Identification of Neuroprotective Factors Associated with Successful Ageing and Risk of Cognitive Impairment among Malaysia Older Adults - PubMed (original) (raw)
Identification of Neuroprotective Factors Associated with Successful Ageing and Risk of Cognitive Impairment among Malaysia Older Adults
Huijin Lau et al. Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res. 2017.
Abstract
The increase of ageing population has raised public attention on the concept of successful ageing. Studies have shown that vitamin D, telomere length, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) have been associated with cognitive function. Therefore, this study aimed to identify neuroprotective factors for cognitive decline in different ageing groups. A total of 300 older adults aged 60 years and above were recruited in this population based cross-sectional study. Participants were categorized into three groups: mild cognitive impairment (MCI) (n = 100), usual ageing (UA) (n = 100), and successful ageing (SA) (n = 100). Dietary vitamin D intake was assessed through Diet History Questionnaire (DHQ). Out of the 300 participants, only 150 were subjected to fasting blood sample collection. These samples were used for serum vitamin D and plasma BDNF measurements. Whole blood telomere length was measured using RT-PCR method. The results show that the reduction of the risk of MCI was achieved by higher serum vitamin D level (OR: 0.96, 95% CI: 0.92-0.99, p < 0.05), higher plasma BDNF level (OR: 0.51, 95% CI: 0.30-0.88, p < 0.05), and longer telomere (OR: 0.97, 95% CI: 0.95-0.99, p < 0.001). In conclusion, participants with higher vitamin D level, higher BDNF level, and longer telomere length were more likely to age successfully.
Figures
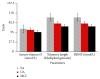
Figure 1
Comparison of selected neuroprotective factors between ageing groups. BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; SA: successful ageing; UA: usual ageing; MCI: mild cognitive impairment. One-way ANOVA and post hoc test LSD. Serum vitamin D and BDNF significant between MCI and SA; telomere length significant between UA and SA.
Similar articles
- The association between vitamin D and BDNF on cognition in older adults in Southern Brazil.
Quialheiro A, D Orsi E, Moreira JD, Xavier AJ, Peres MA. Quialheiro A, et al. Rev Saude Publica. 2023 Jan 6;56:109. doi: 10.11606/s1518-8787.2022056004134. eCollection 2023. Rev Saude Publica. 2023. PMID: 36629701 Free PMC article. - Predictors of poor cognitive status among older Malaysian adults: baseline findings from the LRGS TUA cohort study.
Vanoh D, Shahar S, Din NC, Omar A, Vyrn CA, Razali R, Ibrahim R, Hamid TA. Vanoh D, et al. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2017 Apr;29(2):173-182. doi: 10.1007/s40520-016-0553-2. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2017. PMID: 26980453 - B-Vitamin Intake and Biomarker Status in Relation to Cognitive Decline in Healthy Older Adults in a 4-Year Follow-Up Study.
Hughes CF, Ward M, Tracey F, Hoey L, Molloy AM, Pentieva K, McNulty H. Hughes CF, et al. Nutrients. 2017 Jan 10;9(1):53. doi: 10.3390/nu9010053. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28075382 Free PMC article. - Screening for Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults: An Evidence Update for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].
Patnode CD, Perdue LA, Rossom RC, Rushkin MC, Redmond N, Thomas RG, Lin JS. Patnode CD, et al. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2020 Feb. Report No.: 19-05257-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2020 Feb. Report No.: 19-05257-EF-1. PMID: 32129963 Free Books & Documents. Review. - Screening for Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults: An Evidence Update for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].
Lin JS, O'Connor E, Rossom RC, Perdue LA, Burda BU, Thompson M, Eckstrom E. Lin JS, et al. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2013 Nov. Report No.: 14-05198-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2013 Nov. Report No.: 14-05198-EF-1. PMID: 24354019 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
- Multiparametric MRI for the improved diagnostic accuracy of Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: Research protocol of a case-control study design.
Piersson AD, Ibrahim B, Suppiah S, Mohamad M, Hassan HA, Omar NF, Ibrahim MI, Yusoff AN, Ibrahim N, Saripan MI, Razali RM. Piersson AD, et al. PLoS One. 2021 Sep 21;16(9):e0252883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252883. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34547018 Free PMC article. - Trends of Nanobiosensors in Modern Agriculture Systems.
Kumar P, Chugh P, Ali SS, Chawla W, Sushmita S, Kumar R, Raval AV, Shamim S, Bhatia A, Kumar R. Kumar P, et al. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 13. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-05039-6. Online ahead of print. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39136915 Review. - Localized delivery of brain-derived neurotrophic factor from PLGA microspheres promotes peripheral nerve regeneration in rats.
Shi ZL, Fan ZY, Zhang H, Li ST, Yuan H, Tong JH. Shi ZL, et al. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Mar 18;17(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-02985-x. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35303915 Free PMC article. - Digital Device Use, Risk of Cognitive Impairment, and Cognition in Healthy Older Adults: The Role of Cognitive Reserve.
Liang C, Subramaniam P, Mohd Ridzwan Goh NS, Kok Wai T, Moustafa AA. Liang C, et al. Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;11(21):2822. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11212822. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37957967 Free PMC article. - Cognitive frailty among Malaysian older adults: baseline findings from the LRGS TUA cohort study.
Malek Rivan NF, Shahar S, Rajab NF, Singh DKA, Din NC, Hazlina M, Hamid TATA. Malek Rivan NF, et al. Clin Interv Aging. 2019 Jul 25;14:1343-1352. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S211027. eCollection 2019. Clin Interv Aging. 2019. PMID: 31413555 Free PMC article.
References
- Samad S. A. Population ageing and social protection in Malaysia. Malaysian Journal of Economic Studies. 2013;50(2):139–156.
- Mather K. A., Jorm A. F., Milburn P. J., Tan X., Easteal S., Christensen H. No associations between telomere length and age-sensitive indicators of physical function in mid and later life. Journals of Gerontology - Series A Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2010;65A(8):792–799. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glq050. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources