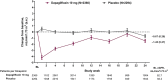
Figure 1
Values for eGFR over time (13‐study pool). eGFR was calculated using the Modification in Diet and Renal Disease (MDRD) formula. BL, baseline; s.e., standard error. Patients at baseline denote the number of treated patients with non‐missing baseline values
Similar articles
- Long-Term Safety of Dapagliflozin in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Pooled Analysis of Phase IIb/III Studies.
Fioretto P, Mansfield TA, Ptaszynska A, Yavin Y, Johnsson E, Parikh S. Fioretto P, et al. Drugs Aging. 2016 Jul;33(7):511-22. doi: 10.1007/s40266-016-0382-1. Drugs Aging. 2016. PMID: 27357173 Free PMC article. - Dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving high doses of insulin: efficacy and safety over 2 years.
Wilding JP, Woo V, Rohwedder K, Sugg J, Parikh S; Dapagliflozin 006 Study Group. Wilding JP, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014 Feb;16(2):124-36. doi: 10.1111/dom.12187. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014. PMID: 23911013 Clinical Trial. - Safety profile of dapagliflozin for type 2 diabetes: pooled analysis of clinical studies for overall safety and rare events.
Ptaszynska A, Johnsson KM, Parikh SJ, de Bruin TW, Apanovitch AM, List JF. Ptaszynska A, et al. Drug Saf. 2014 Oct;37(10):815-29. doi: 10.1007/s40264-014-0213-4. Drug Saf. 2014. PMID: 25096959 - Safety of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors.
McGill JB, Subramanian S. McGill JB, et al. Am J Cardiol. 2019 Dec 15;124 Suppl 1:S45-S52. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.10.029. Am J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31741440 Review. - [Dapagliflozin, the first SGLT-2 inhibitor in the treatment of type 2 diabetes].
Albarrán OG, Ampudia-Blasco FJ. Albarrán OG, et al. Med Clin (Barc). 2013 Sep;141 Suppl 2:36-43. doi: 10.1016/S0025-7753(13)70062-9. Med Clin (Barc). 2013. PMID: 24444523 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
- SGLT2 inhibitor treatment is not associated with an increased risk of osteoporotic fractures when compared to GLP-1 receptor agonists: A nationwide cohort study.
Al-Mashhadi ZK, Viggers R, Starup-Linde J, Vestergaard P, Gregersen S. Al-Mashhadi ZK, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 19;13:861422. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.861422. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36060970 Free PMC article. - Post-transplant diabetes mellitus in patients with solid organ transplants.
Jenssen T, Hartmann A. Jenssen T, et al. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019 Mar;15(3):172-188. doi: 10.1038/s41574-018-0137-7. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30622369 Review. - Safety of Dapagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Saudi Arabia: A Post Authorization Safety Study.
Alguwaihes AM. Alguwaihes AM. Diabetes Ther. 2021 Jul;12(7):1979-1992. doi: 10.1007/s13300-021-01092-0. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Diabetes Ther. 2021. PMID: 34118010 Free PMC article. - Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and risk of serious adverse events: nationwide register based cohort study.
Ueda P, Svanström H, Melbye M, Eliasson B, Svensson AM, Franzén S, Gudbjörnsdottir S, Hveem K, Jonasson C, Pasternak B. Ueda P, et al. BMJ. 2018 Nov 14;363:k4365. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k4365. BMJ. 2018. PMID: 30429124 Free PMC article. - Adverse Effects of Glycemia-Lowering Medications in Type 2 Diabetes.
Razavi-Nematollahi L, Ismail-Beigi F. Razavi-Nematollahi L, et al. Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Nov 20;19(11):132. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1266-7. Curr Diab Rep. 2019. PMID: 31748838 Review.
References
- Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(7):644–657. - PubMed
- Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2117–2128. - PubMed
- Komoroski B, Vachharajani N, Feng Y, Li L, Kornhauser D, Pfister M. Dapagliflozin, a novel, selective SGLT2 inhibitor, improved glycemic control over 2 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009;85:513–519. - PubMed
- Scheen AJ. Pharmacodynamics, efficacy and safety of sodium‐glucose co‐transporter type 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs. 2015;75:33–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical