Effect of Alternate Nostril Breathing Exercise on Experimentally Induced Anxiety in Healthy Volunteers Using the Simulated Public Speaking Model: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
Effect of Alternate Nostril Breathing Exercise on Experimentally Induced Anxiety in Healthy Volunteers Using the Simulated Public Speaking Model: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study
Ashwin Kamath et al. Biomed Res Int. 2017.
Abstract
A randomized controlled pilot study was carried out to determine the effect of a 15-minute practice of ANB exercise on experimentally induced anxiety using the simulated public speaking model in yoga-naïve healthy young adults. Thirty consenting medical students were equally divided into test and control groups. The test group performed alternate nostril breathing exercise for 15 minutes, while the control group sat in a quiet room before participating in the simulated public speaking test (SPST). Visual Analog Mood Scale and Self-Statements during Public Speaking scale were used to measure the mood state at different phases of the SPST. The psychometric scores of both groups were comparable at baseline. Repeated-measures ANOVA showed a significant effect of phase (p < 0.05), but group and gender did not have statistically significant influence on the mean anxiety scores. However, the test group showed a trend towards lower mean scores for the anxiety factor when compared with the control group. Considering the limitations of this pilot study and the trend seen towards lower anxiety in the test group, alternate nostril breathing may have potential anxiolytic effect in acute stressful situations. A study with larger sample size is therefore warranted. This trial is registered with CTRI/2014/03/004460.
Figures
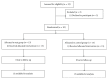
Figure 1
CONSORT diagram.
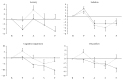
Figure 2
Comparison of the delta scores of Visual Analog Mood Scale (VAMS) factors in the test and control groups during various phases of the simulated public speaking test. The delta scores were obtained by calculating the difference between the VAMS score for each phase and the baseline score. The dark-gray line represents the test group, and the light-gray line represents the control group. The horizontal axis represents the various experimental phases, and the vertical axis represents the VAMS factor scores. The vertical bars represent the standard error. B, baseline; P, prestress; A, anticipatory phase; S, speech performance; F, poststress.
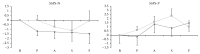
Figure 3
Comparison of the delta scores of Self-Statements during Public Speaking (SSPS) scale in the test and control groups during various phases of the simulated public speaking test. The delta scores were obtained by calculating the difference between the SSPS score for each phase and the baseline score. The dark-gray line represents the test group, and the light-gray line represents the control group. The horizontal axis represents the various experimental phases, and the vertical axis represents the SSPS scores. The vertical bars represent the standard error. B, baseline; P, prestress; A, anticipatory phase; S, speech performance; F, poststress.
Similar articles
- Changes in Shape and Size Discrimination and State Anxiety After Alternate-Nostril Yoga Breathing and Breath Awareness in One Session Each.
Telles S, Vishwakarma B, Gupta RK, Balkrishna A. Telles S, et al. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2019 Apr 22;25:121-127. doi: 10.12659/MSMBR.914956. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2019. PMID: 31006767 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Effects of alternate nostril breathing exercise on respiratory functions in healthy young adults leading stressful lifestyle.
Jahan I, Begum M, Akhter S, Islam MZ, Jahan N, Haque M. Jahan I, et al. J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 19;27(1):e104-e114. doi: 10.15586/jptcp.v27i1.668. J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32320171 Clinical Trial. - Effect of Unilateral Left Nostril Breathing (Chandra Anga Pranayama) on Cognitive Function in Healthy Yoga-Naïve Individuals: A Randomized, Controlled, Pilot Study.
Santhanam Kumar SS, Kamath A, Poojary S. Santhanam Kumar SS, et al. Complement Med Res. 2020;27(5):319-327. doi: 10.1159/000506972. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Complement Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32344403 Clinical Trial. English. - Alternate-Nostril Yoga Breathing Reduced Blood Pressure While Increasing Performance in a Vigilance Test.
Telles S, Verma S, Sharma SK, Gupta RK, Balkrishna A. Telles S, et al. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2017 Dec 29;23:392-398. doi: 10.12659/msmbr.906502. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2017. PMID: 29284770 Free PMC article. - Human experimental anxiety: actual public speaking induces more intense physiological responses than simulated public speaking.
Zuardi AW, Crippa JA, Hallak JE, Gorayeb R. Zuardi AW, et al. Braz J Psychiatry. 2013 Jul-Sep;35(3):248-53. doi: 10.1590/1516-4446-2012-0930. Braz J Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 24142085 Review.
Cited by
- Examining the impact of a restorative breath-based intervention "Sudarshan Kriya Yoga" at work: a field experiment.
Chhajer R, Dagar C. Chhajer R, et al. Front Psychol. 2024 Mar 5;15:1327119. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1327119. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38505368 Free PMC article. - Breathing Practices for Stress and Anxiety Reduction: Conceptual Framework of Implementation Guidelines Based on a Systematic Review of the Published Literature.
Bentley TGK, D'Andrea-Penna G, Rakic M, Arce N, LaFaille M, Berman R, Cooley K, Sprimont P. Bentley TGK, et al. Brain Sci. 2023 Nov 21;13(12):1612. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13121612. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 38137060 Free PMC article. Review. - Effect of breathwork on stress and mental health: A meta-analysis of randomised-controlled trials.
Fincham GW, Strauss C, Montero-Marin J, Cavanagh K. Fincham GW, et al. Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 9;13(1):432. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-27247-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36624160 Free PMC article.
References
- Iyengar B. K. S. Light on Yoga. New York, NY, USA: Schocken Books; 1966.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials