miR-217 inhibits laryngeal cancer metastasis by repressing AEG-1 and PD-L1 expression - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2017 Jul 10;8(37):62143-62153.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19121. eCollection 2017 Sep 22.
Xionghui Mao 1, Shu Zhao 2, Kaibin Song 1, Cheng Xiang 1, Yuanjing Lv 1, Huanyv Jiang 1, Lei Wang 1, Baojun Li 1, Xianguang Yang 1, Zhennan Yuan 1, Cheng Xiu 1, Hongxue Meng 3, Ji Sun 1
Affiliations
- PMID: 28977933
- PMCID: PMC5617493
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19121
miR-217 inhibits laryngeal cancer metastasis by repressing AEG-1 and PD-L1 expression
Susheng Miao et al. Oncotarget. 2017.
Abstract
High incidences of laryngeal cancer have been reported recently. Increasing our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying this malignancy could reveal more effective approaches to treating laryngeal cancer patients and so improve their prognoses. In this study, we explored the biological effects of miR-217 on laryngeal cancer. miR-217 potently inhibited multiple metastatic traits, including cell migration, invasion, proliferation, apoptosis, and EMT, as well as angiogensis. These effects were achieved through downregulation of the miR-217 target gene, AEG-1 and PD-L1. Clinical expression and animal model studies further confirmed our results. These findings provide new insight into the physiological effects of miR-217 in laryngeal cancer and its potential therapeutic use.
Keywords: AEG-1; PD-L1; laryngeal cancer; metastasis; mir-217.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
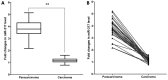
Figure 1. Expression of miR-217 in laryngeal cancer tissues
miR-217 levels were determined by qRT-PCR. (A) Box-plot of miR-217 expression patterns in carcinoma and paracarcinoma tissues (N=29, P < 0.0001). (B) Pairwise comparison of miR-217 expression between carcinoma and matching paracarcinoma tissues showing that miR-217 expression was reduced in 29/29 of the sample pairs.
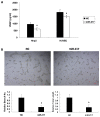
Figure 2. miR-217 modulates metastatic traits in Hep2 cells
Overexpression of miR-217 in Hep2 cells resulted in (A) reduced migratory and invasive capability (N=5; scale bar, 50 μm), (B) reduced cell viability (N=3), and (C) cell cycle arrest (N=3).
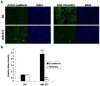
Figure 3. miR-217 inhibits EMT in Hep2 cells
(A) Overexpression of miR-217 resulted in increased E-cadherin and decreased Vimentin in Hep2 cells. DAPI staining was used to detect nuclei. Scale bar, 50 μm. (B) Statistical histogram. N=3.
Figure 4. miR-217 inhibits angiogenesis
miR-217 inhibits (A) VEGF secretion in both Hep2 and HUVEC cells (N=3), and (B) tubule elongation and branching formation in HUVEC cells (N=3). Scale bar, 50 μm.
Figure 5. miR-217 directly regulates AEG-1 and PD-L1 in Hep2 cells
(A) Prediction of miR-217 binding sites on AEG-1 and PD-L1. (B) Prediction of miR-217 mutant binding sites on AEG-1 and PD-L1. (C) Luciferase activity in Hep2 cells infected with miR-217 or control after transfection with the indicated 3′-UTR-driven reporter plasmid or mutant 3′-UTR-driven reporter plasmid (N=3). (D) Real-time PCR results for endogenous AEG-1 and PD-L1 infected with miR-217 or NC (N=3). (E) Western blot results for endogenous AEG-1 and PD-L1 infected with miR-217 or NC.
Figure 6. AEG-1 activates downstream PD-L1
(A) qRT-PCR assay to measure PD-L1 mRNA levels when AEG-1 was overexpressed (N=3). (B) Western blot assay to measure PD-L1 protein levels when AEG-1 was overexpressed . (C) Luciferase assay showing activity for co-transfection of AEG-1 and promoter vector in Hep2 cells (N=3).
Figure 7. Immunohistochemistry detection of clinical human laryngeal carcinoma samples
The number of AEG1 or PD-L1 positive cells was counted in 10 randomly chosen fields for each patient (magnification: ×200). Score: left 3+ and right 1+.
Figure 8. Overexpression of miR-217 strongly inhibits metastasis in vivo
(A) Primary tumor growth upon subcutaneous implantation of 5 × 105 luciferase labeled Hep2 cells infected with the indicated vectors. The experiment was terminated after 6 weeks. (B) Statistical histogram (N=10).
Similar articles
- MicroRNA-217 functions as a prognosis predictor and inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and invasion via an AEG-1 dependent mechanism.
Wang B, Shen ZL, Jiang KW, Zhao G, Wang CY, Yan YC, Yang Y, Zhang JZ, Shen C, Gao ZD, Ye YJ, Wang S. Wang B, et al. BMC Cancer. 2015 May 28;15:437. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1438-z. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26016795 Free PMC article. - Downregulation of miR-34a contributes to the proliferation and migration of laryngeal carcinoma cells by targeting cyclin D1.
Ye J, Li L, Feng P, Wan J, Li J. Ye J, et al. Oncol Rep. 2016 Jul;36(1):390-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4823. Epub 2016 May 19. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27220728 - MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo.
He XX, Chang Y, Meng FY, Wang MY, Xie QH, Tang F, Li PY, Song YH, Lin JS. He XX, et al. Oncogene. 2012 Jul 12;31(28):3357-69. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.500. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22056881 - MicroRNA-377 inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer through targeting AEG-1.
Meng F, Zhang L, Shao Y, Ma Q, Lv H. Meng F, et al. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Nov 1;8(11):13853-63. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26823698 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Advances in tumor immune microenvironment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A review of literature.
Hong Q, Ding S, Xing C, Mu Z. Hong Q, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Mar 1;103(9):e37387. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037387. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38428879 Free PMC article. Review. - Lnc-CCNH-8 promotes immune escape by up-regulating PD-L1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Zhao B, Zheng X, Wang Y, Cheng N, Zhong Y, Zhou Y, Huang J, Wang F, Qi X, Zhuang Q, Wang Y, Liu X. Zhao B, et al. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Jan 23;35(1):102125. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102125. eCollection 2024 Mar 12. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 38356866 Free PMC article. - miRNome expression analysis in canine diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Elshafie NO, Gribskov M, Lichti NI, Sayedahmed EE, Childress MO, Dos Santos AP. Elshafie NO, et al. Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 30;13:1238613. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1238613. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37711209 Free PMC article. - Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Molecular Insights, Preclinical and Clinical Data, and Therapies.
Meliante PG, Barbato C, Zoccali F, Ralli M, Greco A, de Vincentiis M, Colizza A, Petrella C, Ferraguti G, Minni A, Fiore M. Meliante PG, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 6;23(23):15384. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315384. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499710 Free PMC article. Review. - Interplay between programmed death-ligand 1 and non-coding RNAs.
Ghafouri-Fard S, Shoorei H, Hussen BM, Poornajaf Y, Taheri M, Sharifi G. Ghafouri-Fard S, et al. Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 1;13:982902. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.982902. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36405753 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Chu EA, Kim YJ. Laryngeal cancer: diagnosis and preoperative work-up. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2008;41:673–95. v. - PubMed
- Gupta GP, Massagué J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 2006;127:679–95. - PubMed
- Fidler IJ. The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:453–58. - PubMed
- Rothman KJ, Cann CI, Flanders D, Fried MP. Epidemiology of laryngeal cancer. Epidemiol Rev. 1980;2:195–209. - PubMed
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials