Application of Sodium Selenite in the Prevention and Treatment of Cancers - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Application of Sodium Selenite in the Prevention and Treatment of Cancers
Marek Kieliszek et al. Cells. 2017.
Abstract
Selenium is an essential trace element that occurs in nature, in both inorganic and organic forms. This element participates in numerous biochemical processes, including antioxidant potential, but the mechanism of its anti-cancer action is still not well known. It should be noted that the anti-cancer properties of selenium depends on its chemical form, therapeutic doses, and the tumor type. Higher nutritional doses of selenium can stimulate human immune system. There are several hypotheses concerning the anticancer activity of selenium, including oxidation of sulfhydryl groups in proteins causing their conformational alterations. Conformational changes in proteins have the ability to weaken the activity of enzymes involved in the metabolism of cancer cells. In case of human fibrinogen sodium selenite, but not selenate, it inhibits protein disulfide exchange reactions, thus preventing formation of a hydrophobic polymer termed parafibrin, circulatory accumulation, of which is associated with numerous degenerative diseases. Parafibrin can specifically form a protein coat around tumor cells that is completely resistant to degradation induced with lymphocyte protease. In this way, cancer cells become protected against destruction by the organism's immune system. Other possible mechanisms of anticancer action of selenium are being still investigated.
Keywords: blood; cancer; fibrin; parafibrin; polymer; selenium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
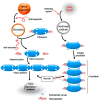
Figure 1
Schematic representation of thrombin-induced blood coagulation (left part) and the conversion of fibrinogen to insoluble polymer under the influence of iron (right part) based on references [7,8].
Similar articles
- Redox-Active Selenium in Health and Disease: A Conceptual Review.
Lipinski B. Lipinski B. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2019;19(9):720-726. doi: 10.2174/1389557517666161104125022. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 27823560 Review. - Sodium Selenite as an Anticancer Agent.
Lipinski B. Lipinski B. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(5):658-661. doi: 10.2174/1871520616666160607011024. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27281365 Review. - Rationale for the treatment of cancer with sodium selenite.
Lipinski B. Lipinski B. Med Hypotheses. 2005;64(4):806-10. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2004.10.012. Med Hypotheses. 2005. PMID: 15694701 - Compendium of the antidiabetic effects of supranutritional selenate doses. In vivo and in vitro investigations with type II diabetic db/db mice.
Mueller AS, Pallauf J. Mueller AS, et al. J Nutr Biochem. 2006 Aug;17(8):548-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.10.006. Epub 2005 Nov 9. J Nutr Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16443359 - Six-day selenium supplementation led to either UVA-photoprotection or toxic effects in human fibroblasts depending on the chemical form and dose of Se.
Hazane-Puch F, Champelovier P, Arnaud J, Trocmé C, Garrel C, Faure P, Laporte F. Hazane-Puch F, et al. Metallomics. 2014 Sep;6(9):1683-92. doi: 10.1039/c4mt00040d. Metallomics. 2014. PMID: 24994457
Cited by
- The Effect of Selenium Nanoparticles on the Osteogenic Differentiation of MC3T3-E1 Cells.
Lee SC, Lee NH, Patel KD, Jang TS, Knowles JC, Kim HW, Lee HH, Lee JH. Lee SC, et al. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Feb 23;11(2):557. doi: 10.3390/nano11020557. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672352 Free PMC article. - Research progress of nanoparticles in diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Xing L, Chen Y, Zheng T. Xing L, et al. Open Life Sci. 2024 Aug 23;19(1):20220932. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0932. eCollection 2024. Open Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39220591 Free PMC article. Review. - Cytotoxicity of Selenium Immunoconjugates against Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells.
Khandelwal S, Boylan M, Spallholz JE, Gollahon L. Khandelwal S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 26;19(11):3352. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113352. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30373175 Free PMC article. - Synthesis of Selenium-Quinone Hybrid Compounds with Potential Antitumor Activity via Rh-Catalyzed C-H Bond Activation and Click Reactions.
Jardim GAM, Lima DJB, Valença WO, Lima DJB, Cavalcanti BC, Pessoa C, Rafique J, Braga AL, Jacob C, da Silva Júnior EN, da Cruz EHG. Jardim GAM, et al. Molecules. 2017 Dec 30;23(1):83. doi: 10.3390/molecules23010083. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29301214 Free PMC article. - Long-term effect of sodium selenite on the integrity and permeability of on-chip microvasculature.
Shaji M, Kitada A, Fujimoto K, Karsten SL, Yokokawa R. Shaji M, et al. APL Bioeng. 2022 Nov 14;6(4):046105. doi: 10.1063/5.0122804. eCollection 2022 Dec. APL Bioeng. 2022. PMID: 36397962 Free PMC article.
References
- Ip C., Hayes C., Budnick M., Ganther H.E. Chemical form of selenium critical metabolites, and cancer prevention. Cancer Res. 1991;51:595–600. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources