Gene losses and partial deletion of small single-copy regions of the chloroplast genomes of two hemiparasitic Taxillus species - PubMed (original) (raw)
Gene losses and partial deletion of small single-copy regions of the chloroplast genomes of two hemiparasitic Taxillus species
Ying Li et al. Sci Rep. 2017.
Abstract
Numerous variations are known to occur in the chloroplast genomes of parasitic plants. We determined the complete chloroplast genome sequences of two hemiparasitic species, Taxillus chinensis and T. sutchuenensis, using Illumina and PacBio sequencing technologies. These species are the first members of the family Loranthaceae to be sequenced. The complete chloroplast genomes of T. chinensis and T. sutchuenensis comprise circular 121,363 and 122,562 bp-long molecules with quadripartite structures, respectively. Compared with the chloroplast genomes of Nicotiana tabacum and Osyris alba, all ndh genes as well as three ribosomal protein genes, seven tRNA genes, four ycf genes, and the infA gene of these two species have been lost. The results of the maximum likelihood and neighbor-joining phylogenetic trees strongly support the theory that Loranthaceae and Viscaceae are monophyletic clades. This research reveals the effect of a parasitic lifestyle on the chloroplast structure and genome content of T. chinensis and T. sutchuenensis, and enhances our understanding of the discrepancies in terms of assembly results between Illumina and PacBio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
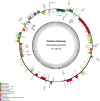
Figure 1
Gene map of the complete chloroplast genome of T. chinensis. Genes on the inside of the circle are transcribed clockwise, while those outside are transcribed counter clockwise. The darker gray in the inner circle corresponds to GC content, whereas the lighter gray corresponds to AT content.
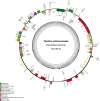
Figure 2
Gene map of the complete chloroplast genome of T. sutchuenensis. Genes on the inside of the circle are transcribed clockwise, while those outside are transcribed counter clockwise. The darker gray in the inner circle corresponds to GC content, whereas the lighter gray corresponds to AT content.
Figure 3
Comparison of the complete chloroplast genomes of six species using the MAUVE algorithm. Local collinear blocks are colored in this figure to indicate syntenic regions, while histograms within each block represent the degree of sequence similarity.
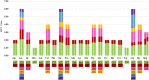
Figure 4
Codon content of 20 amino acid and stop codons in all protein-coding genes of the chloroplast genomes of two species. The histogram on the left-hand side of each amino acid shows codon usage within the T. chinensis chloroplast genome, while the right-hand side illustrates the genome of T. sutchuenensis.
Figure 5
Phylogenetic trees constructed using two methods based on two datasets from different species. (A) ML tree based on 54 protein-coding genes; (B) ML tree based on matK genes; (C) NJ tree based on 54 protein-coding genes; (D) NJ tree based on matK genes. Number at nodes are values for bootstrap support.
Similar articles
- Gene Losses and Homology of the Chloroplast Genomes of Taxillus and Phacellaria Species.
Wu L, Fan P, Zhou J, Li Y, Xu Z, Lin Y, Wang Y, Song J, Yao H. Wu L, et al. Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 19;14(4):943. doi: 10.3390/genes14040943. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107701 Free PMC article. - Gene Losses and Variations in Chloroplast Genome of Parasitic Plant Macrosolen and Phylogenetic Relationships within Santalales.
Nie L, Cui Y, Wu L, Zhou J, Xu Z, Li Y, Li X, Wang Y, Yao H. Nie L, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 19;20(22):5812. doi: 10.3390/ijms20225812. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31752332 Free PMC article. - Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Taxillus chinensis (Loranthaceae): a hemiparasitic shrub in South China.
Liu B, Zhang Y, Shi Y. Liu B, et al. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019 Sep 19;4(2):3077-3078. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1666680. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019. PMID: 33365863 Free PMC article. - The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Taxillus yadoriki (Loranthaceae): a hemi-parasitic evergreen shrub in East Asia.
Cho WB, Han EK, Son DC, Lee JH. Cho WB, et al. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020 Aug 17;5(3):3172-3173. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1806755. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020. PMID: 33458100 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Complete chloroplast genomes of two Siraitia Merrill species: Comparative analysis, positive selection and novel molecular marker development.
Shi H, Yang M, Mo C, Xie W, Liu C, Wu B, Ma X. Shi H, et al. PLoS One. 2019 Dec 20;14(12):e0226865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226865. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31860647 Free PMC article. - Comparative and Phylogenetic Analyses of Ginger (Zingiber officinale) in the Family Zingiberaceae Based on the Complete Chloroplast Genome.
Cui Y, Nie L, Sun W, Xu Z, Wang Y, Yu J, Song J, Yao H. Cui Y, et al. Plants (Basel). 2019 Aug 12;8(8):283. doi: 10.3390/plants8080283. Plants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31409043 Free PMC article. - Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Scurrula notothixoides (Loranthaceae): a hemiparasitic shrub in South China.
Yuan LX, Wang JH, Chen CR, Zhao KK, Zhu ZX, Wang HF. Yuan LX, et al. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2018 May 11;3(2):580-581. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2018.1471366. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2018. PMID: 33474249 Free PMC article. - Chromosome-Level Genome Assembly of the Hemiparasitic Taxillus chinensis (DC.) Danser.
Fu J, Wan L, Song L, He L, Jiang N, Long H, Huo J, Ji X, Hu F, Wei S, Pan L. Fu J, et al. Genome Biol Evol. 2022 May 3;14(5):evac060. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evac060. Genome Biol Evol. 2022. PMID: 35482027 Free PMC article.
References
- Raubeson, L. A. & Jansen, R. K. In: Diversity and Evolution of Plants; Genotypic and Phenotypic Variation in Higher Plants (ed R. Henry) 45–68 (CABI Publishing, 2005).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous