The influence of vascular endothelial growth factor-A and matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in angiogenesis, metastasis, and prognosis of endometrial cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2017 Sep 19:10:4617-4624.
doi: 10.2147/OTT.S132558. eCollection 2017.
Affiliations
- PMID: 29033580
- PMCID: PMC5614795
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S132558
Review
The influence of vascular endothelial growth factor-A and matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in angiogenesis, metastasis, and prognosis of endometrial cancer
Anna M Mahecha et al. Onco Targets Ther. 2017.
Abstract
Angiogenesis (the growth of new blood vessels) is essential in most of the body's physiological processes, such as in the normal functioning of the endometrium during and after the menstrual cycle. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) are the mostly expressed angiogenic factors, especially, during the process of endometrial degeneration and remodeling. In carcinogenesis, tumor hypoxia-induced factors, through the process of "angiogenic switch", stimulate the production of angiogenic factors, particularly VEGF and MMP. Subsequently, these angiogenic factors are associated with degradation, differentiation, proliferation, and migration of vascular endothelial cells, enhancing the formation of new blood vessels to supply the tumor with oxygen and nutrients. This process is equally significant for tumor development and metastasis. Hence, like in other cancers, the overexpression of MMP and VEGF in endometrial cancer (EC) seems to play a significant role in its tumorigenesis and metastasis. This research will discuss the influence of MMP and VEGF on angiogenesis, metastasis, and the prognosis of EC as well as the clinical importance of the factors in the diagnosis of EC.
Keywords: angiogenic factors; angiogenic switch; endometrioid endometrial carcinoma; microvascular density.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
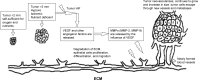
Figure 1
Influence of VEGF-A in EC. Abbreviations: EC, endometrial cancer; ECM, extracellular matrix; HIF, hypoxia-induced factor; VEGF-A, vascular endothelial growth factor-A.
Similar articles
- Association of hypoxia-inducible factors 1alpha and 2alpha with activated angiogenic pathways and prognosis in patients with endometrial carcinoma.
Sivridis E, Giatromanolaki A, Gatter KC, Harris AL, Koukourakis MI; Tumor and Angiogenesis Research Group. Sivridis E, et al. Cancer. 2002 Sep 1;95(5):1055-63. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10774. Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12209691 - Vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF), an emerging target for cancer chemotherapy.
Shinkaruk S, Bayle M, Laïn G, Déléris G. Shinkaruk S, et al. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2003 Mar;3(2):95-117. doi: 10.2174/1568011033353452. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2003. PMID: 12678905 Review. - Angiogenesis in renal cell carcinoma: Evaluation of microvessel density, vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinases.
Zhang X, Yamashita M, Uetsuki H, Kakehi Y. Zhang X, et al. Int J Urol. 2002 Sep;9(9):509-14. doi: 10.1046/j.1442-2042.2002.00511.x. Int J Urol. 2002. PMID: 12410931 - Targeting tumor micro-environment for design and development of novel anti-angiogenic agents arresting tumor growth.
Gacche RN, Meshram RJ. Gacche RN, et al. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013 Nov;113(2):333-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24139944 Review.
Cited by
- Transcriptional Profiling of Hypoxia-Regulated Non-coding RNAs in Human Primary Endothelial Cells.
Moreau PR, Örd T, Downes NL, Niskanen H, Bouvy-Liivrand M, Aavik E, Ylä-Herttuala S, Kaikkonen MU. Moreau PR, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018 Nov 5;5:159. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2018.00159. eCollection 2018. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018. PMID: 30456215 Free PMC article. - HTLV-1-associated genes as potential biomarkers for endometrial cancer.
Du G, Zhang W, Zhang Z, Zeng M, Wang Y. Du G, et al. Oncol Lett. 2019 Jul;18(1):699-705. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10389. Epub 2019 May 21. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31289544 Free PMC article. - Endothelial cell CD36 deficiency prevents normal angiogenesis and vascular repair.
Bou Khzam L, Son NH, Mullick AE, Abumrad NA, Goldberg IJ. Bou Khzam L, et al. Am J Transl Res. 2020 Dec 15;12(12):7737-7761. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 33437358 Free PMC article. - TSPO deficiency promotes the progression of malignant peripheral sheath tumors by regulating the G2/M phase of the cell cycle via CDK1.
Zhang X, Hu C, Sun S, Guo C, Bu Y, Wang Z, Liu Z, Zhang X, Li D, Liu S. Zhang X, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 31;14(1):26235. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77933-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39482412 Free PMC article. - Restoration of microRNA-29c in type I endometrioid cancer reduced endometrial cancer cell growth.
Van Sinderen M, Griffiths M, Menkhorst E, Niven K, Dimitriadis E. Van Sinderen M, et al. Oncol Lett. 2019 Sep;18(3):2684-2693. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10588. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31404303 Free PMC article.
References
- Polverini PJ. Angiogenesis and wound healing: basic discoveries, clinical implications, and therapeutic opportunities. Endod Top. 2011;24(1):130–145.
- DiPietro LA. Angiogenesis and scar formation in healing wounds. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013;25(1):87–91. - PubMed
- Demir R, Yaba A, Huppertz B. Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis in the endometrium during menstrual cycle and implantation. Acta Histochem. 2010;112(3):203–214. - PubMed
- Abu El-Asrar AM, Nawaz MI, Kangave D, Siddiquei MM, Ola MS, Opdenakker G. Angiogenesis regulatory factors in the vitreous from patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 2013;50(4):545–551. - PubMed
- Zhou J, Wang S, Xia X. Role of intravitreal inflammatory cytokines and angiogenic factors in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Curr Eye Res. 2012;37(5):416–420. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources