Secukinumab in Active Rheumatoid Arthritis after Anti-TNFα Therapy: A Randomized, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Secukinumab in Active Rheumatoid Arthritis after Anti-TNFα Therapy: A Randomized, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Study
Hasan Tahir et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2017 Dec.
Abstract
Introduction: 'REASSURE' (NCT01377012), a phase 3 study, evaluated the efficacy and safety of secukinumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who had an inadequate response to, or intolerance of, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNF-inhibitors).
Methods: A total of 637 patients were randomized (1:1:1) to receive intravenous secukinumab 10 mg/kg (baseline, weeks 2 and 4) followed by subcutaneous secukinumab 150 mg or 75 mg every 4 weeks (starting from week 8) or placebo at the same dosing schedule. The primary endpoint was the American College of Rheumatology 20% improvement criteria (ACR20) at week 24. Other predefined hierarchical endpoints included Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index, van der Heijde modified total Sharp score (vdH-mTSS) at week 24, and major clinical response (MCR; continuous 6 month period of ACR70 response) at 1 year.
Results: The primary efficacy endpoint was met with both secukinumab dose groups: ACR20 response rate at week 24 was 35.2% for both secukinumab dose groups (P = 0.0009) vs 19.6% for placebo. The improvements in secondary endpoints were greater in the secukinumab dose groups vs placebo but did not meet statistical significance. The overall safety profile was similar across all treatment groups.
Conclusion: Secukinumab demonstrated efficacy in reducing disease activity over placebo as measured by ACR20 in patients with active RA who had an inadequate response to TNF-inhibitors. Secukinumab demonstrated a safety profile similar to other biologics currently approved for RA.
Funding: Novartis Pharma AG.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01377012.
Keywords: ACR; Autoimmune; Biologic; Clinical trial; HAQ-DI; IL-17A; Randomized; Rheumatoid arthritis; Secukinumab; vdH-mTSS.
Figures
Fig. 1
Study design
Fig. 2
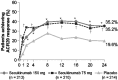
ACR20 response using non-responder imputation over 24 weeks. Symbols indicate P ≤ 0.05. *P < 0.05 for secukinumab 150 mg vs placebo; †P < 0.05 for secukinumab 75 mg vs placebo. P values are adjusted for multiplicity of testing for secukinumab 150 mg and secukinumab 75 mg vs placebo at week 24. ACR American College of Rheumatology, ACR20 improvement of ≥ 20% in ACR disease activity, IV intravenous, n number of subjects randomized
Similar articles
- Secukinumab in Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Phase III Randomized, Double-Blind, Active Comparator- and Placebo-Controlled Study.
Blanco FJ, Möricke R, Dokoupilova E, Codding C, Neal J, Andersson M, Rohrer S, Richards H. Blanco FJ, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Jun;69(6):1144-1153. doi: 10.1002/art.40070. Epub 2017 May 3. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28217871 Clinical Trial. - Efficacy and Safety of Subcutaneous and Intravenous Loading Dose Regimens of Secukinumab in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from a Randomized Phase II Study.
Tlustochowicz W, Rahman P, Seriolo B, Krammer G, Porter B, Widmer A, Richards HB. Tlustochowicz W, et al. J Rheumatol. 2016 Mar;43(3):495-503. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.150117. Epub 2016 Feb 1. J Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26834211 Clinical Trial. - Secukinumab after anti-tumour necrosis factor-α therapy: a phase III study in active rheumatoid arthritis.
Dokoupilová E, Aelion J, Takeuchi T, Malavolta N, Sfikakis PP, Wang Y, Rohrer S, Richards HB. Dokoupilová E, et al. Scand J Rheumatol. 2018 Jul;47(4):276-281. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2017.1390605. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Scand J Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29458278 Clinical Trial. - Comparative effectiveness of abatacept, apremilast, secukinumab and ustekinumab treatment of psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.
Kawalec P, Holko P, Moćko P, Pilc A. Kawalec P, et al. Rheumatol Int. 2018 Feb;38(2):189-201. doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3919-7. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Rheumatol Int. 2018. PMID: 29285605 Free PMC article. Review. - Golimumab: Review of the efficacy and tolerability of a recently approved tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor.
Boyce EG, Halilovic J, Stan-Ugbene O. Boyce EG, et al. Clin Ther. 2010 Sep;32(10):1681-703. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.09.003. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 21194591 Review.
Cited by
- Radiographic progression in clinical trials in rheumatoid arthritis: a systemic literature review of trials performed by industry.
Park YJ, Gherghe AM, van der Heijde D. Park YJ, et al. RMD Open. 2020 Jul;6(2):e001277. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001277. RMD Open. 2020. PMID: 32669455 Free PMC article. - Risk of Infections and Cancer in Patients With Rheumatologic Diseases Receiving Interleukin Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.
Bilal J, Berlinberg A, Riaz IB, Faridi W, Bhattacharjee S, Ortega G, Murad MH, Wang Z, Prokop LJ, Alhifany AA, Kwoh CK. Bilal J, et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Oct 2;2(10):e1913102. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.13102. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31626313 Free PMC article. - Incidence rates of inflammatory bowel disease in patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis treated with secukinumab: a retrospective analysis of pooled data from 21 clinical trials.
Schreiber S, Colombel JF, Feagan BG, Reich K, Deodhar AA, McInnes IB, Porter B, Das Gupta A, Pricop L, Fox T. Schreiber S, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Apr;78(4):473-479. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214273. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 30674475 Free PMC article. - Interleukin-17: A Putative Novel Pharmacological Target for Pathological Pain.
Gao SJ, Liu L, Li DY, Liu DQ, Zhang LQ, Wu JY, Song FH, Zhou YQ, Mei W. Gao SJ, et al. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024;22(2):204-216. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666230811142713. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37581321 Free PMC article. Review. - Migration and homeostasis of regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis.
Kotschenreuther K, Yan S, Kofler DM. Kotschenreuther K, et al. Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 9;13:947636. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.947636. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36016949 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, Dougados M, Furie RA, Genovese MC, et al. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(9):2793–2806. doi: 10.1002/art.22025. - DOI - PubMed
- Rituximab: Highlights of prescribing information. 2017. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2010/103705s5311lbl.pdf (cited 12 July 2017).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous